What is a Tax Credit?

A tax credit is a financial incentive provided by the government to individuals or businesses to reduce their tax liability. Unlike a tax deduction, which reduces the amount of taxable income, a tax credit directly reduces the amount of tax owed. This means that if you have a tax credit of $1,000, for example, your tax liability will be reduced by that amount.
Tax credits are typically offered for specific purposes, such as promoting renewable energy, supporting education, or encouraging investment in certain industries. They are designed to incentivize behavior that benefits the economy, the environment, or society as a whole.
Additionally, tax credits can be refundable or non-refundable. A refundable tax credit means that if the credit exceeds your tax liability, you will receive the excess as a refund. On the other hand, a non-refundable tax credit can only reduce your tax liability to zero, and any excess credit cannot be refunded.
How Does a Tax Credit Work?

A tax credit is a type of financial incentive provided by the government to individuals and businesses to encourage certain behaviors or activities. Unlike a tax deduction, which reduces the amount of taxable income, a tax credit directly reduces the amount of tax owed. This means that a tax credit has a dollar-for-dollar impact on your tax liability.
When you qualify for a tax credit, you can subtract the credit amount from the total tax you owe. For example, if you have a tax liability of $5,000 and qualify for a $1,000 tax credit, your new tax liability will be reduced to $4,000.
In order to claim a tax credit, you must meet certain qualifications and requirements set by the government. These qualifications can vary depending on the type of tax credit. For example, some tax credits are available only to individuals with low income, while others may be specific to certain industries or activities.
| Key Points |
|---|
| – Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed. |
| – Some tax credits are refundable, while others are non-refundable. |
| – Qualifications and requirements for tax credits vary. |
| – Tax credits can change from year to year. |
Qualifications for Tax Credits
Qualifying for tax credits can provide significant financial benefits for individuals and businesses. However, it is important to understand the qualifications and requirements in order to take advantage of these credits. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Income Level: Many tax credits are income-based, meaning that individuals or businesses must meet certain income thresholds in order to qualify. These thresholds can vary depending on the specific credit and the jurisdiction in which it is offered.
2. Filing Status: Some tax credits are only available to individuals or businesses with specific filing statuses, such as married filing jointly or head of household. It is important to understand the requirements for each credit and ensure that you meet the necessary filing status criteria.
3. Eligible Expenses: Certain tax credits are designed to incentivize specific behaviors or activities, such as energy-efficient home improvements or education expenses. To qualify for these credits, individuals or businesses must incur eligible expenses and provide documentation to support their claims.
4. Documentation: In order to claim tax credits, individuals and businesses must provide proper documentation to support their eligibility. This may include receipts, invoices, or other forms of proof that demonstrate the expenses incurred or the actions taken to qualify for the credit.
5. Timing: Some tax credits have specific time limits or deadlines for claiming the credit. It is important to be aware of these deadlines and ensure that you file your taxes and claim the credits within the required timeframe.
6. Other Requirements: In addition to the factors mentioned above, some tax credits may have additional requirements or restrictions. For example, certain credits may only be available to first-time homebuyers or individuals with disabilities. It is important to thoroughly research each credit to understand all of the qualifications and requirements.
Types of Tax Credits
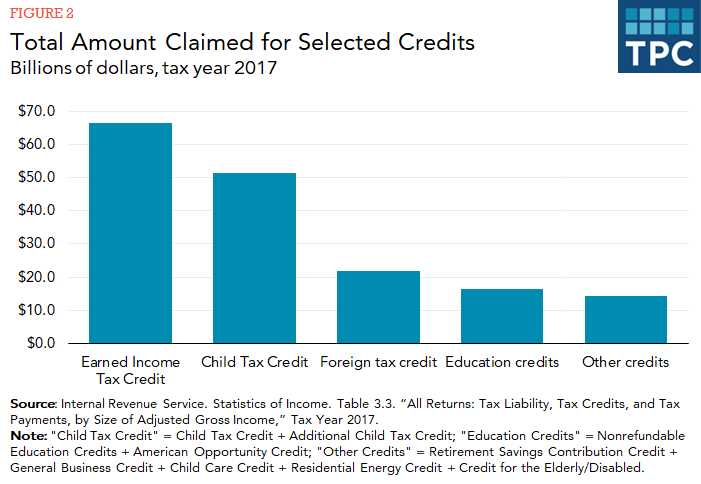
1. Child Tax Credit: This tax credit is available to individuals who have qualifying children under the age of 17. The credit can reduce your tax liability by up to $2,000 per child. To qualify, you must meet certain income requirements and provide the necessary documentation.
2. Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): The EITC is a refundable tax credit available to low-income individuals and families. The credit amount is based on your income and the number of qualifying children you have. It is designed to provide financial assistance to those who are working but earning low wages.
4. Energy Tax Credits: Energy tax credits are available for individuals who make certain energy-efficient improvements to their homes or purchase qualifying energy-efficient products. These credits can help offset the costs of these investments and encourage the use of renewable energy sources.
5. Healthcare Tax Credits: The Affordable Care Act introduced several tax credits to help individuals and small businesses afford health insurance coverage. These credits include the Premium Tax Credit, which helps lower-income individuals and families pay for insurance premiums, and the Small Business Health Care Tax Credit, which assists small businesses in providing health coverage to their employees.
6. Business Tax Credits: There are various tax credits available to businesses, including the Research and Development Tax Credit, the Work Opportunity Tax Credit, and the Investment Tax Credit. These credits are designed to incentivize business growth, job creation, and innovation.
Benefits of Tax Credits

1. Lower Tax Liability
The primary benefit of tax credits is that they lower your overall tax liability. Unlike deductions, which reduce your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. This means that if you have a tax credit of $1,000 and you owe $5,000 in taxes, your liability will be reduced to $4,000.
2. Increased Refunds
Another advantage of tax credits is that they can increase your tax refund. If your tax credits exceed the amount of tax you owe, you may be eligible for a refund. For example, if you have a tax credit of $2,000 and you owe $1,500 in taxes, you would receive a refund of $500.
3. Incentives for Specific Actions
Tax credits are often used as incentives to encourage specific actions or behaviors. For example, there are tax credits available for energy-efficient home improvements, adoption expenses, and higher education expenses. These credits not only help individuals save money on their taxes but also promote activities that benefit society as a whole.
Overall, tax credits provide significant benefits to individuals and businesses by reducing tax liability, increasing refunds, and incentivizing certain actions. It is important to understand the qualifications and types of tax credits available to ensure you are taking full advantage of these valuable tools.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
