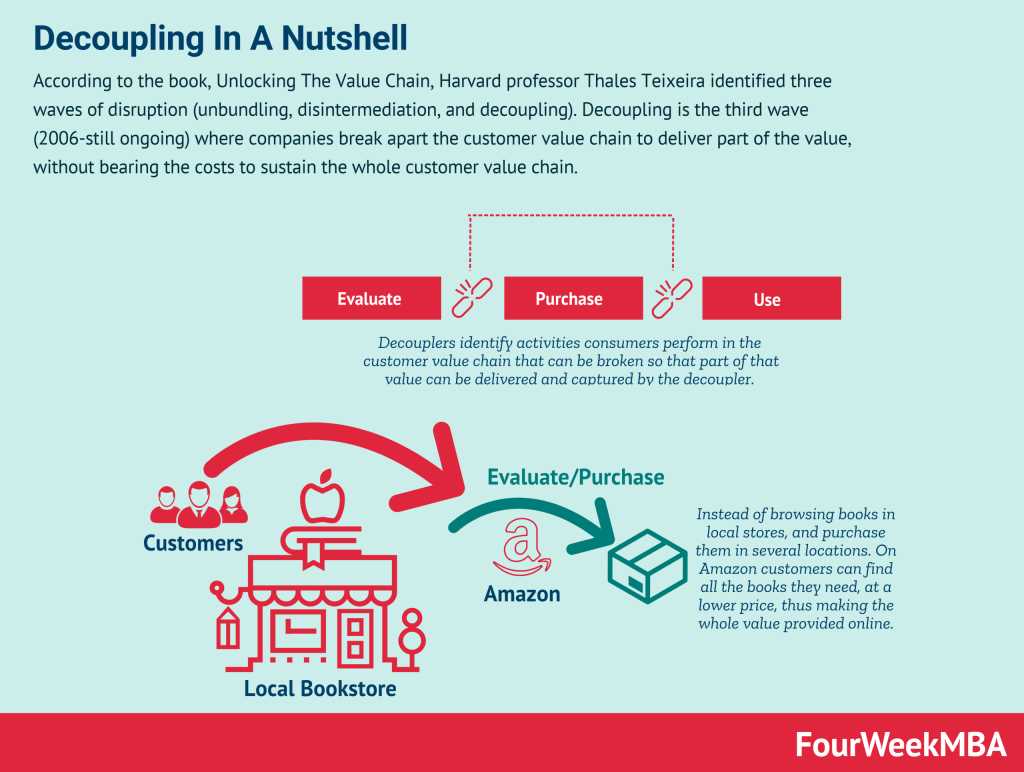
Disintermediation: Definition and Examples in Business Finance

Disintermediation is a term used in business finance to describe the process of removing intermediaries or middlemen from a transaction or business relationship. It involves bypassing traditional channels or intermediaries in order to directly connect buyers and sellers or providers and consumers.
This concept has gained significant importance in the modern business landscape, primarily due to advancements in technology and the rise of the internet. Disintermediation has become more prevalent as businesses and consumers have gained the ability to connect and transact directly without the need for intermediaries.
Examples of Disintermediation
One of the most prominent examples of disintermediation is the rise of e-commerce platforms. Online marketplaces such as Amazon and eBay have disrupted traditional retail by allowing consumers to purchase products directly from sellers, bypassing the need for physical stores and traditional distribution channels.
Another example is the peer-to-peer lending industry. Platforms like LendingClub and Prosper enable individuals to lend money directly to borrowers, eliminating the need for traditional banks as intermediaries. This allows borrowers to access loans at potentially lower interest rates, while lenders can earn higher returns on their investments.
Impact of Disintermediation on Portfolio Management
Furthermore, disintermediation has allowed individual investors to access a wider range of investment options. Through online trading platforms, investors can directly purchase stocks, bonds, and other securities without the need for a broker or financial advisor. This has democratized investing and provided individuals with greater control over their investment decisions.
What is Disintermediation?
Disintermediation is a term used in business finance to describe the process of eliminating intermediaries or middlemen in a transaction or supply chain. It involves the direct interaction between the producer or supplier and the end consumer, bypassing traditional distribution channels or intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, or brokers.
Disintermediation has become more prevalent with the rise of the internet and e-commerce. Online platforms and marketplaces have provided businesses and consumers with direct access to products and services, reducing the need for intermediaries. This has resulted in increased efficiency, cost savings, and greater control over the entire supply chain.
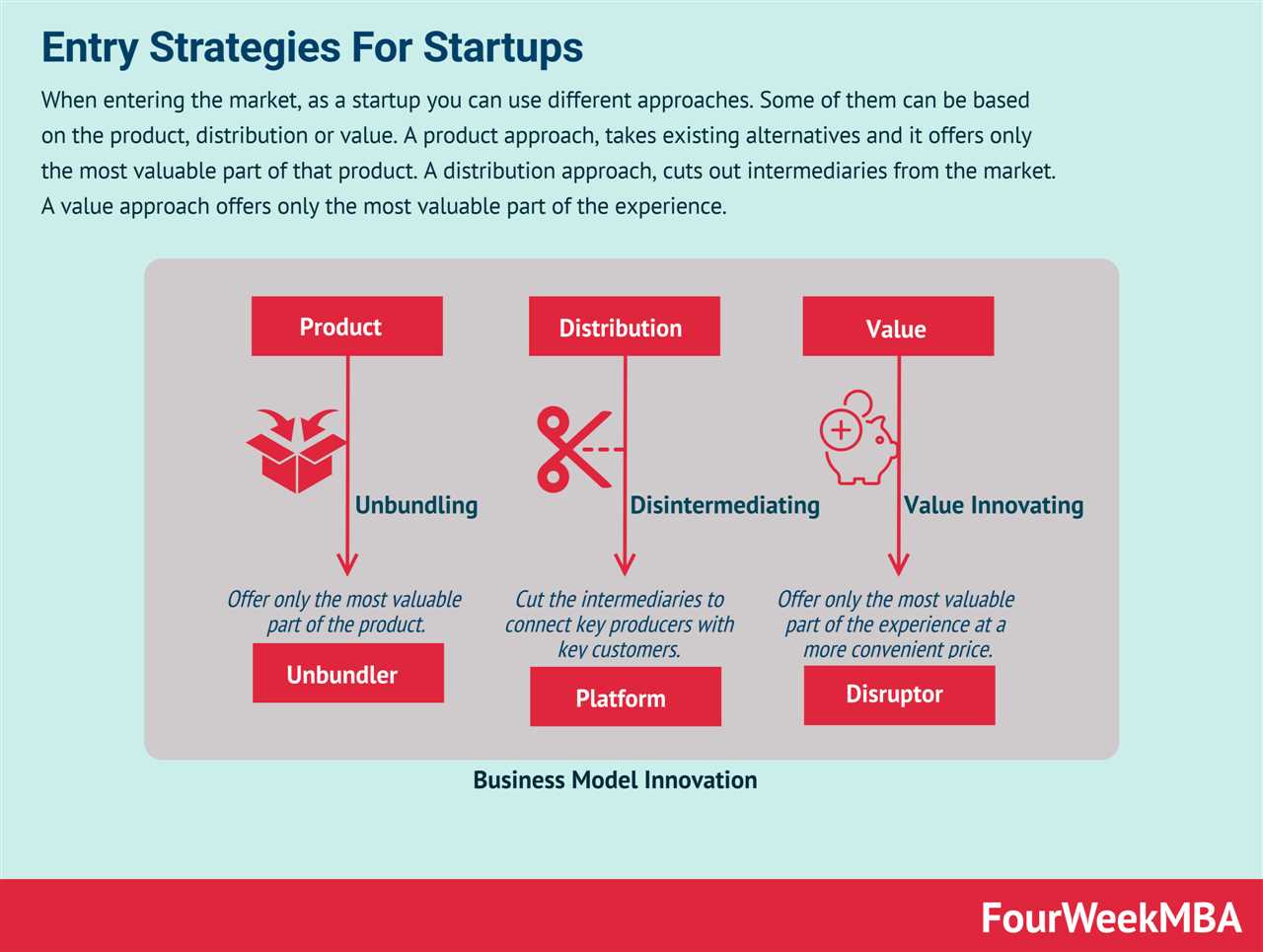
Advantages of Disintermediation
There are several advantages associated with disintermediation:
- Cost savings: By eliminating intermediaries, businesses can reduce costs associated with distribution, marketing, and sales commissions. This can result in lower prices for consumers or higher profit margins for businesses.
- Efficiency: Direct interaction between producers and consumers allows for faster and more efficient transactions. There is no need to wait for intermediaries to process orders or handle logistics.
- Greater control: Disintermediation gives businesses greater control over their products, brand image, and customer relationships. They can tailor their offerings to specific customer needs and preferences.
- Transparency: With disintermediation, there is greater transparency in pricing and product information. Consumers can directly compare prices and make informed purchasing decisions.
Disadvantages of Disintermediation
While disintermediation offers numerous benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages:
- Loss of expertise: Intermediaries often possess specialized knowledge and expertise in their respective industries. By bypassing them, businesses may lose access to valuable insights and advice.
- Logistical challenges: Without intermediaries, businesses may face logistical challenges in terms of storage, shipping, and fulfillment. They need to establish their own infrastructure or find alternative solutions.
- Increased competition: Disintermediation can lead to increased competition as more businesses enter the market. This can make it harder for businesses to differentiate themselves and attract customers.
- Trust and security: Intermediaries often provide a sense of trust and security in transactions. Without them, businesses and consumers may need to rely on other mechanisms to ensure the integrity of the transaction.
Disintermediation in Business Finance
Disintermediation is a term used in business finance to describe the process of removing intermediaries from a transaction or financial process. It involves bypassing traditional intermediaries such as banks, brokers, or financial institutions and conducting transactions directly between two parties.
Disintermediation has become more prevalent in recent years due to advancements in technology and the rise of online platforms. These platforms allow individuals and businesses to connect and transact directly, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
One of the main reasons for disintermediation is cost reduction. By cutting out intermediaries, businesses can save on fees and commissions that would otherwise be paid to banks or brokers. This can result in significant cost savings, especially for large transactions or frequent transactions.
Another benefit of disintermediation is increased efficiency. By eliminating intermediaries, transactions can be completed more quickly and with fewer complications. This can be particularly advantageous in time-sensitive situations or when dealing with complex financial products.
However, disintermediation is not without its challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential loss of expertise and guidance that intermediaries provide. Banks and brokers often have extensive knowledge and experience in financial matters, which can be valuable for individuals and businesses seeking advice.
Additionally, disintermediation can increase the risk of fraud or security breaches. Without the oversight of intermediaries, individuals may be more vulnerable to scams or fraudulent activities. It is important for individuals and businesses to exercise caution and conduct thorough due diligence when engaging in direct transactions.
Examples of Disintermediation
Disintermediation is a concept that has gained significant attention in the world of business finance. It refers to the process of eliminating intermediaries in a supply chain or financial transaction, allowing for direct interaction between the parties involved. This can have various implications for businesses and consumers alike. Here are some examples of disintermediation in different industries:
1. Retail Industry:
In the retail industry, disintermediation has become increasingly prevalent with the rise of e-commerce. Online retailers such as Amazon have disrupted traditional brick-and-mortar stores by allowing consumers to purchase products directly from manufacturers or wholesalers. This eliminates the need for intermediaries such as distributors or physical retail stores, resulting in lower prices for consumers.
2. Financial Services:
In the financial services sector, disintermediation has been facilitated by advancements in technology. Peer-to-peer lending platforms, for example, connect borrowers directly with lenders, bypassing traditional banks. This allows borrowers to access loans at lower interest rates, while lenders can earn higher returns on their investments compared to traditional savings accounts.
3. Travel Industry:
The travel industry has also experienced disintermediation through the emergence of online travel agencies (OTAs). These platforms enable consumers to book flights, hotels, and other travel services directly, eliminating the need for travel agents. This not only provides convenience for travelers but also allows for greater price transparency and competition among service providers.
4. Media and Entertainment:
Streaming services such as Netflix and Spotify have disrupted traditional media and entertainment industries by allowing users to access content directly without intermediaries like cable companies or record labels. This has democratized access to entertainment and empowered content creators to reach a global audience without relying on traditional distribution channels.
5. Real Estate:
In the real estate industry, disintermediation has been facilitated by online platforms that connect buyers and sellers directly. These platforms provide a transparent marketplace where buyers can browse listings, negotiate prices, and complete transactions without the need for real estate agents. This can result in cost savings for both buyers and sellers.
Overall, disintermediation has transformed various industries by removing barriers and inefficiencies in the supply chain. It has empowered consumers, increased competition, and facilitated direct interactions between parties. As technology continues to advance, disintermediation is expected to play an even greater role in shaping the future of business finance.
Impact of Disintermediation on Portfolio Management
Disintermediation, the process of removing intermediaries from a supply chain, has a significant impact on portfolio management in the field of business finance. This article will explore how disintermediation affects portfolio management and the strategies that portfolio managers can employ to navigate this changing landscape.
Definition of Disintermediation
Disintermediation refers to the elimination of intermediaries, such as banks or brokers, from a transaction or business process. This can occur when technology enables direct communication and transactions between buyers and sellers, bypassing traditional intermediaries.
Disintermediation has become increasingly prevalent in recent years due to advancements in technology and the rise of the internet. This has allowed businesses and consumers to connect directly, reducing the need for intermediaries and streamlining the transaction process.
Impact on Portfolio Management
Disintermediation has a significant impact on portfolio management, particularly in the context of investment management. Traditionally, portfolio managers relied on intermediaries, such as brokers or investment banks, to execute trades and manage investments on their behalf.
However, with the rise of online trading platforms and robo-advisors, investors now have the ability to bypass traditional intermediaries and manage their portfolios directly. This has led to increased competition in the industry and a shift in power from intermediaries to individual investors.
Portfolio managers must adapt to this changing landscape by leveraging technology and providing value-added services to differentiate themselves. This may include offering personalized investment advice, utilizing data analytics to identify investment opportunities, or providing educational resources to help investors make informed decisions.
Strategies for Portfolio Managers
To navigate the impact of disintermediation, portfolio managers can employ several strategies:
- Embrace technology: Portfolio managers should embrace technology and leverage it to enhance their investment processes. This may involve utilizing automated trading algorithms, implementing data analytics tools, or adopting machine learning techniques to analyze market trends and make informed investment decisions.
- Focus on value-added services: Portfolio managers should differentiate themselves by offering value-added services that go beyond basic investment management. This may include financial planning, tax optimization strategies, or personalized investment advice tailored to individual client goals and risk profiles.
- Build strong client relationships: In a disintermediated landscape, building strong client relationships is crucial. Portfolio managers should prioritize communication and provide regular updates to clients, demonstrating their expertise and commitment to helping clients achieve their financial goals.
- Stay informed and adaptable: Disintermediation is an ongoing process, and portfolio managers must stay informed about industry trends and adapt their strategies accordingly. This may involve attending industry conferences, networking with peers, and continuously learning about new technologies and investment opportunities.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
