Nordic Model vs U.S. Economic System: A Comparative Analysis
When comparing the Nordic Model to the U.S. Economic System, it is evident that there are significant differences in their approaches to economic policies and social welfare. The Nordic Model, which is implemented in countries such as Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland, emphasizes social welfare and equality, while the U.S. Economic System focuses more on free-market capitalism and individualism.
One of the key differences between the two systems is the level of government intervention and regulation. In the Nordic Model, the government plays a more active role in regulating the economy and providing social welfare programs. This includes universal healthcare, free education, generous unemployment benefits, and strong labor protections. On the other hand, the U.S. Economic System relies more on market forces and individual responsibility, with a smaller role for government intervention.
Another area of contrast is income inequality and wealth distribution. The Nordic Model aims to reduce income inequality by implementing progressive tax systems and redistributive policies. This means that the wealthy are taxed at higher rates, and the revenue is used to fund social welfare programs that benefit the less fortunate. In contrast, the U.S. Economic System has a higher level of income inequality, with a larger wealth gap between the rich and the poor.
Overall, the Nordic Model and the U.S. Economic System represent two different approaches to economic policies and social welfare. While the Nordic Model prioritizes social welfare and equality through government intervention and regulation, the U.S. Economic System emphasizes free-market capitalism and individualism. Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the effectiveness of each approach may vary depending on the specific context and goals of a country.
| Nordic Model | U.S. Economic System |
|---|---|
| Government intervention and regulation | Reliance on market forces |
| Social welfare programs | Individual responsibility |
| Progressive tax systems | Income inequality |
Economic Policies and Social Welfare
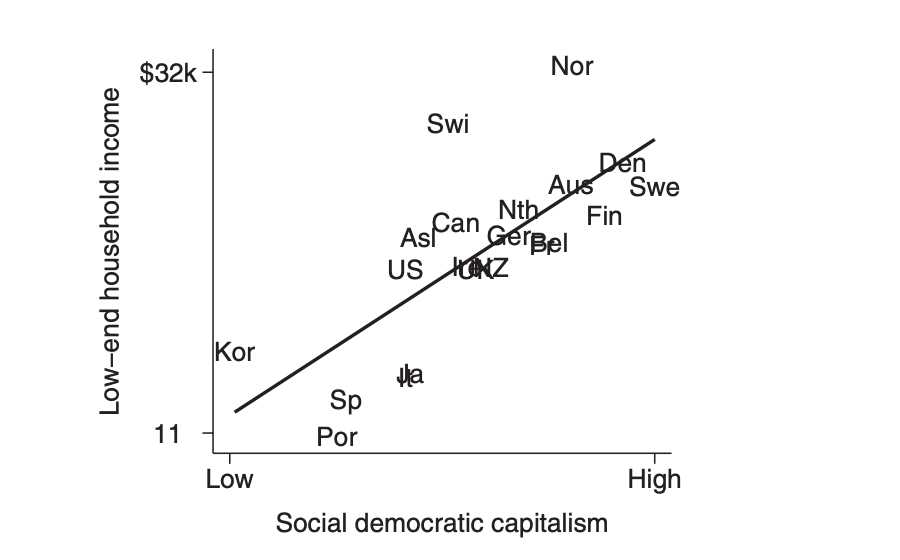
One of the key differences between the Nordic Model and the U.S. Economic System is their approach to economic policies and social welfare. The Nordic countries, including Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden, have implemented a comprehensive welfare state that provides a wide range of social benefits to their citizens.
Under the Nordic Model, the government plays a significant role in ensuring social welfare through high taxes and extensive social programs. These programs include universal healthcare, free education, generous parental leave, and unemployment benefits. The aim is to create a society with equal opportunities and a high standard of living for all citizens.
In contrast, the U.S. Economic System relies more on market forces and individual responsibility. The government provides some social welfare programs, such as Medicare and Social Security, but they are less comprehensive compared to the Nordic countries. The U.S. emphasizes individual freedom and limited government intervention in the economy.
The Nordic Model’s focus on social welfare has led to lower levels of poverty and income inequality compared to the U.S. In the Nordic countries, there is a strong emphasis on income redistribution through progressive taxation and generous social benefits. This helps to reduce poverty and ensure a more equal distribution of wealth.
However, critics argue that the high taxes required to fund the Nordic welfare state can hinder economic growth and discourage entrepreneurship. They argue that the U.S. Economic System, with its lower taxes and emphasis on individual freedom, promotes innovation and economic dynamism.
Overall, the Nordic Model and the U.S. Economic System have different approaches to economic policies and social welfare. The Nordic countries prioritize social welfare through high taxes and extensive social programs, while the U.S. relies more on market forces and individual responsibility. Each system has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them ultimately depends on the values and priorities of each society.
Income Inequality and Wealth Distribution
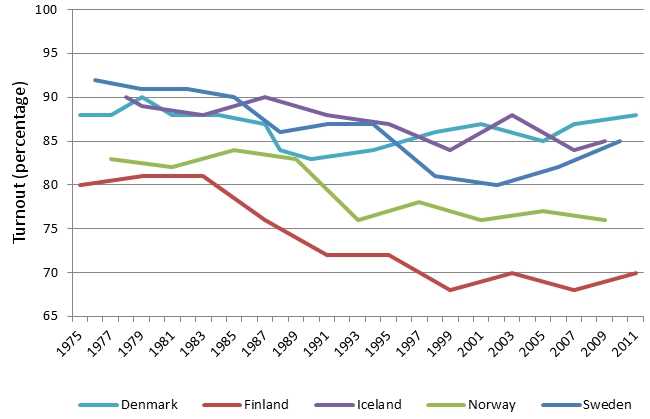
Income inequality and wealth distribution are two important factors that highlight the differences between the Nordic Model and the U.S. economic system. The Nordic Model prioritizes social welfare and aims to reduce income inequality through progressive taxation and extensive social welfare programs.
In the Nordic countries, such as Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Finland, there is a strong emphasis on equality and social cohesion. These countries have implemented policies that aim to redistribute wealth and provide equal opportunities for all citizens. Progressive taxation is one of the key tools used to achieve this goal. High-income individuals and corporations are taxed at higher rates, while low-income individuals receive various benefits and subsidies.
Additionally, the Nordic countries have comprehensive social welfare programs that provide citizens with access to healthcare, education, childcare, and unemployment benefits. These programs are funded through high tax rates, but they ensure that all citizens have access to essential services and support.
On the other hand, the U.S. economic system has a higher level of income inequality and wealth concentration. The U.S. relies more on market forces and individual initiative, which can lead to greater disparities in income and wealth. The tax system in the U.S. is generally less progressive compared to the Nordic countries, with lower tax rates for high-income individuals and corporations.
Government Role and Regulation
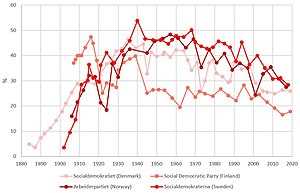
In the Nordic Model, the government plays a significant role in regulating the economy and ensuring social welfare. The government in Nordic countries, such as Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Finland, takes an active approach in shaping the economy and providing a safety net for its citizens.
One of the key aspects of the Nordic Model is the high level of government intervention in the economy. The government implements policies and regulations to ensure fair competition, protect workers’ rights, and promote social equality. This includes strict labor laws, strong unions, and generous social welfare programs.
The government in Nordic countries also invests heavily in education, healthcare, and infrastructure. This helps to create a well-educated workforce, a healthy population, and efficient transportation networks. These investments contribute to the overall economic development and productivity of the countries.
Furthermore, the government in the Nordic Model takes an active role in redistributing wealth and reducing income inequality. Through progressive taxation, the government collects more taxes from higher-income individuals and redistributes it to provide social benefits for those in need. This helps to reduce poverty and ensure a more equal distribution of wealth.
On the other hand, the U.S. economic system has a more laissez-faire approach, with less government intervention and regulation. The U.S. government focuses more on promoting free market competition and individual liberty. While there are regulations in place to protect consumers and maintain fair competition, the level of government intervention is generally lower compared to the Nordic Model.
In the U.S., the government’s role is primarily focused on maintaining law and order, protecting property rights, and providing a basic social safety net. The government provides limited social welfare programs, such as Medicaid and Social Security, but they are not as comprehensive as those in the Nordic countries.
Overall, the government’s role and regulation in the Nordic Model are more extensive compared to the U.S. economic system. The Nordic countries prioritize social welfare, income equality, and economic stability, which requires a higher level of government intervention and regulation. In contrast, the U.S. economic system emphasizes individual liberty and free market competition, resulting in a less interventionist government approach.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
