Licensing Fee: Definition, How It Works vs Royalty, and Examples
A licensing fee is a type of payment made by an individual or company to obtain the rights to use a certain intellectual property or product. This fee is typically paid to the owner or licensor of the intellectual property, such as a trademark, patent, or copyrighted material.
Compared to a royalty, which is a percentage of the revenue generated from the use of the intellectual property, a licensing fee is a fixed amount that is paid upfront or on a regular basis. It is a one-time or recurring cost that allows the licensee to use the intellectual property for a specific period of time.
For example, a software company may charge a licensing fee to allow another company to use their software for a certain number of users or for a specific period of time. The licensing fee would be a predetermined amount that the licensee would pay to the software company in exchange for the right to use the software.
Another example is in the entertainment industry, where licensing fees are often paid to obtain the rights to use a song in a movie or television show. The licensing fee would be negotiated between the production company and the owner of the song, and would typically be a one-time payment.
Licensing fees can vary greatly depending on the value and popularity of the intellectual property being licensed. They can be a significant source of revenue for the owner of the intellectual property, especially if the property is in high demand.
| Licensing Fee | Royalty |
|---|---|
| Fixed amount | Percentage of revenue |
| Paid upfront or on a regular basis | Paid based on usage or sales |
| Allows use of intellectual property for a specific period of time | Continued use of intellectual property |
What is a Licensing Fee?
A licensing fee is a payment made by one party (the licensee) to another party (the licensor) in exchange for the right to use or access a certain product, service, or intellectual property. It is a common practice in various industries, including software, entertainment, franchising, and technology.
The licensing fee serves as a form of compensation for the licensor, who owns the rights to the product or intellectual property. By paying the fee, the licensee gains the legal right to use, distribute, or sell the licensed product or service.
Licensing fees can vary in amount and structure depending on the specific agreement between the licensor and licensee. They can be a one-time payment or recurring payments, such as monthly or annual fees. The fee can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the revenue generated from the licensed product or service.
It is important for both parties to negotiate and agree upon the terms of the licensing fee before entering into a licensing agreement. This includes determining the duration of the license, any restrictions or limitations on usage, and any additional fees or royalties that may be required.
Overall, licensing fees play a crucial role in allowing businesses to monetize their intellectual property and generate revenue from their creations. They provide a way for licensors to profit from their inventions, while also enabling licensees to access and benefit from valuable products or services.
How Licensing Fee Works Compared to Royalty
Licensing Fees
For example, if a small business wants to use a patented technology developed by another company, they may negotiate a licensing fee with the patent holder. This fee could be a one-time payment or an annual fee, depending on the terms of the agreement. Once the licensing fee is paid, the small business can use the patented technology within the agreed-upon terms.
Royalties
Royalties, on the other hand, are ongoing payments made by the licensee to the licensor based on a percentage of the revenue generated from the use of the intellectual property. Unlike licensing fees, royalties are typically paid on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, and are often calculated as a percentage of the licensee’s sales or profits.
For instance, if a musician licenses their song to a film production company, they may receive royalties based on a percentage of the film’s box office revenue or soundtrack sales. The amount of royalties earned can vary depending on the success of the film or the popularity of the song.
Comparison

The main difference between licensing fees and royalties is the payment structure. Licensing fees are usually one-time or periodic payments made upfront, while royalties are ongoing payments based on a percentage of revenue. Additionally, licensing fees are typically negotiated between the parties, whereas royalties are often based on a predetermined percentage outlined in a licensing agreement.
Another difference is the level of risk involved. With licensing fees, the licensee pays a fixed amount regardless of the success or failure of their use of the intellectual property. On the other hand, royalties are tied to the licensee’s revenue, meaning that the licensor shares in the risk and potential reward of the licensee’s business activities.
Examples of Licensing Fees
1. Software Licensing Fee
One common example of a licensing fee is in the software industry. Software companies often charge a licensing fee to businesses or individuals who want to use their software. This fee grants the licensee the right to use the software for a specified period of time or under certain conditions.
2. Franchise Licensing Fee
Franchise businesses also require licensing fees. When someone wants to open a franchise of a well-known brand, they must pay a licensing fee to the franchisor. This fee gives the franchisee the right to use the brand name, trademarks, and business model of the franchisor.
3. Music Licensing Fee
Artists and musicians often charge licensing fees for the use of their music in various media, such as commercials, films, or television shows. The licensing fee allows the licensee to use the music for a specific purpose and duration, while the licensor receives compensation for the use of their intellectual property.
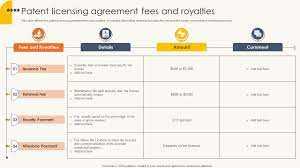
4. Patent Licensing Fee
Patent holders can charge licensing fees to companies or individuals who want to use their patented technology or invention. The licensing fee grants the licensee the right to use the patented technology while providing the licensor with financial compensation for the use of their intellectual property.
5. Brand Licensing Fee
Companies with well-known brands often charge licensing fees to other businesses that want to use their brand name or logo on their products. This allows the licensee to benefit from the reputation and recognition of the established brand, while the licensor receives a fee for granting the right to use their brand.
These are just a few examples of licensing fees in various industries. The specific terms and conditions of licensing agreements can vary greatly depending on the nature of the intellectual property or product being licensed. It is important for both parties to carefully negotiate and define the terms of the licensing fee to ensure a fair and mutually beneficial agreement.
Small Business Regulations for Licensing Fees
1. Research and Understand the Licensing Requirements: Before starting a business or entering into any licensing agreements, it is important to thoroughly research and understand the licensing requirements for your specific industry. This includes knowing which licenses are necessary, how to obtain them, and what fees are associated with each license.
2. Obtain the Necessary Licenses: Once you have identified the licenses that are required for your business, you must take the necessary steps to obtain them. This may involve filling out applications, providing documentation, and paying the required licensing fees. It is important to follow the proper procedures to ensure that your business is operating legally.
3. Keep Track of Renewal Dates: Many licenses have expiration dates and require renewal on a regular basis. It is important for small businesses to keep track of these renewal dates to avoid any penalties or fines for operating with an expired license. Set up reminders or utilize software systems to help you stay organized and ensure that your licenses are always up to date.
4. Understand the Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failing to comply with licensing regulations can have serious consequences for small businesses. This can include fines, penalties, legal action, and even the closure of your business. It is important to understand the potential consequences and take the necessary steps to ensure that your business is in compliance with all licensing requirements.
5. Seek Professional Advice: If you are unsure about any aspect of licensing fees or regulations, it is always a good idea to seek professional advice. Consult with an attorney or a licensing expert who can provide guidance and ensure that you are following all necessary regulations.
6. Budget for Licensing Fees: Licensing fees can vary greatly depending on the type of license and the specific terms of the agreement. It is important for small businesses to budget for these fees and include them in their financial planning. By accurately estimating and budgeting for licensing fees, you can avoid any unexpected financial burdens and ensure that your business remains financially stable.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
