What is Corporate Hierarchy?
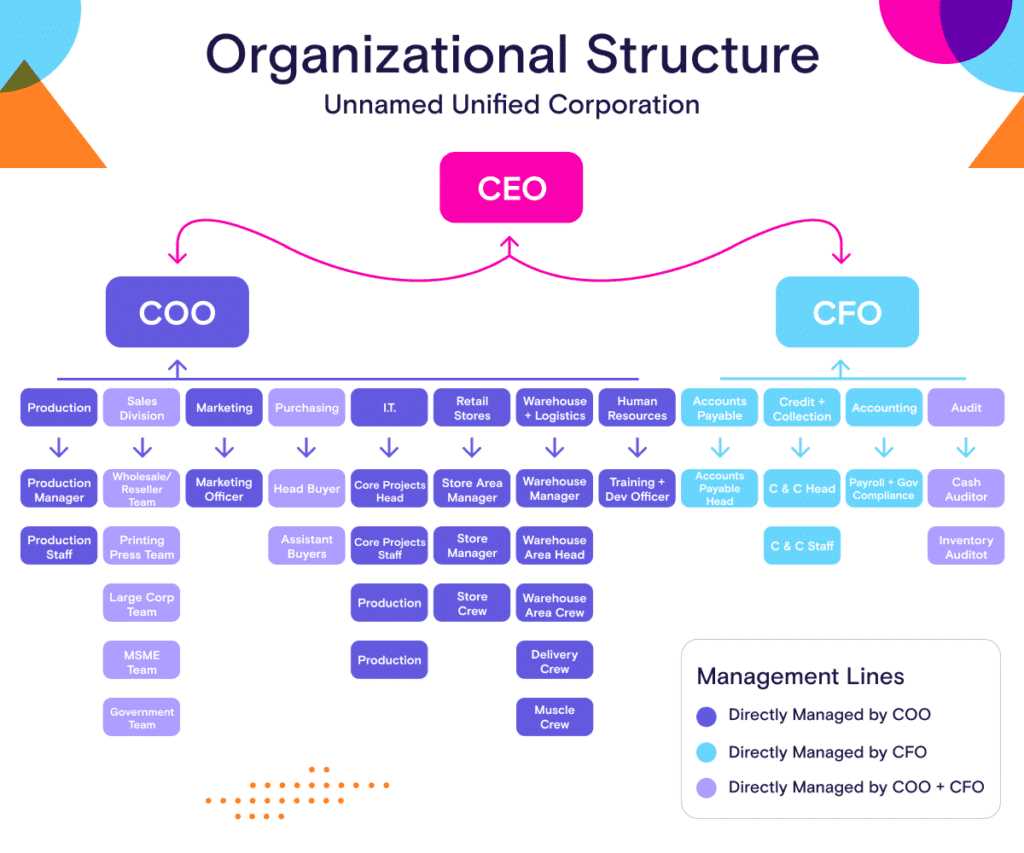
Corporate hierarchy refers to the structure and organization of a company or organization. It defines the relationships, roles, and responsibilities of individuals within the company, and how they interact with one another.
The corporate hierarchy is typically represented as a pyramid, with the CEO or president at the top, followed by senior executives, middle managers, and then employees at the bottom. This hierarchical structure helps to establish clear lines of authority and accountability within the organization.
Corporate hierarchy plays a crucial role in the functioning of a company. It helps to ensure that tasks and responsibilities are properly delegated and that decisions are made efficiently. It also provides a framework for communication and collaboration, allowing employees to understand their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
One of the key benefits of a corporate hierarchy is that it provides employees with a clear path for career advancement. As individuals gain experience and demonstrate their abilities, they can move up the hierarchy and take on more responsibility. This can be motivating for employees and help to retain top talent within the organization.
However, corporate hierarchy can also have its drawbacks. It can create a rigid and bureaucratic organizational culture, where decisions are slow to be made and innovation is stifled. It can also lead to a lack of communication and collaboration between different levels of the hierarchy, hindering the flow of information and ideas.
Overall, corporate hierarchy is an important aspect of any organization. It provides structure and order, helps to define roles and responsibilities, and allows for career advancement. However, it is important for companies to strike a balance between hierarchy and flexibility, in order to foster innovation and adapt to changing market conditions.
Operations in Corporate Hierarchy
In a corporate hierarchy, operations refer to the various activities and processes that are carried out within the organization to achieve its goals and objectives. These operations can be categorized into different departments or functional areas, each responsible for a specific set of tasks.
1. Sales and Marketing
The sales and marketing department is responsible for promoting and selling the company’s products or services. This includes market research, advertising, sales forecasting, lead generation, and customer relationship management.
2. Finance and Accounting
The finance and accounting department handles the company’s financial transactions, including budgeting, financial planning, payroll management, accounts payable and receivable, and financial reporting. They ensure the company’s financial stability and compliance with regulations.
3. Human Resources
The human resources department is responsible for managing the company’s workforce. This includes recruitment and hiring, employee training and development, performance management, compensation and benefits administration, and employee relations.
4. Operations and Production
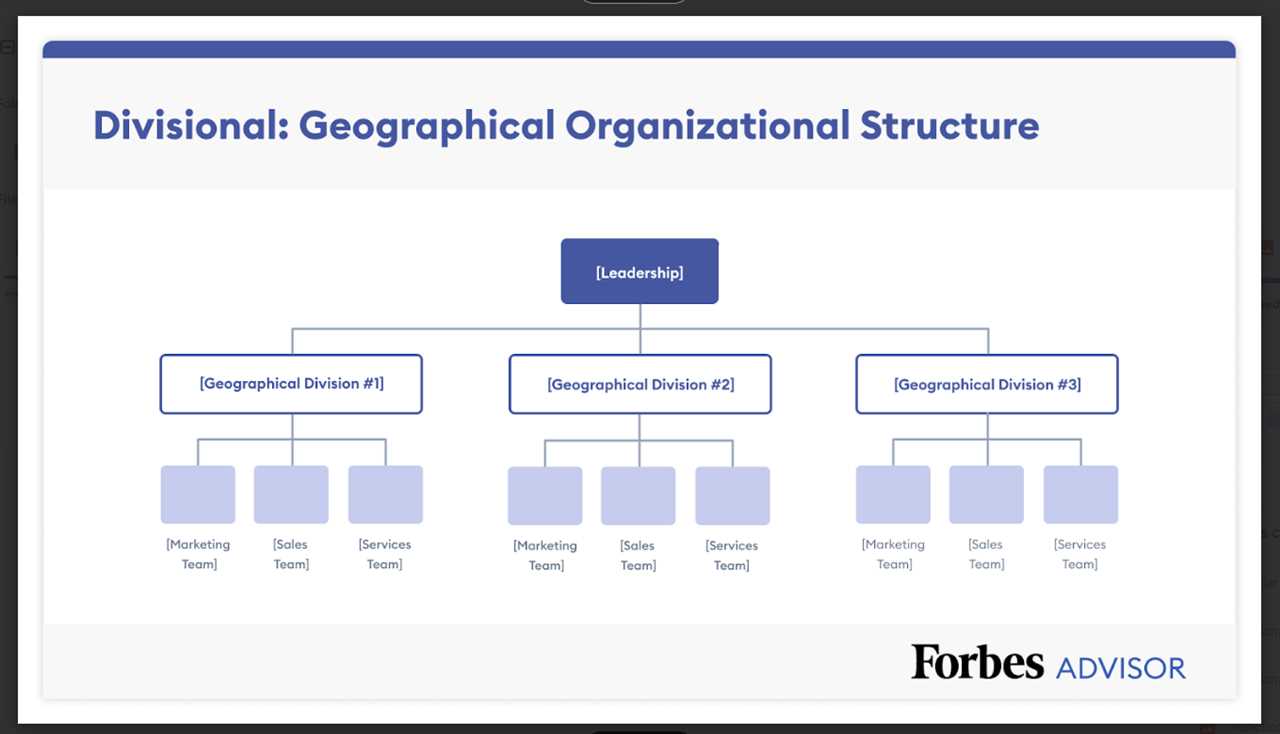
The operations and production department is responsible for the manufacturing or delivery of the company’s products or services. They oversee the production process, manage inventory, ensure quality control, and optimize operational efficiency.
5. Information Technology
The information technology department manages the company’s technology infrastructure and systems. They are responsible for maintaining hardware and software, managing data and information security, providing technical support, and implementing new technologies to improve business processes.
6. Research and Development
The research and development department focuses on innovation and product improvement. They conduct research, develop new products or services, test prototypes, and analyze market trends to ensure the company remains competitive in the industry.
7. Customer Service
The customer service department handles customer inquiries, complaints, and support. They provide assistance and resolve issues to ensure customer satisfaction and maintain positive relationships with clients.
Overall, the operations in a corporate hierarchy are interconnected and work together to achieve the company’s goals. Each department plays a crucial role in the success and growth of the organization.
| Department | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Sales and Marketing | Promotion, sales, market research |
| Finance and Accounting | Budgeting, financial planning, payroll |
| Human Resources | Recruitment, training, performance management |
| Operations and Production | Manufacturing, quality control, inventory management |
| Information Technology | Infrastructure management, data security |
| Research and Development | Innovation, product development |
| Customer Service | Inquiries, support, complaint resolution |
Structure of Corporate Hierarchy
Levels of Hierarchy
Corporate hierarchies typically consist of multiple levels, each representing a different level of authority and responsibility. The number of levels may vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. The topmost level usually consists of the executive leadership, including the CEO, CFO, and other C-suite executives. Below them, there are middle managers, department heads, and supervisors, followed by the frontline employees.
Each level of the hierarchy has its own set of responsibilities and decision-making authority. The higher the level, the greater the decision-making power and responsibility. This hierarchical structure helps in maintaining order, streamlining communication, and ensuring accountability within the organization.
Reporting Lines
In a corporate hierarchy, reporting lines define the flow of information and decision-making within the organization. Each employee reports to a higher-level manager, who in turn reports to their respective manager. This creates a chain of command that facilitates the efficient flow of information and ensures that decisions are made at the appropriate levels.
Reporting lines also help in establishing accountability and clarifying roles and responsibilities. Employees know who they report to and who they can seek guidance from. This clear reporting structure minimizes confusion and ensures that everyone is aware of their role in achieving the organization’s goals.
Communication Channels
Effective communication is crucial for the smooth functioning of a corporate hierarchy. Communication channels refer to the various methods and channels through which information is shared within the organization. These channels can include face-to-face meetings, emails, memos, phone calls, and digital collaboration tools.
The structure of corporate hierarchy influences the communication channels used within the organization. For example, top-level executives may communicate through formal meetings and emails, while frontline employees may rely more on face-to-face interactions and team meetings. It is important to establish clear communication channels to ensure that information flows efficiently and effectively throughout the organization.
Conclusion
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clear reporting lines | Potential for bureaucracy |
| Defined roles and responsibilities | Potential for lack of flexibility |
| Efficient decision-making | Potential for communication gaps |
| Accountability | Potential for power struggles |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
