What is Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT)?
A Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) is a type of satellite communication system that uses small dish antennas to transmit and receive data. It is commonly used in remote areas where traditional wired or wireless communication infrastructure is not available or feasible.
Definition and Explanation

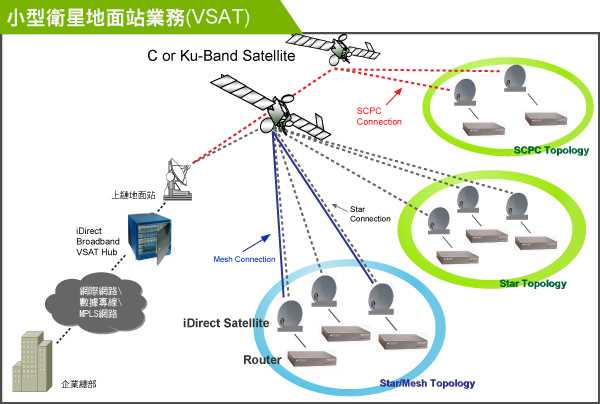
VSAT technology utilizes geostationary satellites to establish communication links between the hub station and the remote terminals. Geostationary satellites are positioned at a fixed point above the Earth’s equator, allowing them to remain in the same position relative to the Earth’s surface. This enables continuous communication between the hub station and the remote terminals.
The dish antennas used in VSAT systems are relatively small, typically ranging from 0.75 meters to 2.4 meters in diameter. Despite their small size, these antennas are capable of transmitting and receiving data at high speeds, making VSAT a viable solution for various applications, including internet access, voice and video communication, and data transfer.
How VSAT Works
When a user initiates a communication request, such as accessing a website or making a phone call, the data is first transmitted from the remote terminal to the hub station via the dish antenna. The hub station then routes the data to its intended destination, which could be another remote terminal or a device connected to the wider communication network.
Similarly, when data is received, the hub station transmits it to the appropriate remote terminal, which then delivers it to the end user. This bidirectional communication process allows for seamless data transmission and reception between the hub station and the remote terminals.
Applications of VSAT
VSAT technology has a wide range of applications across various industries. It is commonly used in the following areas:
- Telecommunications: VSAT enables reliable and high-speed internet access in remote areas where traditional wired or wireless networks are not available.
- Oil and Gas: VSAT is used for offshore communication, allowing remote oil rigs and platforms to stay connected with onshore facilities.
- Banking and Finance: VSAT provides secure and efficient communication for banking and financial institutions, especially in areas with limited infrastructure.
- Emergency Services: VSAT is used for emergency communication during natural disasters or in remote locations where traditional communication networks are disrupted.
- Transportation and Logistics: VSAT enables real-time tracking and communication for ships, airplanes, and other vehicles in remote areas.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VSAT
There are several advantages of using VSAT technology:
- Global Coverage: VSAT can provide connectivity in even the most remote areas, making it a valuable solution for businesses and individuals operating in such locations.
- Reliability: VSAT systems are designed to be highly reliable, with minimal downtime and consistent performance.
- Scalability: VSAT networks can be easily expanded or upgraded to accommodate increasing data demands.
- Flexibility: VSAT can be deployed quickly and easily, making it a flexible solution for temporary or mobile communication needs.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Cost: VSAT systems can be expensive to install and maintain, especially for small-scale deployments.
- Latency: Due to the distance between the satellite and the Earth’s surface, VSAT communication can experience higher latency compared to terrestrial networks.
- Weather Dependence: VSAT signals can be affected by adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow, leading to potential disruptions in communication.
Despite these drawbacks, VSAT technology continues to be a valuable solution for bridging the communication gap in remote areas and providing reliable connectivity in various industries.
Definition and Explanation
A Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) is a satellite communication system that uses small dish antennas to transmit and receive data. It is a two-way satellite ground station that provides communication services to remote locations where traditional wired or wireless networks are not available or are unreliable.
VSAT systems are commonly used in various industries and applications, including telecommunications, banking, oil and gas, maritime, and government sectors. They provide reliable and cost-effective connectivity solutions for remote sites, allowing businesses and organizations to communicate and access data in real-time.
One of the key advantages of VSAT systems is their ability to provide wide coverage and reach remote locations that are not easily accessible by traditional communication networks. They can be deployed in rural areas, offshore platforms, or even in mobile vehicles, providing connectivity in areas where other options are limited.
Another advantage of VSAT systems is their scalability. They can be easily expanded or upgraded to accommodate increasing data demands. This flexibility makes them suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using VSAT systems. One of the main drawbacks is the latency or delay in signal transmission due to the long distance between the satellite and the ground station. This can affect real-time applications such as voice and video calls.
Additionally, VSAT systems require a clear line of sight to the satellite, which can be challenging in areas with dense vegetation or tall buildings. The installation and maintenance of VSAT systems can also be costly, especially in remote locations where access is difficult.
How VSAT Works
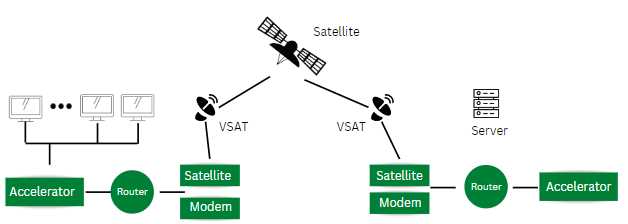
A Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) is a satellite communication system that allows for two-way communication between a central hub and remote terminals. The system consists of three main components: the hub station, the satellite, and the remote terminals.
The satellite acts as a relay station in the VSAT system. It receives signals from the hub station and retransmits them to the remote terminals. Similarly, it receives signals from the remote terminals and relays them back to the hub station. The satellite is positioned in geostationary orbit, which means it stays fixed relative to the Earth’s surface, allowing for continuous communication with the hub station and remote terminals.
When a user at a remote terminal wants to communicate with the hub station, they send a signal to the satellite using their dish antenna. The satellite receives the signal and relays it to the hub station. The hub station processes the signal and sends a response back to the satellite, which then relays it to the remote terminal. This two-way communication allows for real-time data transmission between the hub station and the remote terminals.
VSAT systems use a technique called frequency division multiple access (FDMA) to allow multiple remote terminals to communicate with the hub station simultaneously. Each remote terminal is assigned a specific frequency band for communication, which prevents interference between terminals.
In addition to data transmission, VSAT systems can also support other services such as voice communication, video conferencing, and internet access. The system can be used in various industries, including telecommunications, banking, oil and gas, and maritime.
| Advantages of VSAT | Disadvantages of VSAT |
|---|---|
| Wide coverage area | High initial setup cost |
| Reliable and secure communication | Dependence on satellite connectivity |
| Flexible and scalable system | Signal latency due to long distance communication |
| Easy installation and maintenance | Weather conditions can affect signal quality |
Applications of VSAT
Very Small Aperture Terminals (VSATs) have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the key applications of VSAT:
- Telecommunications: VSATs are commonly used for telecommunications purposes, providing reliable and high-speed communication links between remote locations and central hubs. They are used for voice, data, and video transmission, enabling businesses to connect their branches, remote offices, and even offshore locations.
- Internet Connectivity: VSATs play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide by providing internet connectivity to underserved areas where terrestrial infrastructure is limited or unavailable. They are used to establish internet access in rural and remote regions, enabling individuals, businesses, and communities to connect to the global network.
- Banking and Financial Services: VSATs are widely used in the banking and financial sector to establish secure and reliable communication links between bank branches, ATMs, and central data centers. This ensures seamless transaction processing, real-time data synchronization, and secure access to banking services in remote areas.
- Oil and Gas Industry: VSATs are extensively used in the oil and gas industry for remote monitoring, control, and communication purposes. They enable real-time data transmission from offshore platforms, remote drilling sites, and pipeline networks, facilitating efficient operations, safety monitoring, and emergency response.
- Government and Defense: VSATs are utilized by government agencies and defense organizations for secure communication, command and control, surveillance, and intelligence gathering. They provide reliable and encrypted communication channels for military operations, disaster response, and remote monitoring of critical infrastructure.
- Education and E-Learning: VSATs are employed in the education sector to deliver distance learning programs, virtual classrooms, and online training courses. They enable students and teachers in remote areas to access educational resources, participate in interactive sessions, and collaborate with peers and experts from around the world.
- Broadcasting and Media: VSATs are used in the broadcasting and media industry for content distribution, satellite news gathering (SNG), and live event coverage. They enable the transmission of television and radio signals, video feeds, and multimedia content to a wide audience, even in remote or geographically challenging locations.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: VSATs are employed in agriculture and rural development projects to provide farmers with access to weather information, market prices, agricultural best practices, and e-commerce platforms. They enable remote monitoring of crops, livestock, and irrigation systems, facilitating precision farming and sustainable rural development.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of VSAT technology. With its versatility, reliability, and scalability, VSAT continues to play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide and connecting the world.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VSAT
Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) technology has both advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when deciding whether to implement it.
Advantages:

1. Wide Coverage: VSAT systems can provide connectivity to remote areas where traditional wired networks are not available. This makes it a valuable solution for businesses and organizations operating in rural or underserved locations.
2. Scalability: VSAT networks can be easily expanded to accommodate increasing data demands. Additional VSAT terminals can be added to the network without significant infrastructure changes, making it a flexible option for businesses that anticipate growth.
3. Quick Deployment: VSAT terminals can be set up relatively quickly compared to traditional wired networks. This is especially beneficial in emergency situations or for temporary connectivity needs, such as during events or disaster recovery.
5. Cost-Effective: In some cases, VSAT can be a cost-effective solution compared to laying down new cables or leasing dedicated lines. It eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure investments and can provide connectivity at a lower cost in certain scenarios.
Disadvantages:
1. Latency: VSAT networks typically have higher latency compared to wired networks. This can result in slower response times for certain applications, such as real-time video conferencing or online gaming.
2. Bandwidth Limitations: VSAT networks often have limited bandwidth capacity, especially in shared networks. This can lead to slower speeds and congestion during peak usage periods, affecting the overall user experience.
3. Weather Interference: VSAT signals can be affected by adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or strong winds. This can cause temporary disruptions or degradation of service, impacting communication reliability.
4. Initial Cost: While VSAT can be cost-effective in the long run, the initial setup costs can be higher compared to traditional wired networks. This includes the purchase and installation of VSAT terminals, satellite equipment, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
5. Dependence on Satellite Infrastructure: VSAT networks rely on satellite infrastructure, which can be subject to technical issues or satellite failures. This dependency introduces a level of risk and potential service interruptions.
Despite these disadvantages, VSAT technology remains a valuable solution for many businesses and organizations, offering reliable connectivity in remote areas and flexible scalability options. It is important to carefully evaluate the specific needs and requirements before implementing a VSAT network.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
