Pretax Profit Margin
The pretax profit margin is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability before taxes are deducted. It is an important metric for investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s financial performance.
Definition:
The pretax profit margin is calculated by dividing the company’s pretax profit by its total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage. It represents the percentage of each dollar of revenue that is left as pretax profit after deducting all expenses except for taxes.
Uses:
The pretax profit margin is used to assess a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations before tax obligations. It helps investors and analysts understand how efficiently a company is managing its costs and generating profits. A higher pretax profit margin indicates better profitability, while a lower margin may suggest inefficiency or higher costs.
Calculation:
The pretax profit margin is calculated using the formula:
Pretax Profit Margin = (Pretax Profit / Total Revenue) x 100
Example:
Let’s say Company A has a pretax profit of $500,000 and total revenue of $2,000,000. The pretax profit margin would be:
Pretax Profit Margin = ($500,000 / $2,000,000) x 100 = 25%
This means that for every dollar of revenue, Company A is able to generate a pretax profit of 25 cents.
Financial Ratios:
The pretax profit margin is one of many financial ratios used to assess a company’s financial health and performance. Other important ratios include the gross profit margin, net profit margin, return on assets, and return on equity.
Definition
The pretax profit margin is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability before taxes are deducted. It is calculated by dividing the company’s pretax profit by its total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage.
This ratio is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and efficiency. It shows how well a company is able to generate profits from its operations before considering the impact of taxes.
The pretax profit margin is often used by investors, analysts, and lenders to assess a company’s profitability and compare it to its competitors or industry benchmarks. A higher pretax profit margin indicates that a company is more efficient in generating profits and has better control over its costs.
Overall, the pretax profit margin provides valuable insights into a company’s profitability and financial performance. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions and evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations.
Definition of Pretax Profit Margin
Pretax profit margin is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability before accounting for taxes. It is calculated by dividing the company’s pretax profit by its total revenue. This ratio is important because it provides insight into how efficiently a company is generating profits from its operations, without considering the impact of taxes.
By analyzing the pretax profit margin, investors and analysts can assess a company’s ability to generate profits and its overall financial health. A higher pretax profit margin indicates that a company is able to generate more profit from its revenue, which is generally seen as a positive sign.
Overall, the pretax profit margin is a useful tool for investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s profitability and efficiency. It provides valuable insights into how well a company is able to generate profits from its operations, without considering the impact of taxes.
Calculation of Pretax Profit Margin
The pretax profit margin is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability before taxes are deducted. It is calculated by dividing the company’s pretax profit by its total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage.
To calculate the pretax profit margin, you need to know the company’s pretax profit and total revenue. Pretax profit is the company’s profit before taxes are deducted, while total revenue is the total amount of money generated from sales or other sources of income.
The formula for calculating the pretax profit margin is as follows:
Pretax Profit Margin = (Pretax Profit / Total Revenue) x 100
For example, let’s say a company has a pretax profit of $500,000 and total revenue of $2,000,000. To calculate the pretax profit margin, you would divide $500,000 by $2,000,000 and multiply by 100:
Pretax Profit Margin = ($500,000 / $2,000,000) x 100 = 25%
This means that the company’s pretax profit margin is 25%, indicating that for every dollar of revenue generated, the company has a pretax profit of 25 cents.
The pretax profit margin is an important financial ratio as it provides insight into a company’s ability to generate profits before taxes. A higher pretax profit margin indicates that the company is more efficient at generating profits from its revenue, while a lower pretax profit margin may indicate inefficiency or higher operating costs.
Investors and analysts often use the pretax profit margin to compare the profitability of different companies within the same industry. It can also be used to track a company’s profitability over time and identify trends or changes in its financial performance.
Pretax Profit Margin Calculation Example
Calculating the pretax profit margin is a useful tool for analyzing a company’s profitability before taxes. It helps investors and analysts understand how efficiently a company is generating profits from its operations.
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of the pretax profit margin:
| Revenue | Operating Expenses | Interest Expenses | Income Taxes | Pretax Profit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $1,000,000 | $800,000 | $50,000 | $30,000 | $120,000 |
| Year 2 | $1,200,000 | $900,000 | $60,000 | $40,000 | $200,000 |
To calculate the pretax profit margin, we use the formula:
Pretax Profit Margin = (Pretax Profit / Revenue) * 100
For Year 1:
Pretax Profit Margin = ($120,000 / $1,000,000) * 100 = 12%
For Year 2:
Pretax Profit Margin = ($200,000 / $1,200,000) * 100 = 16.67%
From the example above, we can see that the pretax profit margin increased from 12% in Year 1 to 16.67% in Year 2. This indicates that the company’s profitability improved over time.
Analysts and investors can use the pretax profit margin to compare a company’s profitability with its industry peers or historical performance. A higher pretax profit margin generally indicates better profitability, while a lower margin may suggest inefficiency or higher expenses.
The pretax profit margin is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability before taxes are taken into account. It is a useful metric for investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
Definition
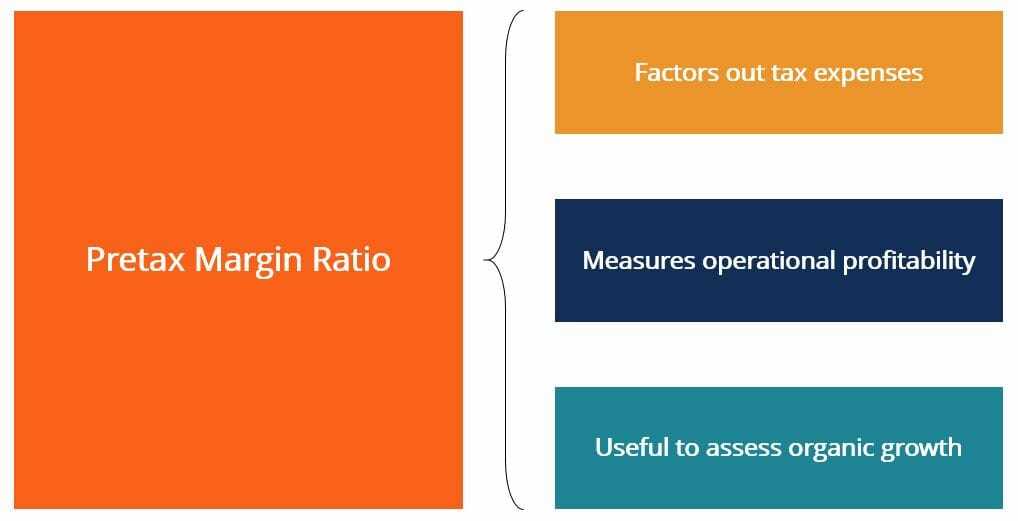
The pretax profit margin is calculated by dividing a company’s pretax profit by its total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage. It represents the percentage of revenue that is left after deducting all expenses except for taxes.
Uses
The pretax profit margin is a key indicator of a company’s operational efficiency and profitability. It allows investors and analysts to compare the profitability of different companies within the same industry or sector. A higher pretax profit margin indicates that a company is able to generate more profits from its operations, while a lower pretax profit margin may suggest inefficiencies or higher costs.
Additionally, the pretax profit margin can be used to assess a company’s financial health and stability. A consistently high pretax profit margin may indicate a strong and sustainable business model, while a declining pretax profit margin may signal potential financial difficulties.
Calculation
The pretax profit margin is calculated using the following formula:
Pretax Profit Margin = (Pretax Profit / Total Revenue) * 100
Where:
- Pretax Profit is the company’s profit before taxes.
- Total Revenue is the company’s total sales or revenue.
Example
Let’s say Company A has a pretax profit of $500,000 and total revenue of $2,000,000. Using the formula, we can calculate the pretax profit margin as follows:
Pretax Profit Margin = ($500,000 / $2,000,000) * 100 = 25%
This means that Company A has a pretax profit margin of 25%, indicating that it generates a profit of 25 cents for every dollar of revenue before taxes.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
