What is a Bill of Exchange?
The bill of exchange serves as a legal contract between the parties involved and provides a guarantee of payment. It is commonly used in situations where the buyer and seller are located in different countries, and it helps to mitigate the risk of non-payment or default.
Once the bill of exchange is accepted by the buyer, it becomes a binding legal obligation for the drawee to make the payment on the specified due date. The payee can then present the bill of exchange to a bank for collection or negotiate it to receive immediate payment.
There are different types of bills of exchange, including sight bills, which are payable on demand, and time bills, which have a specified maturity date. The bill of exchange is a widely used financial instrument in international trade and plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth and secure transactions.
Definition, Examples, and How It Works

The bill of exchange serves as a legally binding contract between the parties involved and provides a guarantee of payment. It is commonly used in situations where the buyer and seller are located in different countries and need a secure method of payment.
Examples of Bill of Exchange

Here are a few examples of how a bill of exchange can be used:
How a Bill of Exchange Works
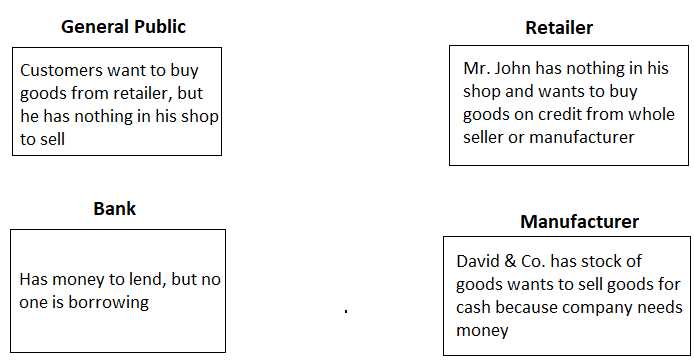
The process of using a bill of exchange involves several steps:
- The drawer creates the bill of exchange, specifying the amount of money to be paid, the payee, and the future date of payment.
- Once the bill of exchange is accepted, it can be traded or sold to a third party. This allows the drawer to receive immediate payment for the goods or services, even before the payment is due.
- On the specified future date, the drawee makes the payment to the payee, who then transfers the funds to the drawer.
In summary, a bill of exchange is a valuable tool in international trade that provides a secure method of payment for buyers and sellers in different countries. It ensures that both parties fulfill their financial obligations and helps to facilitate smooth transactions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Provides a secure method of payment | Requires trust between the parties involved |
| Allows for immediate payment to the seller | May incur additional costs, such as bank fees |
| Can be traded or sold to a third party | Requires adherence to specific legal requirements |
What is a Bill of Exchange in Supply Chain Management?
A bill of exchange is a financial document that is commonly used in supply chain management to facilitate the transfer of goods and services between parties. It is a written order from one party (the drawer) to another party (the drawee) to pay a specified amount of money to a third party (the payee) at a future date.
The bill of exchange serves as a legally binding agreement between the parties involved and provides a guarantee of payment for the goods or services provided. It is often used in international trade transactions, where it helps to mitigate the risk of non-payment and provides a secure method of payment.
Here are some key features of a bill of exchange:
- Amount and currency: The bill of exchange specifies the amount of money to be paid and the currency in which the payment should be made.
- Due date: The bill of exchange includes a due date, which is the date on which the payment should be made.
- Endorsement: The bill of exchange can be transferred to a third party through endorsement, which is the signing of the document by the payee.
In supply chain management, the bill of exchange plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and secure transactions between buyers and sellers. It provides a clear and enforceable payment mechanism, reduces the risk of non-payment, and helps to build trust and confidence between trading partners.
Overall, the bill of exchange is an essential tool in supply chain management, enabling efficient and reliable payment processes in domestic and international trade.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
