Market Maker Definition
A market maker is a financial institution or individual that plays a crucial role in the functioning of financial markets. They are responsible for providing liquidity by buying and selling securities, such as stocks, bonds, or derivatives, on behalf of their clients.
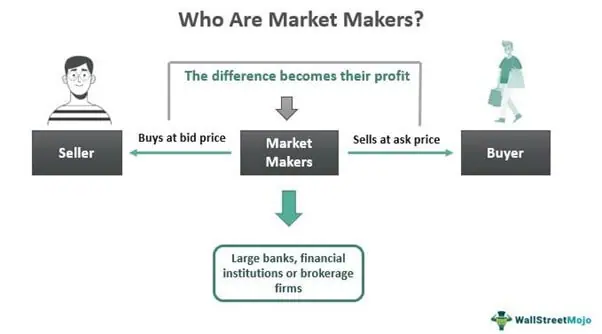
Market makers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in the market. They ensure that there is a continuous flow of trading activity by always being ready to buy or sell securities at quoted prices. This helps to maintain market stability and efficiency.
Profit-Making Strategies of Market Makers
Market makers employ various strategies to make profits. One common strategy is called “scalping,” where market makers take advantage of small price discrepancies in the market by buying at the bid price and selling at the ask price, capturing the spread as profit.
Another strategy is called “quote stuffing,” where market makers flood the market with a large number of quotes to create confusion and exploit price movements. This allows them to profit from the bid-ask spread as traders react to the changing quotes.
Exploring the MARKETS catname
The role of market makers is particularly important in the MARKETS catname. This market is known for its high trading volume and liquidity, making it attractive to both institutional and retail investors. Market makers in the MARKETS catname help to ensure that there is always a buyer or seller available, even during times of high volatility.
The Importance of Market Makers in the MARKETS catname
Market makers play a vital role in the MARKETS catname by providing liquidity and maintaining market stability. Without market makers, the market could become illiquid, leading to wider spreads and increased price volatility. Their presence ensures that investors can buy or sell securities at fair prices, contributing to the overall efficiency of the MARKETS catname.
Market makers play a crucial role in the financial markets by providing liquidity and ensuring smooth trading operations. They are individuals or firms that facilitate the buying and selling of financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives, by quoting both bid and ask prices.
One of the primary functions of market makers is to maintain an orderly market. They do this by constantly providing bid and ask prices, which allows investors to buy or sell securities at any time. Without market makers, there would be less liquidity in the market, making it difficult for investors to execute their trades.
Market makers also help narrow the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. By quoting both bid and ask prices, market makers ensure that there is a fair and competitive market for buyers and sellers.
Furthermore, market makers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. When an investor wants to buy a security, the market maker sells it to them from their own inventory. Conversely, when an investor wants to sell a security, the market maker buys it from them and adds it to their inventory. This allows for efficient and seamless transactions in the market.
Market makers also play a vital role in price discovery.

By constantly quoting bid and ask prices, market makers help determine the fair value of a security. They analyze market trends, news, and other factors to adjust their bid and ask prices accordingly. This price discovery process helps investors make informed decisions about buying or selling securities.
Market makers can also engage in proprietary trading.
While their primary role is to facilitate trading for others, market makers can also take positions in the market for their own profit. They can use their expertise and market knowledge to identify opportunities and make profitable trades. However, they must balance their role as market makers with their proprietary trading activities to avoid any conflicts of interest.
Profit-Making Strategies of Market Makers
Market makers play a crucial role in the financial markets by providing liquidity and facilitating smooth trading. They are responsible for ensuring that there is always a buyer or seller for a particular asset, which helps to maintain an orderly market. In order to make a profit, market makers employ various strategies that take advantage of the bid-ask spread and market volatility.
Market Volatility: Market makers also take advantage of market volatility to generate profits. When the market is highly volatile, the bid-ask spread tends to widen, providing market makers with more opportunities for profit. They can adjust their quotes to reflect the increased risk and uncertainty, allowing them to capture a larger spread.
Arbitrage: Another strategy employed by market makers is arbitrage. Arbitrage involves taking advantage of price discrepancies between different markets or exchanges. Market makers can buy an asset at a lower price in one market and sell it at a higher price in another, pocketing the difference as profit. This strategy requires quick execution and sophisticated trading systems to capitalize on small price differences.
Order Flow: Market makers also profit from order flow. They receive orders from various market participants and can use this information to their advantage. By analyzing the order flow, market makers can anticipate market movements and adjust their quotes accordingly. This allows them to capture a larger spread and generate profits.
Risk Management: Lastly, market makers employ risk management strategies to protect themselves from adverse market conditions. They constantly monitor their positions and adjust their quotes to manage their exposure. By hedging their positions and diversifying their portfolios, market makers can mitigate potential losses and ensure their long-term profitability.
Exploring the MARKETS catname
MARKETS catname is a popular and dynamic market that attracts traders from all over the world. With its diverse range of financial instruments and opportunities, it offers a unique platform for investors to trade and profit.
When exploring the MARKETS catname, it is important to understand the various factors that influence its performance. These factors can include economic indicators, geopolitical events, market sentiment, and industry trends. By staying informed and analyzing these factors, traders can make more informed decisions and increase their chances of success.
One of the key advantages of trading in the MARKETS catname is its liquidity. The market is highly liquid, meaning that there is a large volume of buyers and sellers, which allows for easy entry and exit from trades. This liquidity also helps to ensure that prices are fair and transparent, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Another important aspect of the MARKETS catname is its volatility. Volatility refers to the rapid and significant price movements in the market. While volatility can present risks, it also offers opportunities for traders to profit. By carefully analyzing market trends and using appropriate risk management strategies, traders can take advantage of these price movements and generate profits.
Furthermore, the MARKETS catname offers a wide range of trading instruments, including stocks, currencies, commodities, and indices. This diversity allows traders to diversify their portfolios and spread their risk across different assets. By having exposure to multiple markets and instruments, traders can increase their chances of finding profitable opportunities.
Lastly, the MARKETS catname is supported by advanced trading platforms and technology. These platforms provide traders with access to real-time market data, advanced charting tools, and various order types. This technology enables traders to execute trades quickly and efficiently, enhancing their overall trading experience.
The Importance of Market Makers in [MARKETS catname]
![The Importance of Market Makers in [MARKETS catname]](/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/market-maker-definition-understanding-their-role_3.jpg)
Market makers play a crucial role in the [MARKETS catname] by providing liquidity and ensuring smooth trading operations. They are essential participants in the financial markets, acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers.
One of the primary functions of market makers is to maintain an orderly market by continuously quoting bid and ask prices for specific securities or financial instruments. This constant presence of bid and ask prices allows investors to buy or sell assets at any time, even when there is low trading activity.
Market makers also help narrow the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. By narrowing the spread, market makers reduce transaction costs for investors, making it more attractive to trade in the [MARKETS catname].
Furthermore, market makers enhance market efficiency by absorbing excess buying or selling pressure. When there is an imbalance in supply and demand, market makers step in and take the opposite side of the trade, providing liquidity to the market. This ensures that trades can be executed promptly and at fair prices.
Market makers also contribute to price discovery in the [MARKETS catname]. By continuously quoting bid and ask prices, they provide valuable information about the current market sentiment and the fair value of securities. This information is essential for investors to make informed trading decisions.
In addition to their role as liquidity providers, market makers may also engage in proprietary trading to generate profits. They may take positions in securities or financial instruments based on their market expertise and analysis. This profit-making strategy helps sustain their operations and incentivizes their participation in the [MARKETS catname].

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
