What does Underperform Mean?
Underperform is a term commonly used in the world of finance and investing. It refers to a situation where a particular investment or asset fails to meet expectations or perform as well as anticipated. When an investment underperforms, it means that its returns or performance are below average or below a benchmark or index.
Underperformance can occur in various financial markets, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or even entire sectors or industries. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor management, economic downturns, industry-specific challenges, or changes in market conditions.
Underperformance is often measured by comparing the performance of an investment to a benchmark or index. For example, if a stock is expected to generate a return of 10% based on historical performance or analyst projections, but only delivers a return of 5%, it would be considered underperforming.
Underperformance can be temporary or long-term. Temporary underperformance may be due to short-term market fluctuations or specific events affecting the investment. Long-term underperformance, on the other hand, may indicate more fundamental issues with the investment, such as poor management or a decline in the industry’s prospects.
Implications of Underperformance
Underperformance can have significant implications for investors. It can result in financial losses, missed investment opportunities, or a decrease in the overall value of a portfolio. Investors may choose to sell underperforming investments to cut their losses or reallocate their funds to better-performing assets.
For fund managers or financial advisors, underperformance can also have professional consequences. If a fund consistently underperforms its benchmark or peers, investors may choose to withdraw their funds, and the manager’s reputation and job security may be at risk.
Overview of Underperforming
Underperforming refers to a situation where an individual, company, or investment is not performing as well as expected or desired. It can occur in various contexts, such as in academics, business, or financial markets. When something is underperforming, it means that it is not meeting the set goals or standards.
In the academic setting, underperforming typically refers to students who are not meeting the expected level of achievement or are falling behind their peers. This could be due to various factors, such as lack of motivation, learning difficulties, or inadequate support. Underperforming students may have lower grades, struggle with assignments, or exhibit a lack of engagement in the learning process.
In the business world, underperforming can refer to companies or departments that are not meeting their performance targets. This could be reflected in lower sales, decreased profitability, or failure to meet customer expectations. Underperforming businesses may face challenges such as inefficient operations, ineffective marketing strategies, or poor management decisions.
Causes of Underperforming
There can be several reasons behind underperforming in different contexts. In academics, it could be due to a lack of interest in the subject, ineffective teaching methods, or personal issues affecting the student’s ability to focus and learn. In business, underperformance can be caused by factors such as poor leadership, inadequate resources, or intense competition. In investments, underperformance may be a result of market volatility, economic downturns, or poor investment choices.
Addressing Underperformance

To address underperformance, it is important to first identify the underlying causes. In academics, providing additional support, implementing effective teaching strategies, or addressing any personal issues can help students improve their performance. In business, conducting a thorough analysis of the company’s operations, identifying areas of improvement, and implementing strategic changes can help turn around underperforming departments or businesses. In investments, investors may consider diversifying their portfolio, seeking professional advice, or reevaluating their investment strategy to address underperforming assets.
Examples of Underperforming
Underperforming is a term used in various industries to describe a situation where an individual, company, or investment is not meeting expectations or performing below average. Here are some examples of underperforming in different contexts:
1. Underperforming Stocks
In the stock market, underperforming stocks refer to those that have not performed as well as expected or have shown a decline in value. This could be due to various factors such as poor financial performance, negative market sentiment, or unfavorable industry conditions. Investors may consider selling underperforming stocks to cut losses or reallocate their investments to better-performing assets.
2. Underperforming Employees
In the corporate world, underperforming employees are those who fail to meet the expected level of productivity, quality of work, or job performance. This could be due to lack of skills, motivation, or poor fit with the job role. Employers may address underperforming employees through performance evaluations, training programs, or, in severe cases, termination of employment.
3. Underperforming Schools
In the education sector, underperforming schools are those that consistently fail to meet academic standards or achieve satisfactory student outcomes. This could be due to various factors such as inadequate resources, ineffective teaching methods, or low student engagement. Underperforming schools may receive additional support and interventions from educational authorities to improve their performance and ensure better educational opportunities for students.
4. Underperforming Investments
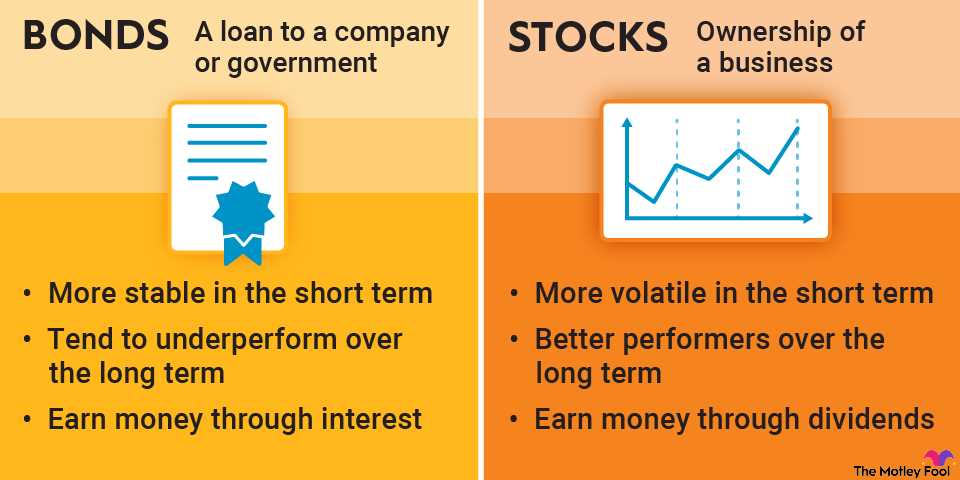
In the world of finance, underperforming investments are those that do not generate the expected returns or fail to outperform the market or benchmark indices. This could be due to poor investment decisions, economic downturns, or unexpected events impacting the investment’s performance. Investors may choose to divest from underperforming investments and allocate their funds to better-performing assets or investment strategies.
Overall, underperforming can have significant implications in various industries and contexts. It is important for individuals, companies, and investors to identify underperforming entities and take appropriate actions to address the issues and improve performance.
Underperforming in Trading
Underperforming in trading refers to a situation where a trader or an investment portfolio fails to achieve the expected level of performance or returns. It is a term commonly used in the financial industry to describe a situation where the performance of a particular investment or trading strategy falls short of its benchmark or market expectations.
There can be various reasons for underperformance in trading. It could be due to poor market timing, incorrect analysis, lack of risk management, or simply bad luck. Traders who underperform may experience losses or lower returns compared to their peers or the overall market.
Underperforming in trading can have significant consequences for traders and investors. It can result in financial losses, missed investment opportunities, and damage to one’s reputation. It is important for traders to regularly evaluate their performance and identify areas of improvement to avoid prolonged underperformance.
One way to address underperformance is through a thorough review of trading strategies and risk management techniques. Traders can analyze their trades, identify patterns, and adjust their strategies accordingly. They can also seek guidance from experienced traders or financial advisors to gain insights and improve their performance.
It is crucial for traders to have realistic expectations and not be discouraged by temporary underperformance. Markets can be volatile and unpredictable, and even the most successful traders may experience periods of underperformance. The key is to learn from mistakes, adapt to changing market conditions, and continuously strive for improvement.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
