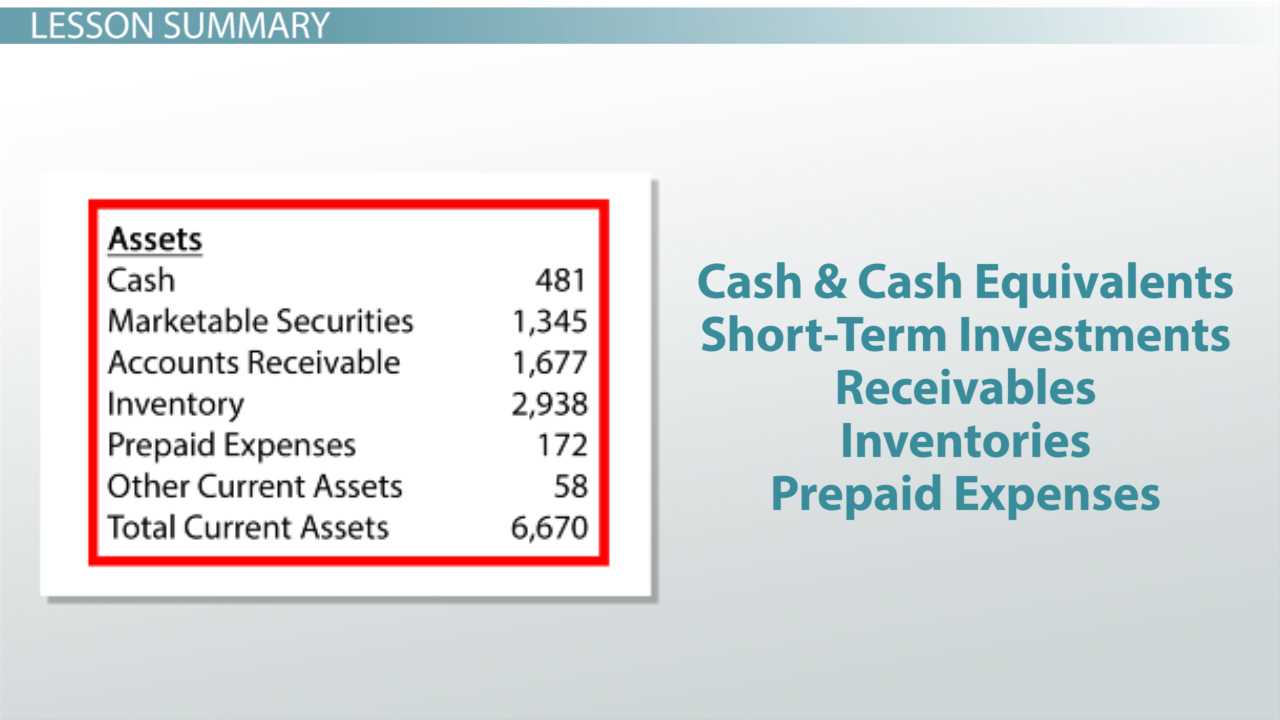
Listed Property Meaning and Examples
Listed property includes assets such as vehicles, computers, cameras, and other equipment that can be used for both business and personal purposes. These assets are often used by small business owners and self-employed individuals.
The IRS has specific guidelines for determining whether a property is considered listed property. Generally, if an asset is used for business purposes less than 50% of the time, it is considered listed property.
Examples of Listed Property
Here are some examples of listed property commonly found in small business taxes:
- Vehicles: Cars, trucks, and vans that are used for both business and personal purposes fall under the category of listed property. The IRS requires detailed records and logs to determine the percentage of business use for these vehicles.
- Computers and Electronics: Laptops, tablets, smartphones, and other electronic devices that are used for both business and personal purposes are considered listed property. The business owner must keep track of the percentage of time these devices are used for business activities.
- Cameras and Video Equipment: If a small business owner uses cameras or video equipment for both business and personal purposes, they are considered listed property. The business owner must maintain records to determine the percentage of business use.
- Home Office Equipment: Items such as desks, chairs, and printers that are used in a home office setting are considered listed property if they are used for both business and personal purposes. The business owner must keep track of the percentage of time these items are used for business activities.
It is important for small business owners to understand the concept of listed property and the specific rules and regulations that apply to these assets. By keeping accurate records and determining the percentage of business use, business owners can ensure they are correctly reporting and deducting expenses related to listed property on their tax returns.
What qualifies as listed property?
Listed property can include a wide range of assets, such as vehicles, computers, cameras, cell phones, and other equipment that can be used for both personal and business purposes. In order for an asset to be considered listed property, it must meet certain criteria set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
One of the main criteria is that the asset must be used for business purposes for at least 50% of the time it is in service. This means that if a small business owner uses their vehicle for both personal and business purposes, they must keep detailed records to determine the percentage of business use.
Why is listed property important?
The classification of an asset as listed property is important because it affects how the asset is depreciated for tax purposes. Depreciation is the process of deducting the cost of an asset over its useful life. Listed property is subject to more strict depreciation rules compared to other assets.
Additionally, listed property is subject to additional recordkeeping requirements. Small business owners must keep detailed records of the business use of listed property, including mileage logs for vehicles and usage logs for other assets. These records are necessary to support any deductions claimed on the tax return.
Examples of listed property in small business taxes
Here are some examples of assets that are commonly considered listed property in small business taxes:
- Vehicles used for both personal and business purposes
- Computers and laptops used for personal and business activities
- Cell phones used for both personal and business calls
- Cameras and video equipment used for personal and business purposes
- Home office equipment used for personal and business use
Definition and Importance of Listed Property
Listed property is a term used in accounting to refer to certain types of assets that are subject to specific tax rules and regulations. These assets are typically used for both personal and business purposes, making it necessary to determine the percentage of business use in order to calculate the allowable deductions.
What qualifies as listed property?
There are several types of assets that can be classified as listed property. Some common examples include:
- Vehicles: Cars, trucks, and motorcycles that are used for both personal and business purposes.
- Computers and electronic devices: Laptops, tablets, smartphones, and other devices that are used for both personal and business purposes.
- Cameras and video equipment: Cameras, camcorders, and other equipment used for both personal and business purposes.
- Cell phones: Cell phones that are used for both personal and business purposes.
- Other tangible property: Any other tangible property that is used for both personal and business purposes, such as furniture, equipment, and tools.
It is important to note that not all assets used for both personal and business purposes are considered listed property. The IRS has specific criteria that must be met in order for an asset to be classified as such. Small business owners should consult with a tax professional or refer to IRS guidelines to determine if their assets qualify as listed property.
Why is it important to properly categorize listed property?
Properly categorizing listed property is crucial for small business owners because it directly affects their tax liability. By accurately determining the percentage of business use for each listed property asset, owners can claim the appropriate deductions and credits on their tax returns.
Additionally, failing to properly categorize listed property can result in penalties or audits from the IRS. The IRS closely scrutinizes deductions and credits related to listed property, so it is essential to maintain accurate records and documentation to support any claims made on tax returns.
Examples of Listed Property in Small Business Taxes
1. Vehicles
One common example of listed property in small business taxes is vehicles. If a small business owner uses a vehicle for both personal and business purposes, they must keep track of the mileage and expenses related to the business use. This information is necessary to calculate the deductible expenses associated with the vehicle.
2. Computers and Electronics
3. Home Office
Many small business owners operate their businesses from home, making the home office another example of listed property. To claim deductions for a home office, the business owner must determine the percentage of their home that is used exclusively for business purposes.
For instance, if a small business owner uses one room in their home as a dedicated office space, they can deduct a portion of their home expenses, such as rent or mortgage interest, property taxes, and utilities, based on the percentage of the home used for business.
It is important for small business owners to keep accurate records of their listed property and the percentage of business use to ensure they are claiming the correct deductions and complying with tax regulations.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
