What is the EFAA?

The Expedited Funds Availability Act (EFAA) is a federal law in the United States that regulates the availability of funds after a deposit is made to a bank account. It was enacted in 1987 to provide consumers with quicker access to their deposited funds.
The EFAA applies to all banks and credit unions that operate in the United States and offer transaction accounts, such as checking and savings accounts. It sets the maximum time frame within which banks must make funds available for withdrawal or use.
Under the EFAA, banks are required to make funds from certain types of deposits available to customers within specific time periods. The act establishes different availability schedules for different types of deposits, such as cash, electronic transfers, and checks.
The purpose of the EFAA is to ensure that consumers have timely access to their deposited funds, allowing them to use the money for their financial needs. It provides transparency and consistency in the availability of funds across different financial institutions.
It is important for consumers to understand the provisions of the EFAA, as it affects their ability to access and use their deposited funds. By knowing their rights under the act, consumers can make informed decisions about their banking transactions and manage their finances effectively.
How does the EFAA work?
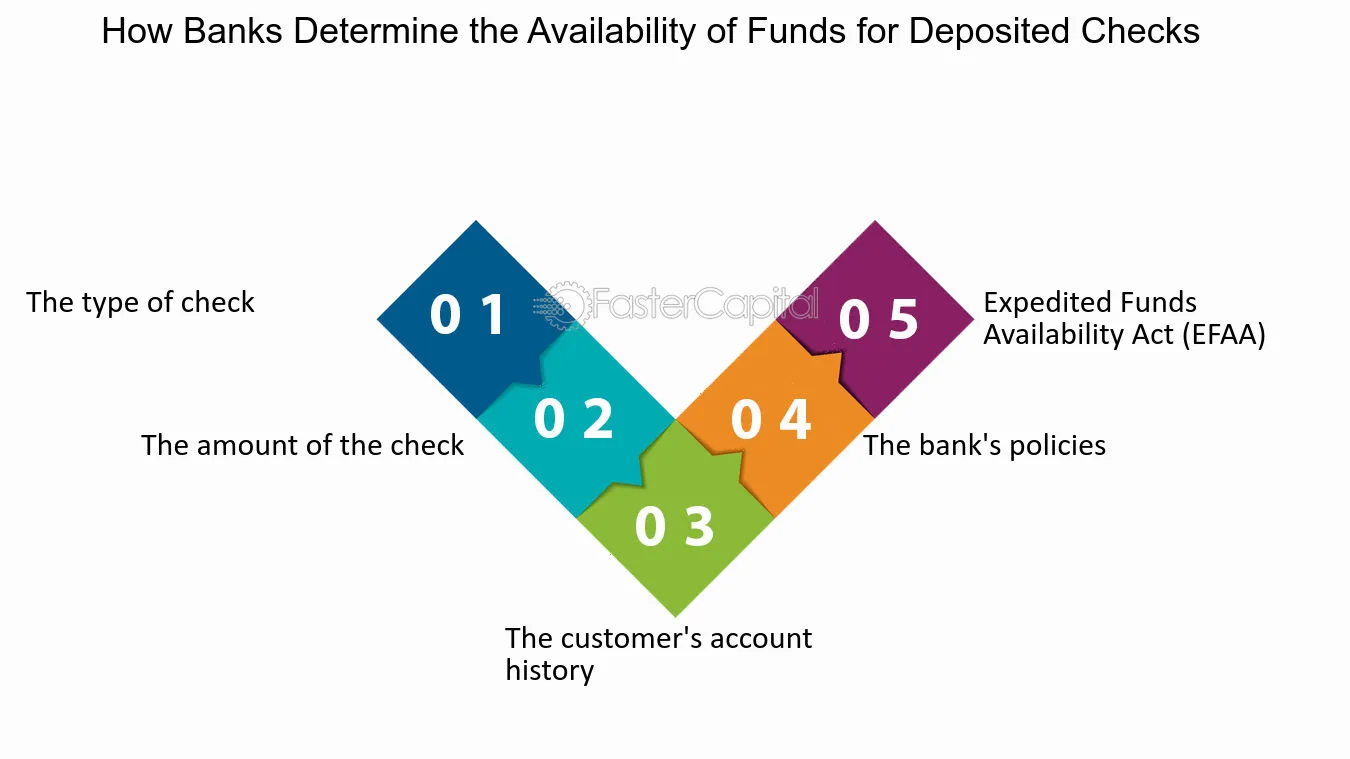
The Expedited Funds Availability Act (EFAA) is a federal law in the United States that regulates the availability of funds after a deposit is made into a bank account. The purpose of the EFAA is to ensure that consumers have timely access to their deposited funds.
Under the EFAA, banks are required to make funds available to customers within a certain timeframe. The specific timeframes depend on the type of deposit and the location of the bank. Generally, the EFAA requires banks to make funds available for withdrawal by the next business day for most types of deposits.
The EFAA also sets certain exceptions and holds for certain types of deposits. For example, if a deposit is made at an ATM, the bank may place a hold on the funds for a longer period of time. Additionally, if a deposit is made by check, the bank may place a hold on the funds until the check clears.
In summary, the EFAA works by establishing rules and timeframes for the availability of funds after a deposit is made. It ensures that consumers have timely access to their deposited funds, while also allowing banks to protect against potential risks and fraud.
Benefits of the EFAA

The Expedited Funds Availability Act (EFAA) provides several benefits to both banks and their customers. These benefits include:
- Quicker access to funds: One of the main advantages of the EFAA is that it allows consumers to have faster access to the funds they deposit. Under the Act, banks are required to make funds available for withdrawal within specific timeframes, depending on the type of deposit. This means that customers can access their money sooner, providing them with greater financial flexibility.
- Reduced risk of overdrafts: By ensuring that funds are made available in a timely manner, the EFAA helps to reduce the risk of overdrafts. When customers have immediate access to their deposited funds, they can more accurately manage their account balances and avoid overdrawing their accounts. This can save customers from incurring costly overdraft fees and penalties.
- Increased convenience: The EFAA makes banking more convenient for customers. With quicker access to funds, customers can make necessary purchases, pay bills, and handle financial obligations more efficiently. This eliminates the need to wait for funds to clear, allowing for smoother financial transactions.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: The EFAA plays a significant role in improving customer satisfaction. When customers can access their funds promptly, they are more likely to have a positive banking experience. This can lead to increased loyalty and trust in the banking institution, fostering long-term relationships between customers and their banks.
- Increased financial inclusion: The EFAA promotes financial inclusion by ensuring that funds are available to customers regardless of their banking history or creditworthiness. This helps to level the playing field and provides equal access to financial services for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
