What is a Tax Break?
A tax break is a reduction in the amount of taxes that an individual or business owes to the government. It is a way to incentivize certain behaviors or activities by providing financial relief through the tax system. Tax breaks can come in various forms, such as deductions, credits, exemptions, or exclusions.
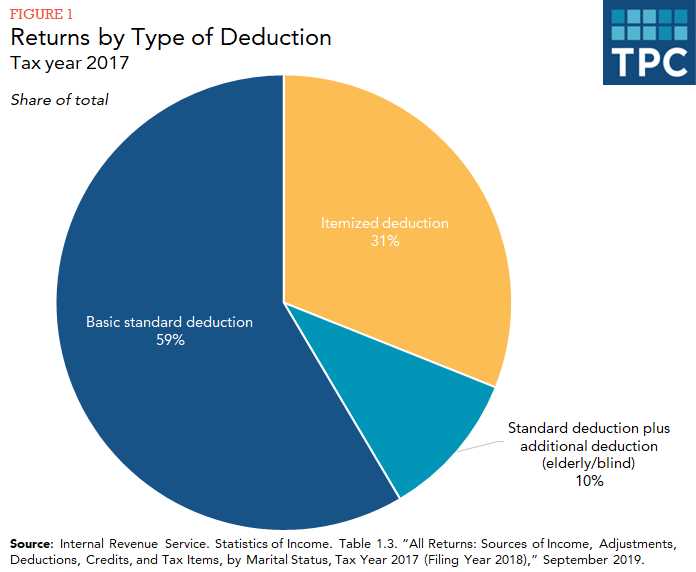
Deductions
Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from an individual’s taxable income, reducing the amount of income that is subject to tax. Common deductions include mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions. By taking advantage of deductions, individuals can lower their overall tax liability.
Credits
Exemptions
Exemptions are specific amounts of income that are not subject to tax. In the past, individuals could claim personal exemptions for themselves and their dependents, which would reduce their taxable income. However, recent changes to the tax law have eliminated personal exemptions.
Exclusions
Exclusions are types of income that are not included in taxable income. For example, certain types of income, such as gifts or inheritances, may be excluded from taxation. Additionally, some benefits, like employer-provided health insurance, may be excluded from taxable income.
Different Types of Tax Breaks
There are several different types of tax breaks that individuals and businesses can take advantage of to reduce their tax liability. These tax breaks can come in the form of deductions, credits, exemptions, and exclusions. Each type of tax break has its own eligibility requirements and can provide different levels of tax savings.
1. Deductions: Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of income that is subject to tax. Common deductions include mortgage interest, student loan interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions. Deductions can be either itemized or taken as a standard deduction, depending on which option provides the greater tax benefit.
2. Credits: Tax credits are dollar-for-dollar reductions in your tax liability. Unlike deductions, which reduce your taxable income, credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. There are several types of tax credits available, including the child tax credit, earned income tax credit, and education credits. Some credits are refundable, meaning that if the credit exceeds your tax liability, you can receive a refund for the difference.
3. Exemptions: Exemptions are a specific dollar amount that can be subtracted from your taxable income for each person in your household. In the past, individuals could claim a personal exemption for themselves, their spouse, and any dependents. However, under recent tax law changes, personal exemptions have been temporarily eliminated.
4. Exclusions: Exclusions are types of income that are not subject to tax. Common examples include certain types of insurance proceeds, gifts and inheritances, and income from certain types of retirement accounts. Exclusions can provide significant tax savings by reducing your overall taxable income.
| Type of Tax Break | Description |
|---|---|
| Deductions | Expenses that can be subtracted from taxable income |
| Credits | Dollar-for-dollar reductions in tax liability |
| Exemptions | Specific dollar amounts subtracted from taxable income for each person in household |
| Exclusions | Types of income not subject to tax |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
