What is an IPO and How Does it Work?
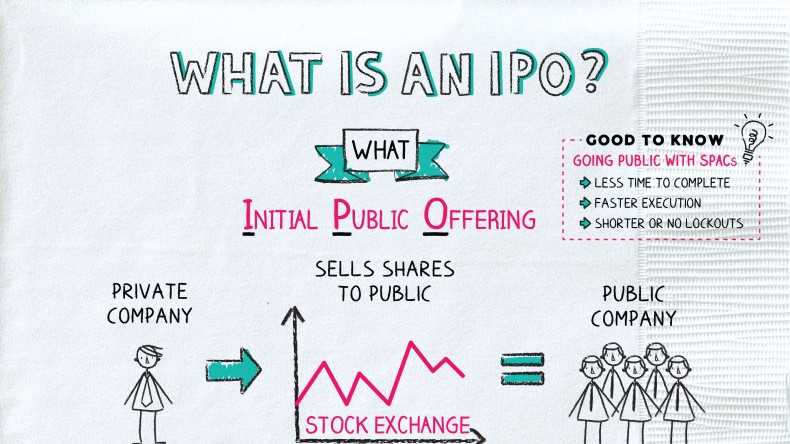
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process by which a private company becomes a publicly traded company by offering its shares to the public for the first time. It is a significant milestone for a company as it allows them to raise capital from a wide range of investors and provides liquidity to existing shareholders.
The IPO Process
The IPO process typically involves several key steps:
- Preparation: The company prepares for the IPO by engaging in a thorough financial and legal due diligence process. This includes preparing financial statements, prospectus, and other required documents.
- Selection of Underwriters: The company selects one or more investment banks to act as underwriters for the IPO. The underwriters help determine the offering price, market the shares to potential investors, and facilitate the sale of the shares.
- Registration: The company files a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that includes detailed information about the company, its financials, and the proposed offering.
- Marketing and Roadshow: The company and its underwriters conduct a marketing campaign to generate interest in the IPO. This includes meeting with potential investors and presenting the investment opportunity in a series of roadshow presentations.
- Pricing: The underwriters and the company determine the final offering price based on investor demand and market conditions. The offering price is typically set at a discount to the estimated value of the company.
- Allocation and Distribution: The underwriters allocate the shares to institutional and retail investors. The shares are then distributed to investors through the underwriters.
- Listing: The company’s shares are listed on a stock exchange, allowing them to be traded by the public. This provides liquidity to existing shareholders and allows the company to raise additional capital in the future.
Benefits of an IPO
An IPO offers several benefits to a company:
- Raising Capital: An IPO allows a company to raise significant capital to fund its growth and expansion plans. This capital can be used to invest in new projects, acquire other companies, or pay off existing debt.
- Enhanced Visibility and Credibility: Going public through an IPO increases a company’s visibility and credibility in the market. It can attract new customers, partners, and employees, and enhance the company’s brand image.
- Liquidity for Shareholders: An IPO provides liquidity to existing shareholders, allowing them to sell their shares and realize their investment. This can be particularly beneficial for early investors, founders, and employees who hold a significant stake in the company.
- Access to Public Markets: Being a publicly traded company provides access to public markets, allowing the company to raise additional capital through secondary offerings or debt issuances in the future.
The Benefits of Going Public through an IPO
Going public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) can provide numerous benefits for a company. It is a process where a privately held company offers its shares to the public for the first time, allowing it to raise capital and become a publicly traded entity. Here are some of the key benefits of going public through an IPO:
| Access to Capital: | One of the primary benefits of an IPO is the ability to raise significant capital. By offering shares to the public, a company can attract a large number of investors who are willing to invest their money in exchange for ownership in the company. This influx of capital can be used to fund expansion plans, invest in research and development, pay off debts, or make acquisitions. |
| Enhanced Reputation: | Going public can enhance a company’s reputation and credibility in the market. Being listed on a stock exchange and subject to regulatory requirements can increase transparency and accountability, which can attract more investors and customers. It also provides a platform for the company to showcase its growth potential and attract talented employees. |
| Liquidity for Shareholders: | For existing shareholders, an IPO provides an opportunity to sell their shares and realize their investments. This liquidity can be especially beneficial for early investors, founders, and employees who hold equity in the company. It allows them to monetize their ownership and diversify their investment portfolios. |
| Valuation and Exit Strategy: | An IPO can help establish a market value for the company. The price at which the shares are sold to the public reflects the market’s perception of the company’s worth. This valuation can be used as a benchmark for future fundraising efforts or potential mergers and acquisitions. Additionally, going public can provide an exit strategy for venture capitalists and other investors who are looking to sell their stakes in the company. |
| Increased Visibility: | Being a publicly traded company can significantly increase a company’s visibility and exposure to the market. It allows the company to attract attention from analysts, media, and potential customers. This increased visibility can lead to greater brand recognition, customer trust, and business opportunities. |
While going public through an IPO offers numerous benefits, it is important for companies to carefully consider the associated costs, regulatory requirements, and potential challenges. It is advisable to seek professional advice from investment bankers, lawyers, and accountants to ensure a successful and smooth transition to the public markets.
Real-life Examples of Successful IPOs

Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) have been a popular way for companies to raise capital and gain public visibility. Many well-known companies have gone through successful IPOs, which have helped them grow and expand their businesses. Here are some real-life examples of successful IPOs:
1. Facebook
In 2012, Facebook had one of the most highly anticipated IPOs in history. The social media giant raised $16 billion, making it the largest technology IPO at the time. Facebook’s IPO gave the company a valuation of over $100 billion, and it became one of the most valuable companies in the world.
2. Alibaba
In 2014, Alibaba, the Chinese e-commerce giant, had its IPO on the New York Stock Exchange. The company raised $25 billion, making it the largest IPO in history. Alibaba’s IPO helped the company expand globally and solidify its position as one of the leading e-commerce companies in the world.
3. Google
Google’s IPO took place in 2004, and it raised $1.67 billion. The IPO helped Google grow its business and expand into new markets. Today, Google is one of the most valuable companies in the world, offering a wide range of products and services.
4. Amazon
Amazon had its IPO in 1997, raising $54 million. The company started as an online bookstore but has since grown into a global e-commerce giant. Amazon’s IPO played a crucial role in its growth and allowed the company to diversify its offerings and become a leader in various industries.
5. Spotify
In 2018, Spotify, the popular music streaming platform, had a direct listing IPO. The company bypassed the traditional underwriting process and allowed its existing shareholders to sell their shares directly to the public. Spotify’s IPO helped the company raise capital and increase its user base.
These are just a few examples of successful IPOs that have helped companies achieve significant growth and success. Going public through an IPO can provide companies with the necessary funds to expand their operations, invest in research and development, and attract new investors. However, it is essential for companies to carefully consider the process and weigh the benefits and risks before deciding to go public.
Key Considerations for Companies Considering an IPO
Going public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) is a significant milestone for any company. It can provide access to capital, increase brand visibility, and create opportunities for growth. However, before deciding to embark on an IPO, companies should carefully consider several key factors.
1. Financial Readiness
2. Market Conditions
Market conditions play a significant role in the success of an IPO. Companies should assess the current market environment, including investor sentiment, industry trends, and the overall economic climate. It is essential to choose the right timing for the IPO to maximize the chances of a successful offering.
3. Corporate Governance
Public companies are subject to more stringent regulatory requirements and increased scrutiny from shareholders and the public. Therefore, companies considering an IPO should have robust corporate governance practices in place. This includes having an independent board of directors, transparent financial reporting, and effective risk management procedures.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Companies must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements when going public. This includes filing registration statements with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), adhering to disclosure obligations, and complying with securities laws. It is crucial to engage experienced legal counsel to navigate the complex regulatory landscape.
5. Investor Relations

Once a company goes public, it becomes accountable to its shareholders and the investment community. Building strong investor relations is essential for maintaining trust and credibility. This involves effective communication, timely and transparent disclosure of financial information, and proactive engagement with shareholders and analysts.
6. Long-Term Strategy
Companies should have a clear long-term strategy in place before going public. Going public is not just about raising capital; it is about positioning the company for sustainable growth and value creation. Companies should have a compelling business plan, a clear vision for the future, and a strategy to execute their growth initiatives.
Overall, going public through an IPO can be a transformative event for a company. However, it is crucial to carefully consider these key factors to ensure a successful and sustainable transition to the public markets.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
