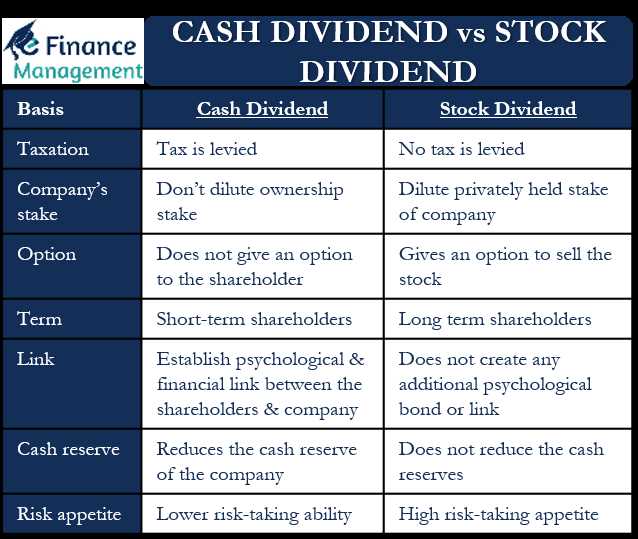
Cash Dividend Definition Example
A cash dividend is a payment made by a company to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash. It is a distribution of a portion of the company’s profits to the shareholders as a reward for their investment in the company.
Example of Cash Dividend

Let’s say Company XYZ has declared a cash dividend of $0.50 per share. If you own 100 shares of Company XYZ, you would receive a cash dividend of $50 ($0.50 x 100 shares).
Receiving a cash dividend is a way for shareholders to benefit from the company’s success. It provides them with a direct return on their investment and can be used as income or reinvested to purchase more shares.
In summary, cash dividends are payments made by companies to their shareholders, providing them with a direct return on their investment. They can be a source of income for shareholders and are a way for companies to share their profits with their owners.
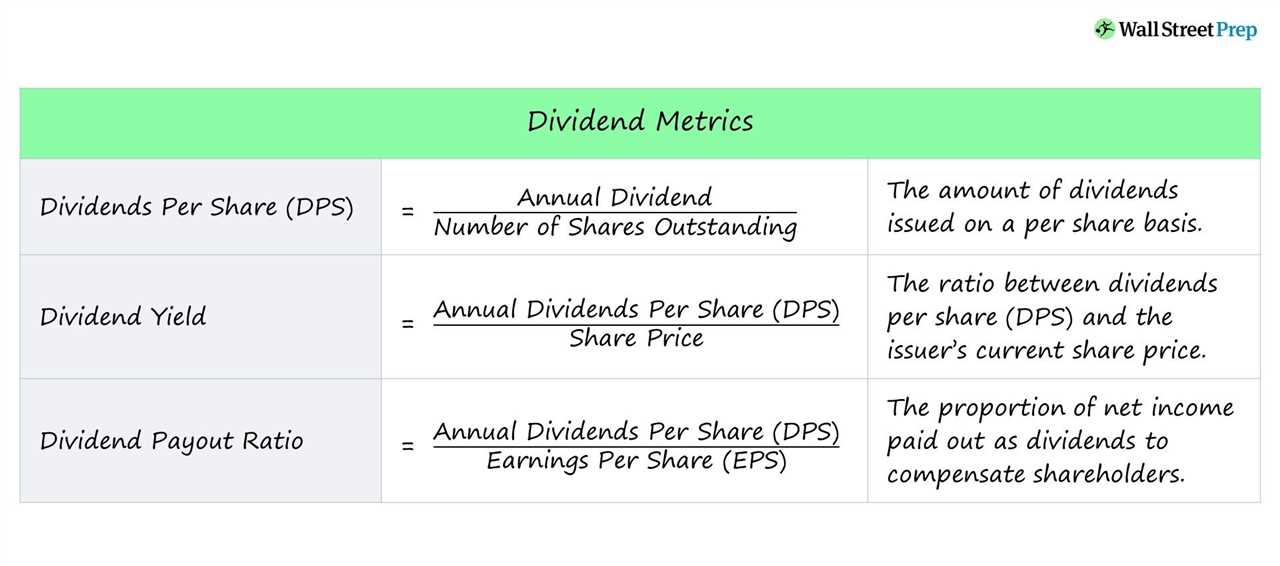
How are cash dividends calculated?
Once the dividend policy is established, the company announces the dividend amount per share. This amount is then multiplied by the number of shares that the shareholder owns to determine the total cash dividend payment.
Why do companies pay cash dividends?

Companies pay cash dividends for several reasons. First and foremost, it is a way for companies to reward their shareholders for their investment in the company. By distributing a portion of their profits as cash dividends, companies can attract and retain investors.
Benefits of Cash Dividends
Cash dividends are a form of payment that companies make to their shareholders as a distribution of profits. They offer several benefits to investors:
1. Regular income: Cash dividends provide investors with a regular stream of income. This can be particularly attractive for those who rely on their investments for income, such as retirees.
2. Stability: Companies that pay regular cash dividends are often seen as stable and financially sound. The ability to consistently generate profits and distribute them to shareholders is a positive sign for the company’s financial health.
4. Potential for growth: Companies that pay cash dividends may still have room for growth. By distributing a portion of their profits as dividends, they can attract investors who are seeking both income and potential capital appreciation.
5. Dividend reinvestment: Some companies offer dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs), which allow shareholders to automatically reinvest their cash dividends to purchase additional shares. This can help investors compound their returns over time.
6. Tax advantages: In some cases, cash dividends may be subject to lower tax rates than other forms of investment income, such as interest or capital gains. This can result in tax advantages for investors, depending on their individual tax situation.
Example of Cash Dividends
One of the best ways to understand cash dividends is through an example. Let’s say you are an investor who owns 100 shares of XYZ Company. The company has announced a cash dividend of $1 per share.
Since you own 100 shares, you will receive a total cash dividend of $100 (100 shares x $1 per share). This means that the company will pay you $100 in cash as a return on your investment.
Receiving cash dividends can be a great way to generate passive income. As an investor, you can choose to reinvest the cash dividends back into the company by purchasing more shares or use the cash for other purposes.
Benefits of Cash Dividends
Cash dividends offer several benefits to investors:
- Regular Income: Cash dividends provide a regular stream of income for investors, especially those who rely on their investments for retirement or other financial goals.
- Stability: Companies that consistently pay cash dividends are often seen as stable and financially healthy. This can attract more investors and potentially increase the stock price.
- Tax Advantages: In some countries, cash dividends may be subject to lower tax rates compared to other forms of investment income.
Overall, cash dividends can be a valuable component of an investment portfolio, providing income and potential growth opportunities.
Stock Dividend Definition Example
A stock dividend is a distribution of additional shares of a company’s stock to its existing shareholders. It is a way for a company to reward its shareholders by providing them with additional ownership in the company.
For example, let’s say Company XYZ declares a stock dividend of 10%. This means that for every 100 shares of stock an investor owns, they will receive an additional 10 shares. So if an investor owns 1,000 shares of Company XYZ, they would receive an additional 100 shares as a stock dividend.
Stock dividends are typically expressed as a percentage of the existing shares outstanding. They are often used by companies that want to conserve cash but still provide a return to their shareholders. By issuing additional shares instead of cash, the company can retain more cash for other purposes such as investment or debt reduction.
When a stock dividend is declared, the company’s total shares outstanding increase, but the proportional ownership of each shareholder remains the same. This means that while the number of shares an investor holds increases, the value of each individual share may decrease slightly.
Overall, stock dividends can be a way for investors to increase their ownership in a company without having to purchase additional shares. They can also be a signal of a company’s confidence in its future prospects, as it is essentially reinvesting in itself by issuing additional shares to its shareholders.
| Advantages of Stock Dividends | Disadvantages of Stock Dividends |
|---|---|
| – Increase in ownership without additional investment | – Dilution of ownership |
| – Potential for future capital gains | – Potential decrease in share value |
| – Signals company’s confidence in future prospects | – Increased administrative burden for the company |
A stock dividend is a distribution of additional shares of a company’s stock to its existing shareholders. It is a way for a company to reward its shareholders by providing them with additional ownership in the company.
When a company declares a stock dividend, it is essentially converting a portion of its retained earnings into additional shares of stock. This means that shareholders receive more shares in the company without any cash outlay.
Stock dividends are usually expressed as a percentage, such as a 5% stock dividend, which means that for every 100 shares a shareholder owns, they will receive an additional 5 shares.
Stock dividends are different from cash dividends, which are payments made to shareholders in the form of cash. While cash dividends provide immediate income to shareholders, stock dividends increase the number of shares a shareholder owns, but do not provide immediate cash flow.
One of the main benefits of stock dividends is that they can increase the liquidity of a company’s stock. By increasing the number of shares outstanding, stock dividends can make it easier for shareholders to buy and sell shares in the market.
Additionally, stock dividends can also be a sign of a company’s financial health and growth potential. When a company declares a stock dividend, it is a signal that the company has enough retained earnings to distribute additional shares to its shareholders.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
