Head of Household Qualifications and Income Tax Brackets
Qualifications for Head of Household Status
To be eligible for head of household status, you must meet the following requirements:
- You must be unmarried or considered unmarried on the last day of the tax year.
- You must have paid more than half the cost of maintaining a home for yourself and a qualifying person.
- You must have a qualifying person who lived with you for more than half the tax year. This can include a child, parent, or other relative.
Meeting these qualifications allows you to file as head of household, which often results in a lower tax liability compared to filing as single or married filing separately.
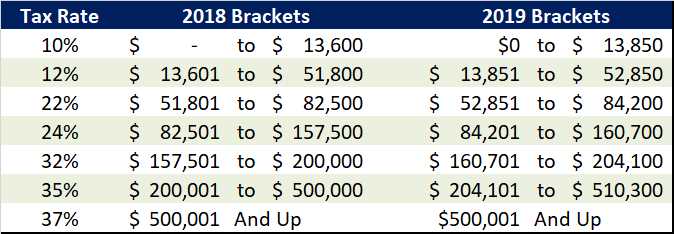
Income Tax Brackets for Head of Household
Once you have determined your eligibility for head of household status, it is important to understand the income tax brackets that apply to you. The tax brackets for head of household filers are different from those for single filers or married couples filing jointly.
| Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|
| 10% | |
| 12% | |
| 22% | |
| 24% | |
| 32% | |
| 35% | |
| 37% | $523,601+ |
These income tax brackets determine the percentage of your income that is subject to federal income tax. As your income increases, you move into higher tax brackets, resulting in a higher tax rate.
Taxpayer Types Explained
So, what exactly does it mean to be a head of household? In simple terms, it means that you are a single or unmarried individual who is financially responsible for supporting a household. This can include providing for a child, a parent, or any other dependent.
To qualify as a head of household, you must meet several criteria. First, you must be unmarried or considered unmarried on the last day of the tax year. This means that you are not legally married or that you are separated from your spouse and have not lived together for the last six months of the year.
Second, you must have paid more than half of the cost of maintaining a home for yourself and your qualifying dependents. This includes expenses such as rent, mortgage interest, property taxes, utilities, and groceries.
Third, you must have a qualifying dependent. This can be a child, a parent, or another relative who meets certain criteria. To be considered a qualifying dependent, the individual must live with you for more than half of the year, be financially dependent on you, and meet certain age and relationship requirements.
It is important to note that if you are married, you cannot file as head of household unless you meet the criteria for being considered unmarried. Additionally, if you are divorced or separated, you may still be eligible to file as head of household if you meet the other qualifications.
Filing as head of household can result in several tax benefits. For example, the income tax brackets for head of household are typically more favorable than those for single individuals. This means that you may be able to keep more of your income and potentially pay a lower tax rate.
In addition, filing as head of household allows you to claim certain tax credits and deductions that are not available to other taxpayer types. These can include the Child Tax Credit, the Earned Income Tax Credit, and deductions for education expenses and child care costs.
To maximize your head of household tax benefits, it is important to keep detailed records of your expenses and ensure that you meet all the qualifications. This includes maintaining documentation of your relationship with your qualifying dependents, as well as receipts and other proof of your household expenses.
Qualifications for Head of Household Status
Being able to file as head of household can provide significant tax benefits for individuals who meet the qualifications. In order to qualify for head of household status, you must meet the following criteria:
| Criteria | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Filing Status | You must be unmarried or considered unmarried on the last day of the tax year. This means you are not married and do not qualify to file as a qualifying widow(er) with a dependent child. |
| Dependent | |
| Residency | You must have paid more than half the cost of keeping up a home for the tax year. This includes expenses such as rent, mortgage interest, property taxes, utilities, and groceries. |
| Support | You must be able to claim the child or dependent as a dependent on your tax return. This means that they cannot have provided more than half of their own support for the year. |
It is important to note that meeting these qualifications is crucial in order to file as head of household and receive the associated tax benefits. Failing to meet any of these criteria may result in the loss of head of household status and the potential for higher tax liability.
Income Tax Brackets for Head of Household
When filing taxes as a head of household, it is important to understand the income tax brackets that apply to this filing status. The income tax brackets determine the percentage of your income that you will owe in taxes. Here is a breakdown of the income tax brackets for head of household filers in the United States:
| Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|
| 10% | |
| 12% | |
| 22% | |
| 24% | |
| 32% | |
| 35% | |
| 37% | $523,601 or more |
These income tax brackets are subject to change each year, so it is important to consult the latest tax laws and regulations to ensure accurate filing. It is also worth noting that these brackets apply to taxable income, which is your total income minus any deductions or credits you may qualify for.
Benefits of Filing as Head of Household
Filing as head of household can provide several benefits for taxpayers. Here are some advantages of claiming this filing status:
1. Lower tax rates:
Head of household filers benefit from lower tax rates compared to single filers. The tax brackets for head of household are typically wider, allowing for more income to be taxed at lower rates.
2. Higher standard deduction:
Head of household filers also enjoy a higher standard deduction compared to single filers. This means that a larger portion of their income is not subject to federal income tax.
3. Additional tax credits:
Claiming head of household status may make you eligible for certain tax credits that are not available to single filers. For example, the Child Tax Credit and the Earned Income Tax Credit can provide significant tax savings.
4. Qualification for certain deductions:
As a head of household, you may qualify for certain deductions that are not available to single filers. For instance, you may be able to deduct expenses related to caring for a dependent or education expenses.
5. Ability to claim dependents:
As a head of household, you can claim certain dependents, such as children or other qualifying relatives, which can further reduce your taxable income.
6. Increased eligibility for certain benefits:
Overall, filing as head of household can provide significant tax savings and financial benefits. However, it is important to ensure that you meet the qualifications for this filing status to avoid any potential penalties or audits from the IRS.
Tips for Maximizing Head of Household Tax Benefits
Filing as head of household can provide significant tax benefits for individuals who qualify. To make the most of these benefits, consider the following tips:
1. Understand the Qualifications
Before filing as head of household, it is important to fully understand the qualifications set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Make sure you meet all the requirements, such as being unmarried or considered unmarried on the last day of the tax year, paying more than half the cost of keeping up a home for a qualifying person, and having a qualifying person live with you for more than half the year.
2. Keep Accurate Records

To ensure you can claim head of household status, it is crucial to keep accurate records of your expenses and the support you provide for the qualifying person. This includes receipts for rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, and other household expenses. Having organized and detailed records will help support your claim if the IRS requests documentation.
3. Claim All Eligible Dependents
If you have multiple dependents, make sure to claim all eligible dependents on your tax return. This can include children, parents, or other relatives who meet the IRS criteria. By claiming all eligible dependents, you can maximize your tax benefits and potentially qualify for a higher tax bracket.
4. Take Advantage of Tax Credits
5. Consider Retirement Contributions
If you have the financial means, consider making contributions to a retirement account, such as an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) or a 401(k) plan. Contributions to these accounts can lower your taxable income, potentially moving you into a lower tax bracket and increasing your overall tax savings.
6. Seek Professional Advice
If you have complex tax situations or are unsure about the best strategies for maximizing your head of household tax benefits, it is advisable to seek professional advice from a tax accountant or tax advisor. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances and help you make informed decisions.
By following these tips, you can maximize your head of household tax benefits and potentially reduce your overall tax liability. Remember to stay informed about any changes in tax laws or regulations that may affect your eligibility or tax benefits.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
