Commercial Paper: Definition
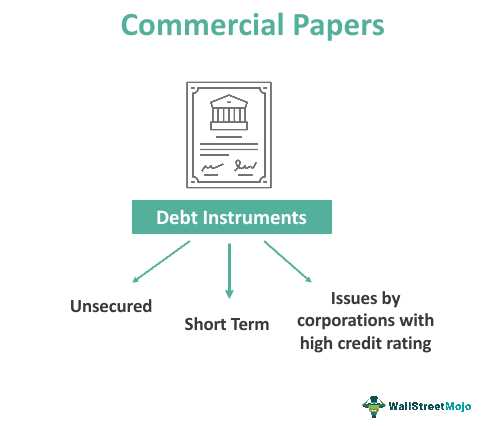
Commercial paper is a short-term debt instrument issued by corporations, financial institutions, and government entities to meet their short-term financing needs. It is typically issued for a period of 1 to 270 days, with the most common maturity being 30 to 60 days.
Characteristics of Commercial Paper
- Unsecured: Commercial paper is typically unsecured, meaning that it is not backed by any collateral. Issuers rely on their creditworthiness and reputation to attract investors.
- Low Denomination: Commercial paper is usually issued in low denominations, making it accessible to a wide range of investors.
- Discounted: Commercial paper is issued at a discount to its face value, and investors earn a return by holding the instrument until maturity.
- High Credit Quality: Commercial paper is generally issued by entities with high credit ratings, reducing the risk of default.
Uses of Commercial Paper
Commercial paper is used by companies and other entities to finance their short-term operational needs, such as funding payroll, purchasing inventory, or covering accounts payable. It provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional bank loans and lines of credit.
Investing in Commercial Paper
Investors can participate in the commercial paper market by purchasing these instruments directly from issuers or through brokers. While commercial paper offers relatively low yields compared to other fixed-income investments, it is considered a safe and liquid investment option.
Overall, commercial paper plays a crucial role in the functioning of the financial markets, providing a flexible and efficient source of short-term funding for businesses and investment opportunities for investors.
Commercial paper is a short-term debt instrument that is issued by corporations, financial institutions, and other entities to meet their short-term funding needs. It is typically issued for a period of 1 to 270 days and is considered a low-risk investment option.
Features of Commercial Paper

Commercial paper is characterized by the following features:
- Maturity: Commercial paper has a fixed maturity date, which is the date on which the issuer must repay the principal amount to the investor.
- Discount: Commercial paper is typically issued at a discount to its face value, which means that investors can purchase it at a price lower than the face value. The difference between the face value and the purchase price represents the investor’s return.
- Unsecured: Commercial paper is usually unsecured, which means that it is not backed by any collateral. However, it is considered a low-risk investment due to the creditworthiness of the issuers.
- High Credit Quality: Commercial paper is typically issued by entities with a high credit rating, such as large corporations and financial institutions. This ensures that the risk of default is minimal.
- Liquidity: Commercial paper is a highly liquid investment option, as it can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market before its maturity date.
Uses of Commercial Paper
Commercial paper is used by companies and financial institutions for various purposes, including:
- Meeting short-term funding needs, such as financing working capital requirements or covering temporary cash flow gaps.
- Refinancing existing debt, as commercial paper can provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional bank loans.
- Managing seasonal fluctuations in cash flows, as commercial paper can be issued and repaid based on the company’s changing funding needs.
Risks Associated with Commercial Paper
While commercial paper is generally considered a low-risk investment, there are certain risks associated with it, including:
- Default Risk: There is a risk that the issuer may default on its payment obligations, especially if it experiences financial difficulties or a credit rating downgrade.
- Market Risk: The price of commercial paper can be affected by changes in interest rates and market conditions, which may result in capital losses for investors.
- Liquidity Risk: Although commercial paper is highly liquid, there may be instances where it becomes difficult to sell or find buyers in the secondary market, especially during periods of market stress.
Conclusion
Commercial paper is a valuable tool for companies and financial institutions to meet their short-term funding needs. It offers various benefits, such as low risk, high credit quality, and liquidity. However, investors should be aware of the associated risks and carefully evaluate the creditworthiness of the issuers before investing in commercial paper.
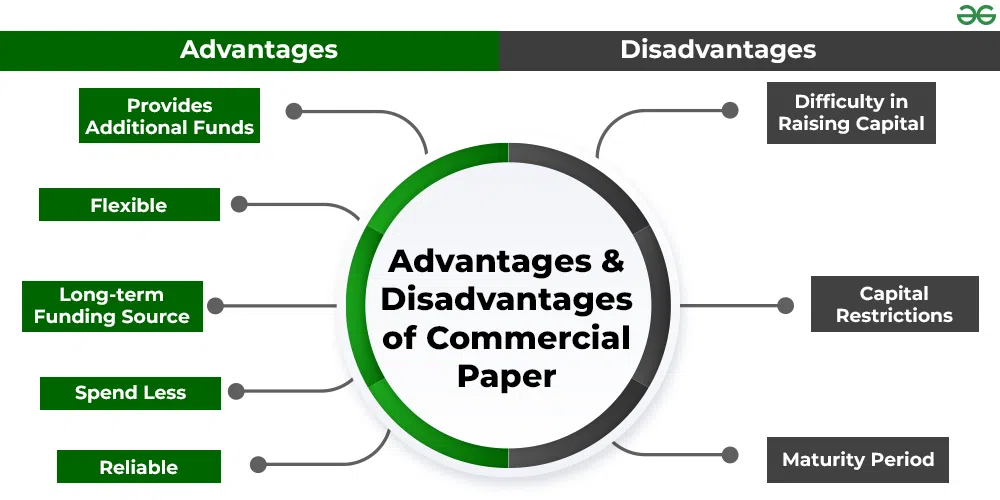
Advantages of Commercial Paper
Commercial paper offers several advantages for both issuers and investors:
- Low Cost: Commercial paper typically offers lower interest rates compared to other forms of short-term financing, making it a cost-effective option for companies in need of funds.
- Flexibility: Commercial paper can be issued for various maturities, ranging from a few days to several months, allowing issuers to tailor their borrowing needs to match their cash flow requirements.
- Quick Access to Funds: Issuing commercial paper is a relatively quick process, allowing companies to access funds quickly when they need them, without going through lengthy loan approval processes.
- Diversification: Investors can diversify their investment portfolios by including commercial paper, which offers an alternative to traditional fixed-income investments like bonds and certificates of deposit.
- High Credit Quality: Commercial paper is typically issued by financially stable and creditworthy companies, making it a relatively safe investment option for investors seeking low-risk opportunities.
- Liquidity: Commercial paper is traded in the secondary market, providing investors with the opportunity to sell their holdings before maturity if they need to access their funds earlier.
Overall, commercial paper provides a convenient and cost-effective financing option for companies while offering investors the opportunity to earn competitive returns with relatively low risk.
Benefits of Commercial Paper
1. Lower Interest Rates
One of the main advantages of commercial paper is that it typically offers lower interest rates compared to other forms of short-term borrowing, such as bank loans. This can result in significant cost savings for businesses that rely on short-term financing.
2. Flexibility
Commercial paper provides issuers with flexibility in terms of the amount and timing of borrowing. Issuers can choose the amount they need to borrow and the maturity date that suits their cash flow needs. This flexibility allows businesses to tailor their financing to their specific requirements.
3. Diversification
Investing in commercial paper allows investors to diversify their portfolios. By including commercial paper in their investment mix, investors can spread their risk across different issuers and industries. This diversification can help mitigate the impact of any potential defaults or credit risks.
4. Liquidity
Commercial paper is highly liquid, meaning it can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market. This liquidity provides investors with the ability to access their funds quickly if needed. It also allows issuers to raise capital efficiently by issuing commercial paper and then repurchasing it when they no longer require the funds.
5. Creditworthiness
Commercial paper is typically issued by large, creditworthy corporations with strong financial positions. Investing in commercial paper allows investors to benefit from the creditworthiness of these issuers. This can provide a level of security and confidence in the investment, particularly for risk-averse investors.
Overall, commercial paper offers a range of benefits, including lower interest rates, flexibility, diversification, liquidity, and the creditworthiness of the issuers. These advantages make commercial paper an attractive option for both issuers and investors seeking short-term financing or investment opportunities.
Example of Commercial Paper
Let’s take a look at an example to better understand how commercial paper works. Imagine a large multinational corporation called XYZ Inc. that needs short-term financing to fund its daily operations. XYZ Inc. decides to issue commercial paper to raise the necessary funds.
XYZ Inc. issues a $1 million commercial paper with a maturity period of 90 days. The commercial paper is sold to various investors, such as banks, mutual funds, and other financial institutions. These investors purchase the commercial paper at a discounted price, let’s say $990,000, which is lower than the face value.
During the 90-day period, the investors hold the commercial paper and earn interest on their investment. At the end of the maturity period, XYZ Inc. repays the investors the full face value of $1 million. The investors earn a profit of $10,000, which is the difference between the discounted price they paid and the face value they received.
This example illustrates how commercial paper provides a convenient and cost-effective way for companies to raise short-term funds. It allows companies to access capital quickly and at a lower cost compared to other financing options. Additionally, investors benefit from earning interest on their investment and can easily trade or sell the commercial paper in the secondary market if they need liquidity before the maturity date.
| Advantages of Commercial Paper | Benefits of Commercial Paper |
|---|---|
| 1. Lower interest rates compared to other forms of short-term financing. | 1. Quick and easy access to capital. |
| 2. Diversification of funding sources. | 2. Cost-effective financing option. |
| 3. Flexibility in terms of maturity periods. | 3. Ability to raise large amounts of funds. |
| 4. High credit quality of issuers. | 4. Potential for profit through discounted purchase and full repayment. |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
