Negotiable Instruments: Definition, Types, and Examples
A negotiable instrument refers to a written document that guarantees the payment of a specific amount of money to the bearer or the person named on the instrument. These instruments are commonly used in financial transactions and play a crucial role in various banking activities, including checking accounts.
Definition of Negotiable Instruments

A negotiable instrument is a legally binding document that allows for the transfer of ownership rights from one party to another. It serves as a substitute for actual money and provides a secure and convenient way to conduct financial transactions.
Types of Negotiable Instruments
There are several types of negotiable instruments, including:
- Promissory Notes: These are written promises to pay a specific amount of money at a future date or on demand. Promissory notes are commonly used in lending and borrowing transactions.
- Checks: Checks are written orders from a depositor to a bank, instructing the bank to pay a specific amount of money to the bearer or a designated payee. They are widely used in checking accounts for various payment purposes.
Examples of Negotiable Instruments
Here are some examples of negotiable instruments:
- A promissory note issued by a borrower to a lender, promising to repay a loan with interest.
- A bill of exchange issued by an exporter to an importer, requesting payment for goods or services.
- A check issued by an individual to a vendor, authorizing the payment for goods or services purchased.
These examples demonstrate the diverse range of negotiable instruments and their applications in different financial transactions.
Definition of Negotiable Instruments
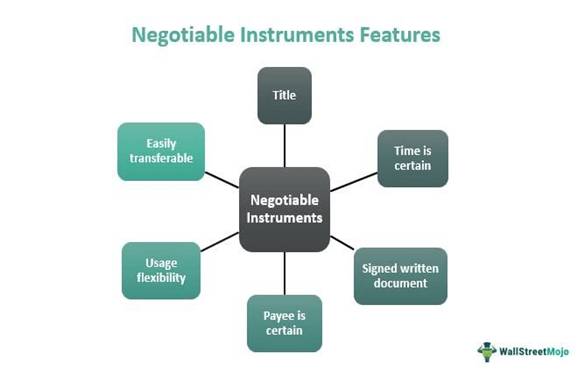
A negotiable instrument is a written document that guarantees the payment of a specific amount of money to the bearer or to a specified person. It is a legally binding contract between the parties involved, and it can be transferred from one person to another by endorsement or delivery.
There are certain criteria that a document must meet in order to be considered a negotiable instrument. First, it must be in writing and signed by the maker or drawer. Second, it must contain an unconditional promise or order to pay a specific amount of money. Third, it must be payable on demand or at a specific time. Fourth, it must be payable to the bearer or to a specified person. Finally, it must be transferable by endorsement or delivery.
There are various types of negotiable instruments, including promissory notes, bills of exchange, and checks. Promissory notes are written promises to pay a certain amount of money on a specific date. Bills of exchange are written orders from one party to another to pay a certain amount of money. Checks are written orders from a depositor to a bank to pay a specific amount of money to the bearer or to a specified person.
Negotiable instruments play a crucial role in checking accounts. When a person writes a check to pay for goods or services, the check becomes a negotiable instrument that can be transferred to the recipient. The recipient can then deposit the check into their own bank account and receive the funds. This allows for convenient and secure transactions, as well as easy record-keeping.
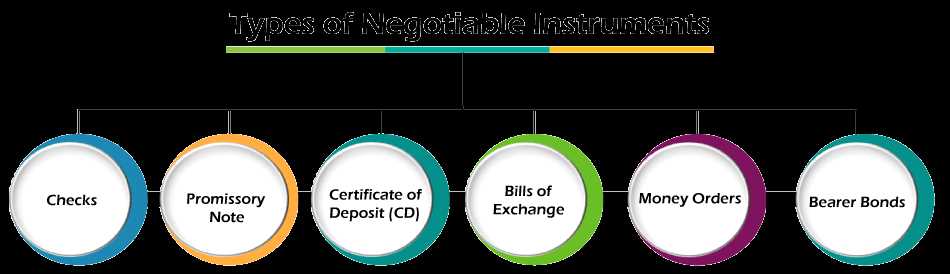
Types of Negotiable Instruments
Negotiable instruments are classified into different types based on their characteristics and usage. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Promissory Notes: A promissory note is a written promise by one party to pay a specific amount of money to another party at a future date or on demand. It is a legally binding contract and is commonly used in business transactions.
2. Bills of Exchange: A bill of exchange is an unconditional order in writing, addressed by one person to another, demanding the payment of a certain sum of money. It is commonly used in international trade and acts as a form of credit instrument.
3. Checks: A check is a written order from an account holder to a bank, instructing the bank to pay a specific amount of money to a designated payee. It is the most common form of negotiable instrument used in checking accounts.
4. Certificates of Deposit: A certificate of deposit (CD) is a time deposit offered by banks and financial institutions. It represents a promissory note issued by the bank, guaranteeing the payment of a fixed amount of money with interest at a specified maturity date.
5. Bank Drafts: A bank draft is a payment instrument issued by a bank, drawn on itself or another bank, and payable to a specific person or entity. It is commonly used for making large payments or international transactions.
6. Money Orders: A money order is a payment instrument issued by a financial institution, such as a post office or a bank, that allows the payer to make a specific amount of money payable to a designated recipient. It is commonly used for sending money through mail or for making payments in situations where checks are not accepted.
These are just a few examples of the types of negotiable instruments that exist. Each type has its own specific characteristics and usage, but they all serve the purpose of facilitating financial transactions and providing a secure means of payment.
Examples of Negotiable Instruments
A negotiable instrument is a document that guarantees the payment of a specific amount of money to the bearer or a designated person. These instruments are commonly used in financial transactions and can be transferred from one party to another.
Here are some examples of negotiable instruments:
1. Checks
A check is a common form of negotiable instrument that allows the account holder to make payments or withdraw money from their checking account. It is a written order to a bank to pay a specific amount of money to the person or business named on the check.
2. Promissory Notes
A promissory note is a written promise to pay a specific amount of money at a future date. It is a legally binding document that outlines the terms and conditions of the loan, including the repayment schedule and interest rate.
3. Bills of Exchange

A bill of exchange is a written order from one party to another to pay a specific amount of money on a specific date. It is commonly used in international trade transactions and acts as a form of credit between parties.
4. Certificates of Deposit
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a negotiable instrument issued by a bank or financial institution. It represents a time deposit with a fixed term and fixed interest rate. The holder of the CD can redeem it for the principal amount plus interest at maturity.
These are just a few examples of negotiable instruments. They play a crucial role in financial transactions, providing a secure and convenient way to transfer money and make payments.
Importance of Negotiable Instruments in Checking Accounts
Checking accounts are a common and convenient way for individuals and businesses to manage their finances. One key aspect of checking accounts is the use of negotiable instruments, which play a crucial role in facilitating transactions and ensuring the smooth flow of funds.
What are Negotiable Instruments?
Negotiable instruments are documents that represent a promise to pay a certain amount of money to the bearer or a designated party. These instruments are transferable from one person to another, making them a reliable form of payment.
Types of Negotiable Instruments
There are several types of negotiable instruments commonly used in checking accounts:
- Checks: Checks are the most common form of negotiable instrument used in checking accounts. They allow the account holder to make payments to individuals or businesses by authorizing the bank to transfer funds from their account to the payee’s account.
- Promissory Notes: Promissory notes are written promises to pay a specific amount of money by a certain date. They are commonly used in lending and borrowing transactions.
- Bills of Exchange: Bills of exchange are similar to checks but are primarily used in international trade. They involve an order to pay a certain amount of money to a specific party.
- Certificates of Deposit: Certificates of deposit (CDs) are negotiable instruments issued by banks that represent a deposit made by an individual or business. They have a fixed term and earn interest.
Examples of Negotiable Instruments
Here are a few examples of how negotiable instruments are used in checking accounts:
- Writing a check to pay for groceries at the supermarket.
- Issuing a promissory note to borrow money from a friend.
- Using a bill of exchange to settle an international trade transaction.
- Investing in a certificate of deposit to earn interest on savings.
The importance of negotiable instruments in checking accounts cannot be overstated. They provide a secure and efficient means of conducting financial transactions, allowing individuals and businesses to easily transfer funds and make payments. Without negotiable instruments, the process of exchanging money would be much more cumbersome and time-consuming.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
