Terms of Trade: Definition, Use as Indicator, and Factors
The terms of trade is a concept in economics that refers to the ratio at which a country can trade its exports for imports from other countries. It is a measure of the relative value of a country’s exports compared to its imports and is often used as an indicator of a country’s economic performance.
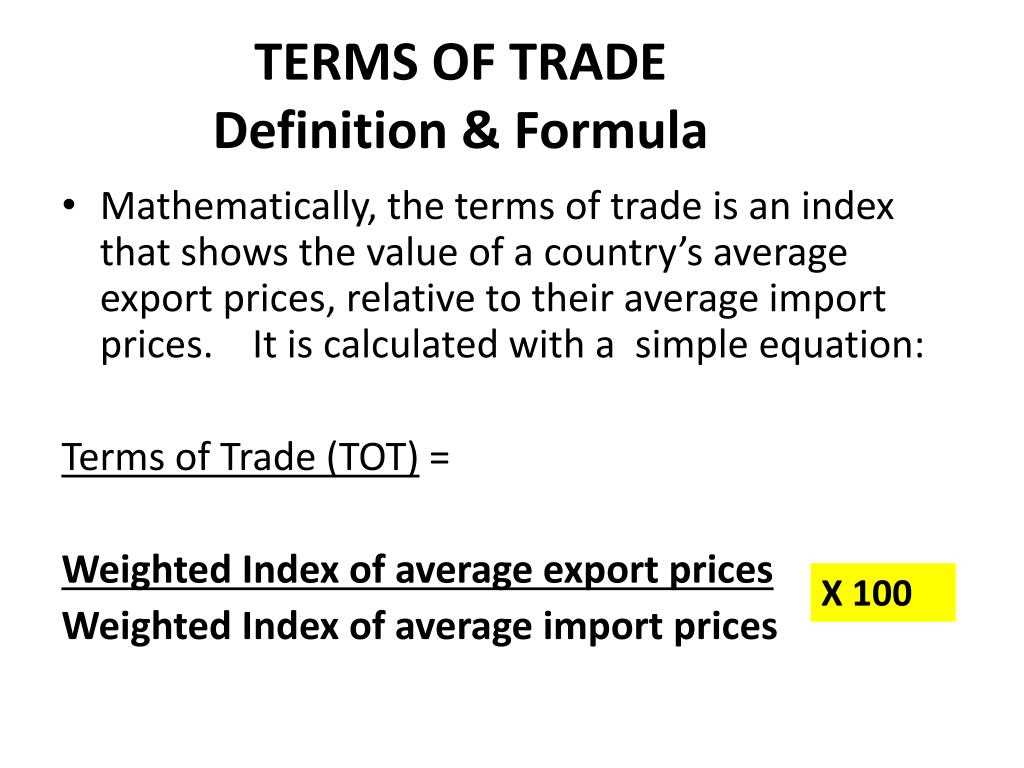
The terms of trade can be calculated by dividing the price index of a country’s exports by the price index of its imports. A higher terms of trade indicates that a country can buy more imports for a given amount of exports, while a lower terms of trade means that a country can buy fewer imports for the same amount of exports.
The terms of trade is an important indicator for policymakers and economists as it provides insights into a country’s competitiveness in international trade. A country with a favorable terms of trade can generate more revenue from its exports, which can contribute to economic growth and development.
There are several factors that can affect a country’s terms of trade. Changes in global demand and supply conditions, fluctuations in exchange rates, trade barriers, and government policies can all influence the terms of trade. For example, if a country’s exports become more in demand globally, its terms of trade may improve. On the other hand, if a country’s imports become more expensive due to a depreciation in its currency, its terms of trade may worsen.
Terms of trade is an important concept in economics that refers to the ratio at which a country can trade its exports for imports. It is a measure of the relative value of a country’s exports compared to its imports and is often used as an indicator of a country’s economic health.
There are several factors that influence the terms of trade. One of the key factors is the demand and supply dynamics of the goods and services being traded. When the demand for a country’s exports is high and the supply of its imports is low, the terms of trade are likely to be favorable. On the other hand, if the demand for a country’s exports is low and the supply of its imports is high, the terms of trade may be unfavorable.
Another factor that affects the terms of trade is the exchange rate. A depreciation in a country’s currency can improve its terms of trade by making its exports cheaper and imports more expensive. Conversely, an appreciation in the currency can worsen the terms of trade by making exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
Additionally, changes in productivity levels and technology can also impact the terms of trade. If a country becomes more efficient in producing a certain good or service, its exports may become more competitive, leading to an improvement in the terms of trade. Conversely, if a country’s productivity levels decline, its terms of trade may deteriorate.
It is important to note that the terms of trade can have significant implications for a country’s economic growth, income distribution, and overall welfare. A favorable terms of trade can boost a country’s export earnings, stimulate economic growth, and improve living standards. On the other hand, an unfavorable terms of trade can lead to a decline in export revenues, slower economic growth, and income inequality.
Using Terms of Trade as an Economic Indicator
The terms of trade is an important economic indicator that measures the ratio between a country’s export prices and its import prices. It provides insights into the relative strength of a country’s exports compared to its imports, and can be used to assess the overall health of its economy.
There are several ways in which the terms of trade can be used as an economic indicator:
- Assessing competitiveness: A country with improving terms of trade may indicate that its exports are becoming more competitive in the global market. This can be a positive sign for the country’s economy, as it suggests that it is able to sell its goods at higher prices relative to its imports.
- Identifying trade imbalances: Changes in the terms of trade can reveal imbalances between a country’s exports and imports. If a country’s terms of trade deteriorate, it means that its import prices are rising faster than its export prices. This could indicate a trade deficit and potential economic challenges.
- Policy implications: Governments can use the terms of trade as a guide for formulating economic policies. For example, if a country’s terms of trade are deteriorating, it may indicate a need to focus on improving export competitiveness or reducing import dependency. On the other hand, if the terms of trade are improving, it may suggest that the country is on the right track and policies can be geared towards sustaining this positive trend.
It is important to note that the terms of trade is just one of many economic indicators that should be considered when assessing the health of an economy. It should be used in conjunction with other indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation to get a comprehensive picture of the overall economic performance.
Factors Affecting Terms of Trade
1. Exchange Rates

Exchange rates play a significant role in determining the terms of trade. A country with a depreciating currency will experience an improvement in its terms of trade as its exports become cheaper and more competitive in the international market. Conversely, a country with an appreciating currency will face a deterioration in its terms of trade, making its exports more expensive and less competitive.
2. Productivity and Efficiency
3. Tariffs and Trade Barriers

Tariffs and trade barriers imposed by countries can have a significant impact on the terms of trade. High import tariffs or restrictive trade policies can reduce a country’s export competitiveness and lead to a deterioration in its terms of trade. On the other hand, reducing trade barriers can improve a country’s terms of trade by increasing market access for its exports.
4. Global Demand and Supply
The global demand and supply for a country’s exports can influence its terms of trade. If there is high demand for a country’s products, it can negotiate better prices and terms of trade. Conversely, if there is an oversupply of similar products in the global market, a country may face lower prices and a deterioration in its terms of trade.
5. Natural Resources
The availability and abundance of natural resources can impact a country’s terms of trade. Countries that are rich in natural resources, such as oil or minerals, can benefit from higher export prices and a favorable terms of trade. However, reliance on a few key resources can also make a country vulnerable to price fluctuations and volatility in global commodity markets.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
