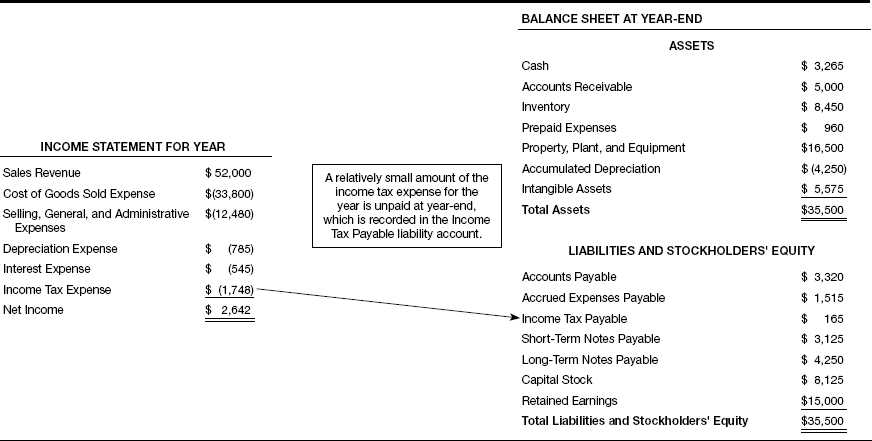
What is Income Tax Payable?
Income tax payable is a financial obligation that individuals and businesses have to pay to the government based on their taxable income. It represents the amount of income tax that is owed to the government for a specific period, typically a year.
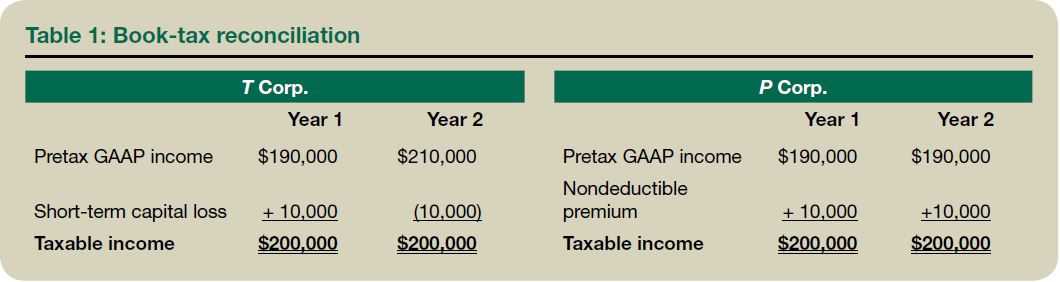
Income tax payable is calculated based on the applicable tax rates and tax laws of the country or jurisdiction in which the individual or business operates. It is an important aspect of financial accounting as it affects the financial statements and overall financial position of an entity.
When individuals or businesses earn income, they are required to report their income to the tax authorities and calculate the amount of income tax they owe. This is done by applying the relevant tax rates to their taxable income, which is the income after deducting allowable expenses and deductions.
Income tax payable is classified as a current liability on the balance sheet, as it represents a debt that is expected to be settled within one year. It is important for individuals and businesses to accurately calculate and record their income tax payable to ensure compliance with tax laws and to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Managing income tax payable involves proper record-keeping, timely payment of taxes, and staying updated with changes in tax laws and regulations. It is also important to consult with tax professionals or accountants to ensure accurate calculations and compliance with tax laws.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Income tax payable is the amount of income tax that individuals and businesses owe to the government. |
| It is calculated based on the applicable tax rates and tax laws. |
| Income tax payable is classified as a current liability on the balance sheet. |
| Proper management of income tax payable involves accurate calculations, timely payments, and staying updated with tax laws. |
Importance of Income Tax Payable in Financial Accounting
1. Accurate Financial Reporting
Income tax payable plays a significant role in ensuring accurate financial reporting. It is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet, reflecting the company’s obligation to pay taxes in the future. By accurately accounting for income tax payable, businesses can provide a clear and transparent picture of their financial position to stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities.
Additionally, income tax payable affects the income statement. The amount of income tax expense is calculated based on the taxable income and the applicable tax rate. This expense is then deducted from the company’s net income, reducing the overall profitability. By accurately accounting for income tax payable, businesses can provide a true representation of their financial performance.
2. Compliance with Tax Laws
Income tax payable is essential for ensuring compliance with tax laws. Businesses and individuals are required to pay their taxes in a timely and accurate manner. Failing to do so can result in penalties, fines, and legal consequences. By properly accounting for income tax payable, businesses can fulfill their tax obligations and avoid any potential legal issues.
3. Financial Planning and Decision Making
Income tax payable is an important factor in financial planning and decision making. By accurately accounting for income tax payable, businesses can forecast and budget for future tax payments. This allows them to effectively manage their cash flow and ensure that they have sufficient funds to meet their tax obligations.
Managing Income Tax Payable in Financial Accounting
Managing income tax payable is a crucial aspect of financial accounting for businesses. It involves accurately calculating and recording the amount of income tax that a company owes to the government.
Here are some key steps to effectively manage income tax payable:
- Proper Documentation: It is essential to maintain proper documentation of all income, expenses, deductions, and credits that impact the calculation of income tax payable. This documentation will be crucial during tax audits or any inquiries from tax authorities.
- Timely Payments: Businesses need to ensure that income tax payable is paid on time to avoid penalties and interest charges. This requires careful planning and budgeting to set aside funds for tax payments.
- Monitoring and Reconciliation: Regular monitoring of income tax payable is necessary to ensure that it aligns with the financial records of the company. Any discrepancies should be investigated and reconciled promptly to maintain accurate financial statements.
- Seeking Professional Advice: Given the complexity of tax laws, businesses may benefit from seeking professional advice from tax consultants or accountants. They can provide guidance on tax planning strategies, potential deductions, and credits that can help minimize the income tax payable.
By effectively managing income tax payable, businesses can ensure compliance with tax laws, avoid penalties, and optimize their tax liabilities. It is an integral part of financial accounting that requires attention to detail, proper documentation, and timely payments.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
