Digital Currency: Types, Characteristics, Pros & Cons, Future Uses
Types of Digital Currency
There are several types of digital currency, each with its own unique features and purposes. Some of the most well-known types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin | The first and most popular cryptocurrency, known for its decentralized nature and limited supply. |
| Ethereum | A blockchain-based platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications. |
| Ripple | A digital payment protocol that facilitates fast and low-cost international money transfers. |
| Litecoin | A peer-to-peer cryptocurrency that offers faster transaction confirmation times compared to Bitcoin. |
Characteristics of Digital Currency
Digital currency shares several key characteristics that set it apart from traditional fiat currency:
- Decentralization: Digital currency operates on decentralized networks, such as blockchain, which eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Security: Cryptography ensures the security and integrity of digital currency transactions, making them highly resistant to fraud and hacking.
- Anonymity: While digital currency transactions are recorded on the blockchain, users can maintain a certain level of anonymity.
- Global Accessibility: Digital currency can be accessed and used by anyone with an internet connection, regardless of geographical location.
- Limited Supply: Many digital currencies have a finite supply, which can lead to scarcity and potential value appreciation.
Pros and Cons of Digital Currency
Like any financial instrument, digital currency has its advantages and disadvantages:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fast and low-cost transactions | Volatility and price fluctuations |
| Decentralization and transparency | Limited merchant acceptance |
| Protection against inflation | Potential for regulatory challenges |
| Financial inclusion for the unbanked | Security risks and hacking |
Future Uses of Digital Currency
The future of digital currency holds immense potential for various industries and sectors. Some potential future uses include:
- Remittances: Digital currency can revolutionize the remittance industry by enabling fast and low-cost cross-border transfers.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain-based digital currencies can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud and counterfeiting.
- Smart Contracts: Digital currency platforms like Ethereum enable the creation and execution of self-executing contracts, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
- Microtransactions: Digital currency can facilitate microtransactions, allowing for new business models and revenue streams.
Types of Digital Currency
Digital currency is a form of currency that exists only in electronic or digital form. It is not physically tangible like traditional currencies such as cash or coins. There are several types of digital currencies, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security. Bitcoin, created in 2009, is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. Other popular cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin. Cryptocurrencies are decentralized and operate on a technology called blockchain, which ensures transparency and security.
2. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are digital currencies issued and regulated by a central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are centralized and controlled by a government or central authority. CBDCs aim to provide the benefits of digital currencies while maintaining the stability and control of traditional fiat currencies. Several countries, including China and Sweden, are exploring the implementation of CBDCs.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that is designed to have a stable value, usually pegged to a fiat currency like the US dollar. They aim to address the volatility issues associated with cryptocurrencies, making them more suitable for everyday transactions. Tether and USD Coin are examples of stablecoins.
4. Digital Fiat Currencies
Digital fiat currencies are digital representations of traditional fiat currencies issued by a government or central bank. These currencies are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing authority. Digital fiat currencies are typically used for online transactions and can be stored in digital wallets.
5. Tokenized Assets
Characteristics of Digital Currency
Decentralization
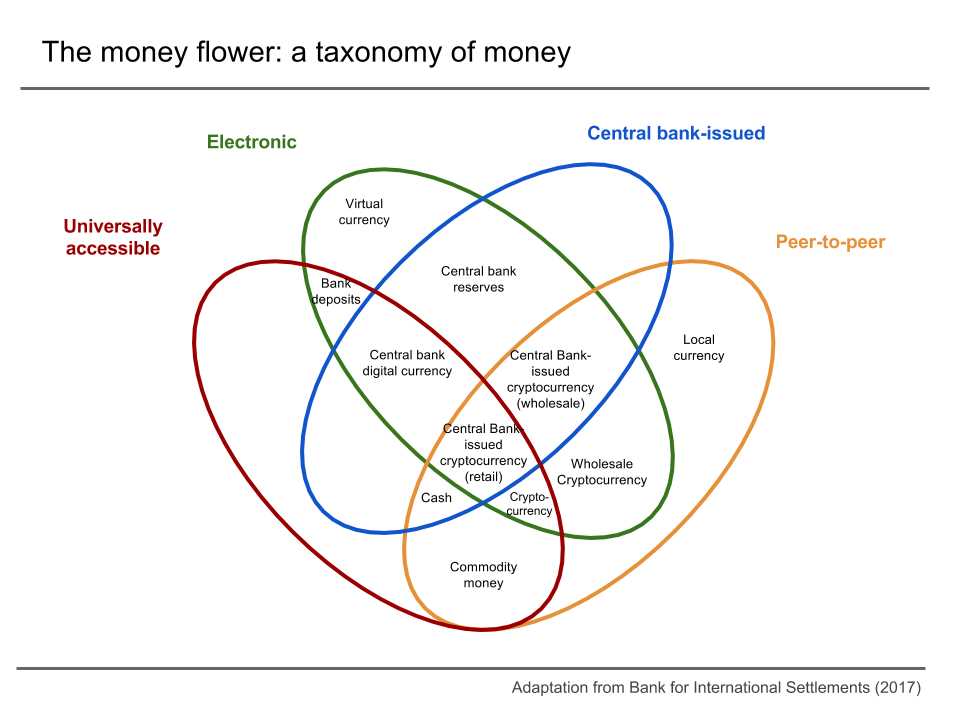
One of the main characteristics of digital currency is decentralization. Unlike traditional currencies that are controlled by central banks or governments, digital currencies operate on a decentralized network called blockchain. This means that no single entity has control over the currency, and transactions are verified by a network of computers spread across the globe.
Security
Digital currencies provide a high level of security due to the use of cryptographic techniques. Transactions made with digital currency are encrypted and stored on the blockchain, making it extremely difficult for hackers to tamper with the transaction data. Additionally, digital currencies often use advanced security measures such as two-factor authentication and biometric verification to protect users’ funds.
Anonymity
Another characteristic of digital currency is the level of anonymity it provides. While traditional banking systems require users to disclose their personal information for transactions, digital currencies allow users to remain pseudonymous. Transactions made with digital currency are recorded on the blockchain, but the identities of the parties involved are not directly linked to the transactions.
Global Accessibility
Digital currencies have the advantage of being accessible to anyone with an internet connection. Unlike traditional banking systems that may have limitations based on geographical location or financial status, digital currencies can be used by anyone, anywhere in the world. This makes it particularly beneficial for individuals in underbanked or unbanked regions.
Speed and Efficiency
Transactions made with digital currency are typically faster and more efficient compared to traditional banking systems. With digital currencies, there is no need for intermediaries such as banks, which can often slow down the transaction process. Additionally, digital currency transactions can be conducted 24/7, allowing for instant transfers and cross-border transactions without the need for currency conversion.
Volatility
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | No single entity has control over the currency, and transactions are verified by a network of computers spread across the globe. |
| Security | Transactions made with digital currency are encrypted and stored on the blockchain, making it difficult for hackers to tamper with the data. |
| Anonymity | |
| Global Accessibility | Digital currencies can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their geographical location or financial status. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Digital currency transactions are faster and more efficient compared to traditional banking systems, with no need for intermediaries. |
| Volatility | Digital currencies can experience significant price fluctuations, making them a risky investment. |
Pros and Cons of Digital Currency
Pros of Digital Currency
1. Security: One of the main advantages of digital currency is the high level of security it provides. Transactions made with digital currency are encrypted and stored on a decentralized network called the blockchain. This makes it extremely difficult for hackers to manipulate or steal funds.
2. Accessibility: Digital currency can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location. This makes it particularly useful for people in developing countries who may not have access to traditional banking services.
3. Lower Transaction Fees: Compared to traditional banking systems, digital currency transactions often have lower fees. This is because there are no intermediaries involved, such as banks or payment processors, which can charge additional fees.
4. Faster Transactions: Digital currency transactions are typically processed much faster than traditional banking transactions. This is because there is no need for manual verification or approval from third parties.
Cons of Digital Currency
2. Lack of Regulation: Digital currency operates outside of traditional financial systems and is not regulated by any central authority. This lack of regulation can lead to concerns about fraud, money laundering, and other illegal activities.
3. Limited Acceptance: While digital currency is gaining acceptance in many parts of the world, it is still not widely accepted as a form of payment. This can limit its usefulness and adoption in certain industries and regions.
Future Uses of Digital Currency

As digital currency continues to gain popularity and acceptance, its future uses are expanding rapidly. Here are some potential future applications of digital currency:
1. E-commerce
2. Cross-border Payments
One of the major advantages of digital currency is its ability to facilitate cross-border payments. Traditional methods of sending money internationally can be slow, expensive, and subject to various regulations. Digital currency can streamline this process by enabling instant and borderless transactions, making it easier for individuals and businesses to send and receive money across different countries.
3. Financial Inclusion
4. Micropayments
Overall, the future uses of digital currency are vast and diverse. As technology continues to advance and more people adopt digital currencies, we can expect to see further innovation and integration of digital currency into various aspects of our daily lives.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
