What is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)?

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a federal tax credit designed to provide financial assistance to low-income working individuals and families. It is one of the largest anti-poverty programs in the United States and aims to reduce the tax burden on those with low incomes.
The EITC is a refundable tax credit, which means that if the credit exceeds the amount of taxes owed, the taxpayer can receive a refund for the difference. This makes it an effective tool for lifting families out of poverty and providing them with additional income.
To qualify for the EITC, individuals must meet certain income and filing status requirements. The amount of the credit depends on the individual’s income, filing status, and number of qualifying children. The credit is phased out as income increases, and there are specific income limits for eligibility.
In addition to providing financial assistance, the EITC also encourages individuals to enter or remain in the workforce. By reducing the tax burden on low-income workers, it incentivizes employment and helps individuals build a stable financial foundation.
Overall, the Earned Income Tax Credit plays a crucial role in alleviating poverty and supporting low-income working individuals and families. It provides a valuable tax benefit that can make a significant difference in the lives of those who need it most.
Qualifications for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
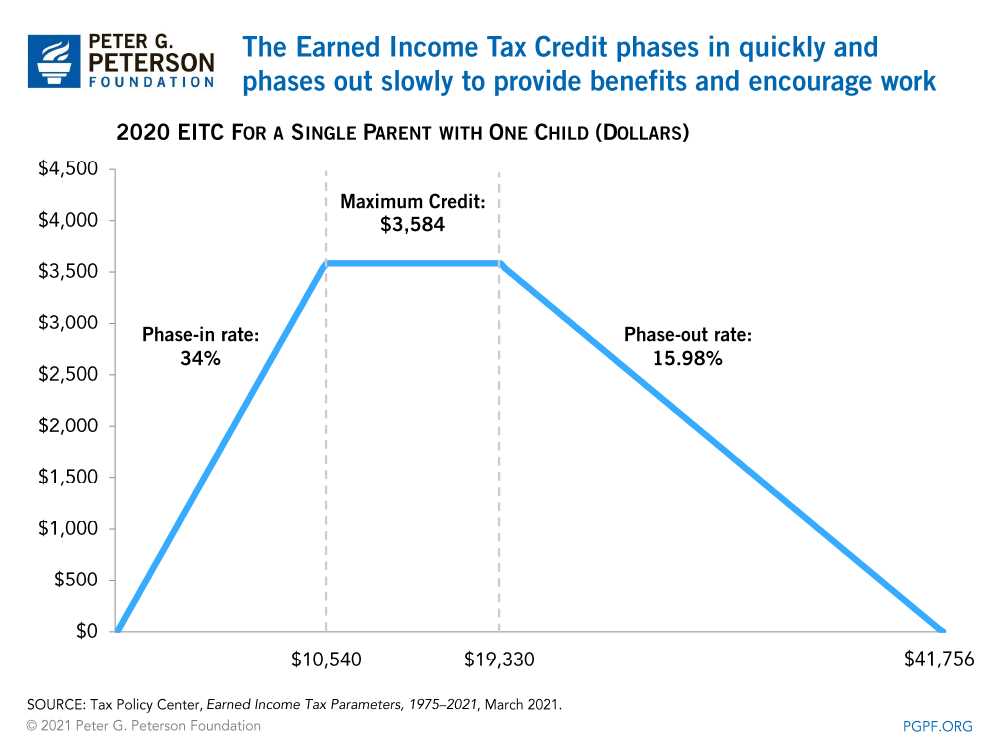
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a tax benefit for low to moderate-income individuals and families. To qualify for the EITC, you must meet certain requirements set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Here are the qualifications you need to meet in order to claim the EITC:
- Earned Income: You must have earned income from employment or self-employment. This includes wages, salaries, tips, and net earnings from self-employment.
- Filing Status: You must file your tax return using one of the following statuses: Single, Married Filing Jointly, Head of Household, or Qualifying Widow(er) with a dependent child.
- Investment Income: Your investment income for the year must be $3,650 or less.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): Your AGI must be below certain limits, which vary depending on your filing status and the number of qualifying children you have. The limits for the 2021 tax year are as follows:
- Single or Head of Household with no qualifying children: AGI must be less than $15,980.
- Married Filing Jointly with no qualifying children: AGI must be less than $21,920.
- Single, Head of Household, or Qualifying Widow(er) with one qualifying child: AGI must be less than $42,158.
- Married Filing Jointly with one qualifying child: AGI must be less than $48,108.
- Single, Head of Household, or Qualifying Widow(er) with two or more qualifying children: AGI must be less than $47,915.
- Married Filing Jointly with two or more qualifying children: AGI must be less than $53,865.
- Qualifying Children: You must have at least one qualifying child who meets the relationship, age, and residency requirements set by the IRS. A qualifying child can be your son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister, half-brother, half-sister, or a descendant of any of them.
- Social Security Number (SSN): You and your qualifying child (if applicable) must have valid SSNs issued by the Social Security Administration. An Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) is not sufficient for claiming the EITC.
- Residency: You must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien for the entire tax year.
- Age: You must be between the ages of 25 and 65 at the end of the tax year, unless you have a qualifying child.
- Other Income: You cannot have more than $10,000 in income from interest, dividends, or certain other sources.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
