What Are Tariffs and How Do They Work?
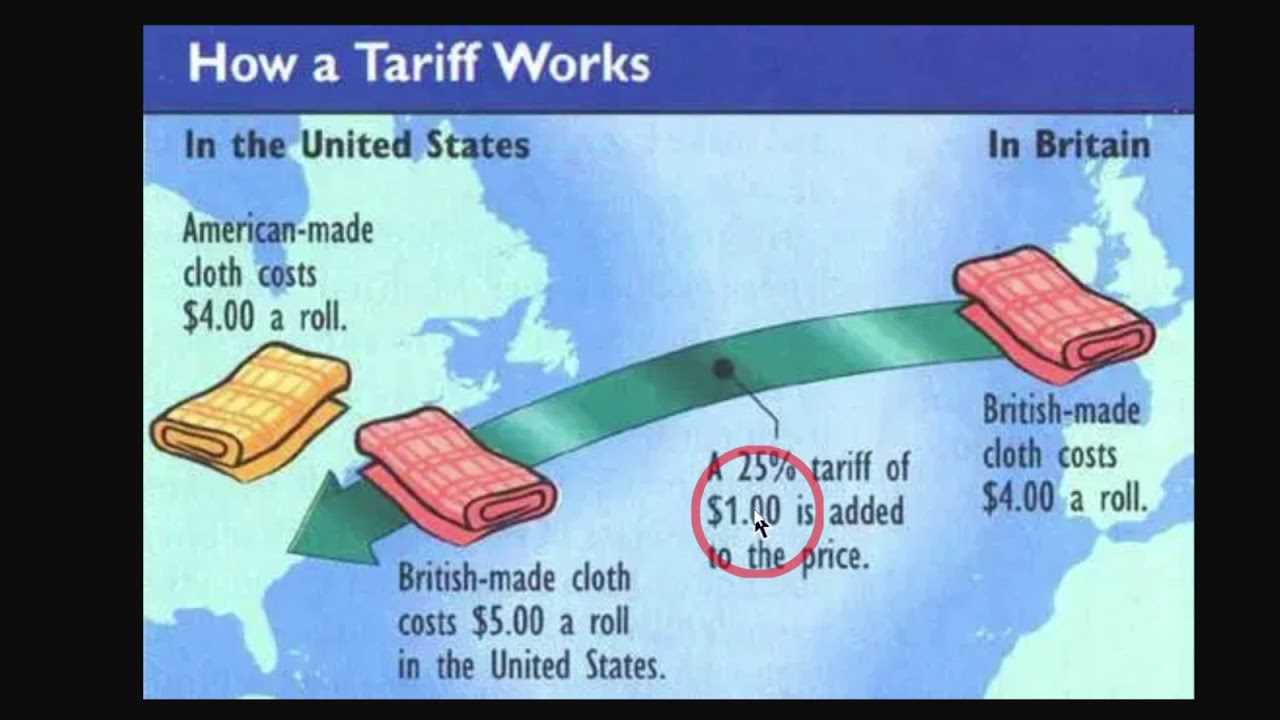
Tariffs are taxes or duties imposed on imported goods and services by a government. They are a form of trade barrier that is used to protect domestic industries and promote economic growth. Tariffs can be applied to specific products or to all imports from a particular country.
The primary purpose of tariffs is to make imported goods more expensive and less competitive compared to domestic products. This is done by adding an extra cost to the price of imported goods, which can make them less attractive to consumers. Tariffs can also be used to generate revenue for the government.
Tariffs work by increasing the cost of imported goods, which can have several effects. First, they can protect domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive, allowing domestic producers to compete more effectively. This can help to preserve jobs and promote economic growth in the domestic market.
However, tariffs can also have negative effects. They can increase the cost of imported goods for consumers, reducing their purchasing power and potentially leading to higher prices for domestic goods as well. Tariffs can also lead to retaliation from other countries, resulting in a trade war that can harm both domestic and international economies.
Tariffs can be implemented in different ways. They can be ad valorem, meaning they are based on a percentage of the value of the imported goods, or specific, meaning they are based on a fixed amount per unit of the imported goods. Tariffs can also be used as a tool for trade negotiations, with countries using them as leverage to gain concessions from trading partners.
| Pros of Tariffs | Cons of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Protect domestic industries | Increase cost of imported goods for consumers |
| Promote economic growth | Potential for trade wars and retaliation |
| Generate revenue for the government | Potential for higher prices for domestic goods |
The Role of Tariffs in Government and Policy
Tariffs play a crucial role in government and policy, serving as a tool for regulating trade and protecting domestic industries. Governments often use tariffs as a means to control imports and exports, ensuring a balance in trade and safeguarding national interests.
Regulating Trade
Tariffs are implemented by governments to regulate the flow of goods and services across borders. By imposing tariffs on certain imported goods, governments can control the quantity and price of these products in the domestic market. This can help protect domestic industries from foreign competition and prevent the dumping of cheap goods that could harm local businesses.
Furthermore, tariffs can be used strategically to encourage or discourage trade with specific countries. Governments may impose higher tariffs on goods from countries they consider to be unfair trade partners or those that engage in practices deemed harmful to their own economy.
Protecting Domestic Industries
Tariffs are often used to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. By imposing tariffs on imported goods, governments can make these products more expensive for consumers, thereby making domestically produced goods more competitive. This can help support local industries, preserve jobs, and promote economic growth.
Additionally, tariffs can be used to address issues such as unfair trade practices, intellectual property violations, or environmental concerns. Governments may impose tariffs as a means of pressuring other countries to comply with certain standards or regulations.
Generating Revenue

Tariffs also serve as a significant source of revenue for governments. By imposing tariffs on imported goods, governments can collect revenue in the form of customs duties. This revenue can be used to fund various government programs, infrastructure development, or public services.
Political Considerations
Tariffs can also be influenced by political considerations. Governments may use tariffs as a tool to appease certain interest groups or to gain leverage in international negotiations. Tariffs can be a way for governments to demonstrate their commitment to protecting domestic industries and ensuring the welfare of their citizens.
| Advantages of Tariffs | Disadvantages of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| – Protect domestic industries | – Increase prices for consumers |
| – Regulate trade | – Potentially lead to trade wars |
| – Generate revenue for the government | – Reduce consumer choices |
| – Address unfair trade practices | – Can be influenced by political considerations |
Why Are Tariffs Important for the Economy?

Tariffs play a significant role in shaping the economy of a country. They are a form of taxation imposed on imported goods, which can have both positive and negative impacts on the economy.
Protection of Domestic Industries
One of the main reasons why tariffs are important is to protect domestic industries. By imposing tariffs on imported goods, the government can make them more expensive compared to domestically produced goods. This creates a competitive advantage for local industries, as it encourages consumers to purchase goods produced within the country. This protectionism helps to safeguard jobs and promote economic growth in domestic industries.
Revenue Generation
Tariffs also serve as a source of revenue for the government. When goods are imported, tariffs are collected, and this revenue can be used to fund various government programs and initiatives. This additional income can contribute to the overall economic development of the country.
Trade Balance and Current Account
Tariffs can also be used to address trade imbalances and maintain a favorable current account balance. By imposing tariffs on certain imported goods, the government can reduce the demand for these products, which in turn can help to decrease imports. This can lead to a reduction in the trade deficit and contribute to a more balanced current account.
However, it is important to note that excessive use of tariffs can also have negative effects on the economy. It can lead to higher prices for consumers, limited choices, and potential retaliation from other countries in the form of their own tariffs. Therefore, careful consideration and balance are necessary when implementing tariff policies.
Implications of Tariffs on International Trade
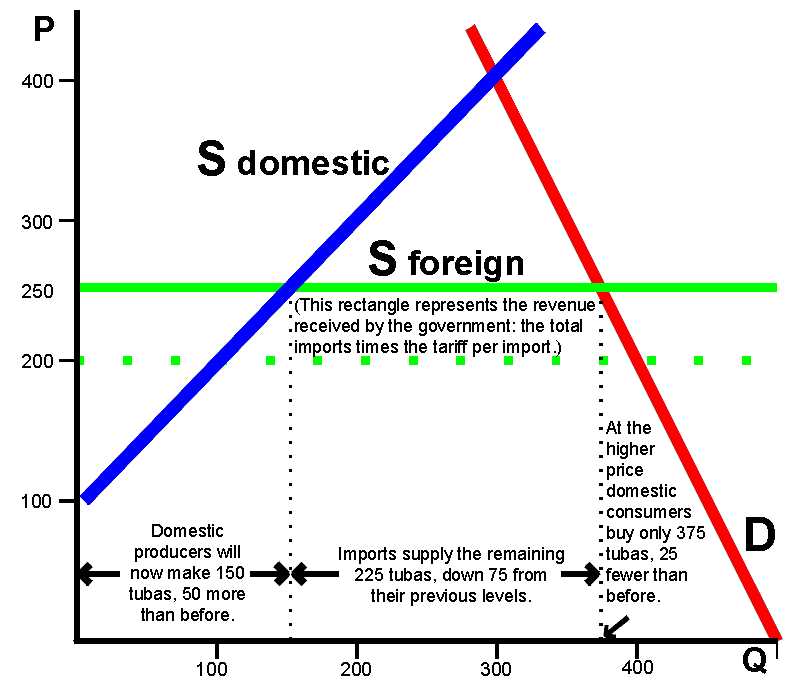
One of the main implications of tariffs on international trade is the impact on the competitiveness of domestic industries. When a country imposes tariffs on imported goods, it raises the cost of those goods, making them less competitive compared to domestically produced goods. This can protect domestic industries from foreign competition and help them grow. However, it can also lead to inefficiencies and higher prices for consumers.
Tariffs also affect the prices of goods and services. By increasing the cost of imported goods, tariffs can lead to higher prices for consumers. This can have a direct impact on the purchasing power of individuals and households, especially for goods that are heavily reliant on imports. Additionally, higher prices can also lead to inflationary pressures in the economy, reducing overall economic growth.
Furthermore, tariffs can have broader implications for the overall economic growth of a country. By restricting imports, tariffs can limit access to foreign markets and hinder the growth of export-oriented industries. This can have a negative impact on the balance of trade and potentially lead to trade deficits. Additionally, tariffs can also result in retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to trade wars and further disruptions in international trade.
It is important to note that the implications of tariffs are not solely negative. In certain cases, tariffs can be used strategically to protect domestic industries, promote economic development, and address unfair trade practices. However, it is crucial to carefully consider the potential consequences and weigh them against the intended benefits.
| Implications of Tariffs on International Trade |
|---|
| 1. Impact on the competitiveness of domestic industries |
| 2. Effect on the prices of goods and services |
| 3. Influence on the overall economic growth of a country |
| 4. Potential for trade deficits and trade wars |
| 5. Strategic use to protect domestic industries and address unfair trade practices |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
