Auditor’s Opinion: Definition, How It Works, Types
An auditor’s opinion is a statement provided by an independent auditor regarding the financial statements of a company. It is an important document that provides an assessment of the accuracy and reliability of the financial information presented by the company.
Definition
An auditor’s opinion is a formal statement issued by an auditor after conducting an audit of a company’s financial statements. It provides an evaluation of whether the financial statements are prepared in accordance with the applicable accounting standards and present a true and fair view of the company’s financial position and performance.
How It Works
The auditor’s opinion is typically included in the company’s annual report and is addressed to the shareholders and other stakeholders. It provides assurance to the users of the financial statements that the information presented is reliable and can be used for decision-making purposes.
Types of Auditor’s Opinions
There are several types of auditor’s opinions that can be issued, depending on the findings of the audit. The most common types include:
- Unqualified Opinion: This is the most favorable opinion that can be issued. It indicates that the financial statements are free from material misstatements and present a true and fair view of the company’s financial position and performance.
- Qualified Opinion: This opinion is issued when the auditor identifies certain limitations in the audit or exceptions to the accounting principles used by the company. It indicates that while the financial statements are generally reliable, there are specific areas that require attention.
- Adverse Opinion: This is the most unfavorable opinion that can be issued. It indicates that the financial statements are materially misstated and do not present a true and fair view of the company’s financial position and performance.
- Disclaimer of Opinion: This opinion is issued when the auditor is unable to form an opinion on the financial statements due to significant limitations in the scope of the audit or the unavailability of sufficient evidence.
It is important for users of the financial statements to understand the type of auditor’s opinion issued, as it provides insights into the reliability of the information presented. A favorable opinion provides greater confidence in the financial statements, while an unfavorable opinion raises concerns about the accuracy of the information.
What is an Auditor’s Opinion?
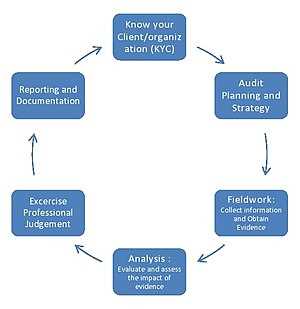
An auditor’s opinion is a statement issued by an independent auditor regarding the financial statements of a company. It is an assessment of the accuracy, completeness, and fairness of the financial information presented in the company’s financial statements.
The auditor’s opinion is an important tool for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders in assessing the reliability of the financial statements. It provides assurance that the financial statements have been prepared in accordance with the applicable accounting standards and that they fairly represent the financial position, results of operations, and cash flows of the company.
Purpose of an Auditor’s Opinion
The main purpose of an auditor’s opinion is to provide an independent and objective assessment of the financial statements. It helps users of the financial statements to make informed decisions based on reliable and trustworthy information. The opinion also serves as a safeguard against fraud, misrepresentation, and errors in the financial reporting process.
The auditor’s opinion is typically included in the company’s annual report, which is made available to shareholders and other interested parties. It provides transparency and accountability, as it allows stakeholders to evaluate the financial health and performance of the company.
Components of an Auditor’s Opinion
An auditor’s opinion typically consists of the following components:
- Introductory paragraph: This states the auditor’s responsibility and the scope of the audit.
- Management’s responsibility paragraph: This states the responsibility of the company’s management for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements.
- Auditor’s opinion paragraph: This expresses the auditor’s opinion on the financial statements.
- Basis for opinion paragraph: This explains the basis for the auditor’s opinion and provides additional information about the audit process.
- Other reporting responsibilities paragraph: This includes any additional reporting responsibilities of the auditor, such as reporting on internal control over financial reporting.
How Does an Auditor’s Opinion Work?
When conducting an audit, an auditor’s opinion is a crucial component of the final report. It provides an assessment of the financial statements and the overall financial health of a company. The auditor’s opinion is based on the evidence gathered during the audit process and is meant to provide assurance to stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, and regulators.
Evaluating Financial Statements
The auditor also evaluates the company’s accounting policies and practices to determine if they are appropriate and consistently applied. They review the company’s internal controls to assess their effectiveness in preventing and detecting fraud or errors in financial reporting.
Forming an Opinion
Based on their examination of the financial statements and supporting documentation, the auditor forms an opinion on the fairness and reliability of the information presented. This opinion is then communicated in a written report, which is included in the company’s annual financial statements.
The auditor’s opinion can take different forms, depending on the findings of the audit. The most common types of auditor’s opinions include:
- Unqualified Opinion: This is the best opinion a company can receive, indicating that the financial statements are presented fairly and in accordance with accounting standards.
- Qualified Opinion: This opinion is issued when the auditor identifies a specific issue or limitation that affects a portion of the financial statements, but does not invalidate the overall fairness of the information.
- Adverse Opinion: This opinion is given when the auditor determines that the financial statements are materially misstated and do not accurately reflect the financial position of the company.
- Disclaimer of Opinion: This opinion is issued when the auditor is unable to form an opinion due to significant limitations or uncertainties in the audit process.
The auditor’s opinion is an important tool for stakeholders in assessing the reliability of a company’s financial statements. It helps them make informed decisions about investing, lending, or doing business with the company.
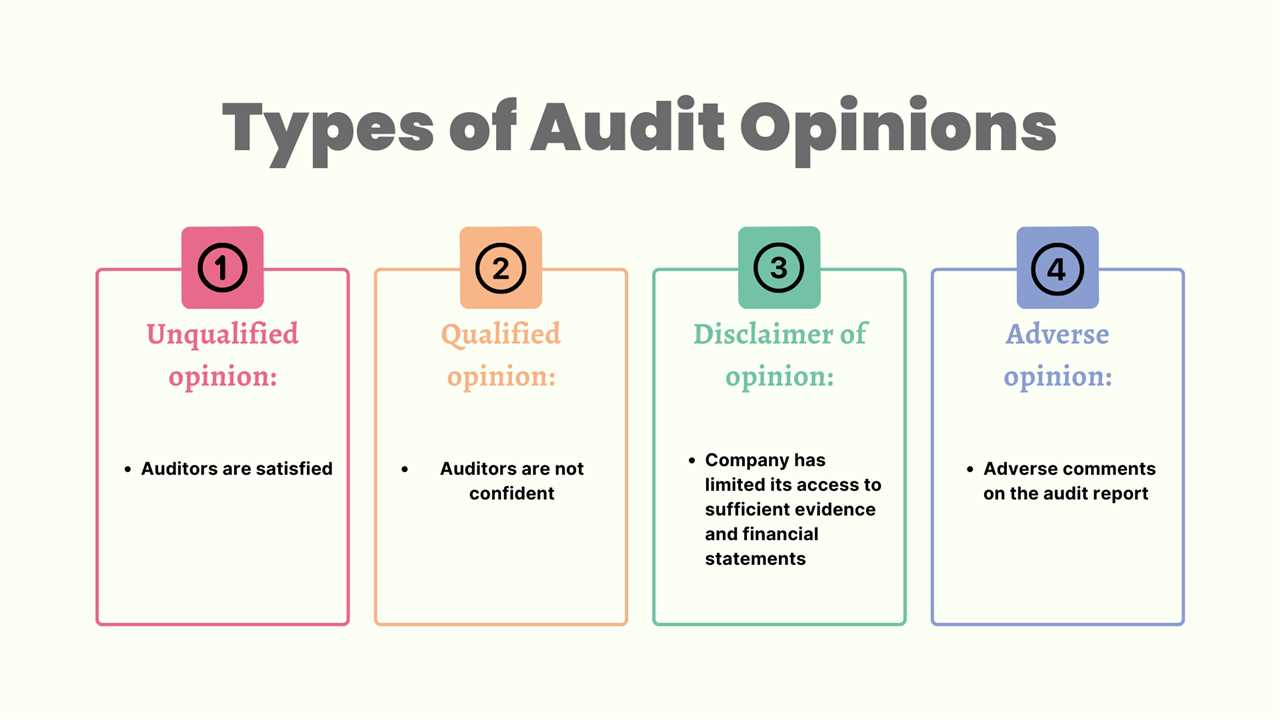
Types of Auditor’s Opinions
An auditor’s opinion is a crucial component of a company’s financial statements. It provides an independent assessment of the company’s financial health and the accuracy of its financial reporting. There are several types of auditor’s opinions that can be issued based on the auditor’s findings. These opinions help stakeholders, such as investors and creditors, make informed decisions about the company.
1. Unqualified Opinion
2. Qualified Opinion
A qualified opinion is issued when the auditor identifies a specific issue or limitation in the financial statements that does not comply with the GAAP. This issue could be due to a lack of sufficient evidence or a disagreement with the company’s accounting policies. While a qualified opinion raises concerns, it is not as severe as an adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion.
3. Adverse Opinion
An adverse opinion is the most severe type of auditor’s opinion. It is issued when the auditor determines that the financial statements are materially misstated and do not comply with the GAAP. This opinion indicates significant issues with the company’s financial reporting, which can negatively impact stakeholders’ confidence in the company’s financial health and performance.
4. Disclaimer of Opinion
A disclaimer of opinion is issued when the auditor is unable to express an opinion on the financial statements. This could be due to various reasons, such as a lack of access to necessary information or significant uncertainties. A disclaimer of opinion indicates that the auditor was unable to gather sufficient evidence to form an opinion on the company’s financial statements.
It is important for stakeholders to carefully review the auditor’s opinion when evaluating a company’s financial statements. The type of opinion issued can provide valuable insights into the company’s financial health and the reliability of its financial reporting. Stakeholders should consider the implications of each type of opinion and seek further information or clarification if necessary.
What is an Auditor’s Opinion?
An auditor’s opinion is a formal statement issued by an independent auditor after conducting an audit of a company’s financial statements. It expresses the auditor’s professional judgment regarding the fairness and reliability of the financial information presented. The opinion is based on the auditor’s evaluation of the company’s accounting practices, internal controls, and compliance with relevant accounting standards.
How Does an Auditor’s Opinion Work?

An auditor’s opinion is formed through a rigorous audit process that involves examining the company’s financial records, conducting tests and procedures, and assessing the overall financial health of the organization. The auditor gathers evidence to support their opinion and ensures that the financial statements are free from material misstatements or errors.
The auditor’s opinion is typically presented in a written report that includes the following elements:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Introductory Paragraph | Provides an overview of the audit and the responsibilities of the auditor and management. |
| Scope Paragraph | Explains the extent of the audit procedures performed and any limitations encountered. |
| Opinion Paragraph | States the auditor’s opinion on the fairness of the financial statements. |
| Basis for Opinion Paragraph | Describes the audit evidence obtained and the reasons for the auditor’s opinion. |
| Other Reporting Responsibilities | Includes any additional information required by auditing standards. |
Types of Auditor’s Opinions
Auditor’s opinions can vary depending on the findings of the audit. The most common types of opinions include:
- Unqualified Opinion: The auditor concludes that the financial statements are presented fairly and in accordance with the applicable accounting standards.
- Qualified Opinion: The auditor expresses a limitation or exception to the opinion due to a specific issue or a departure from the accounting standards.
- Adverse Opinion: The auditor determines that the financial statements are materially misstated and do not present a true and fair view of the company’s financial position.
- Disclaimer of Opinion: The auditor is unable to form an opinion due to significant limitations or uncertainties in the audit procedures.
These opinions provide valuable insights into the reliability and accuracy of a company’s financial statements, helping stakeholders make informed decisions about their investments or business relationships.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
