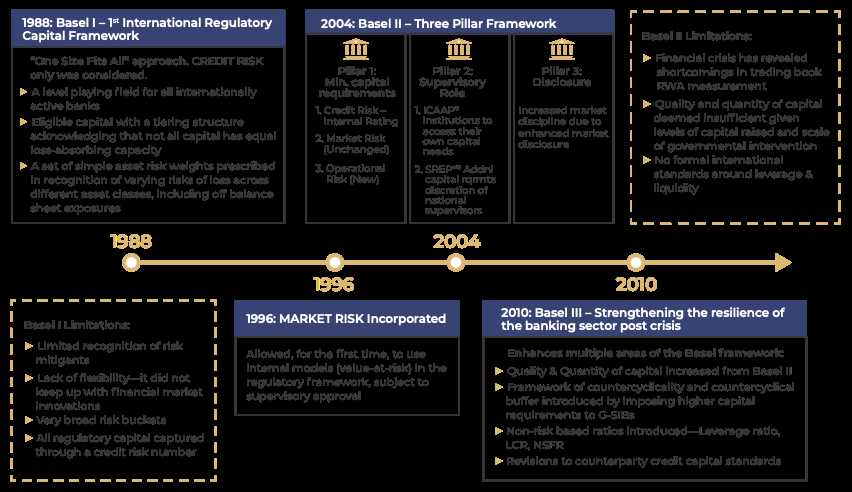
Basel II: Definition, Purpose, and Regulatory Reforms
Basel II is an international regulatory framework that sets out the minimum capital requirements for banks and other financial institutions. It was developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), a committee of banking supervisory authorities from various countries.
Definition
Basel II aims to improve the stability and soundness of the banking system by establishing a more risk-sensitive approach to capital adequacy. It provides a set of guidelines and principles that banks must follow to ensure they have sufficient capital to cover their risks.
Purpose
The main purpose of Basel II is to enhance the ability of banks to withstand financial shocks and reduce the likelihood of systemic banking crises. It seeks to achieve this by aligning capital requirements more closely with the underlying risks faced by banks, thus promoting greater financial stability.
Basel II also aims to encourage banks to adopt better risk management practices and improve their internal controls. By requiring banks to assess and measure their risks more accurately, it helps them identify potential vulnerabilities and take appropriate actions to mitigate them.
Regulatory Reforms
Basel II introduced several regulatory reforms compared to its predecessor, Basel I. One of the key reforms is the adoption of a three-pillar approach, which includes minimum capital requirements, supervisory review, and market discipline.
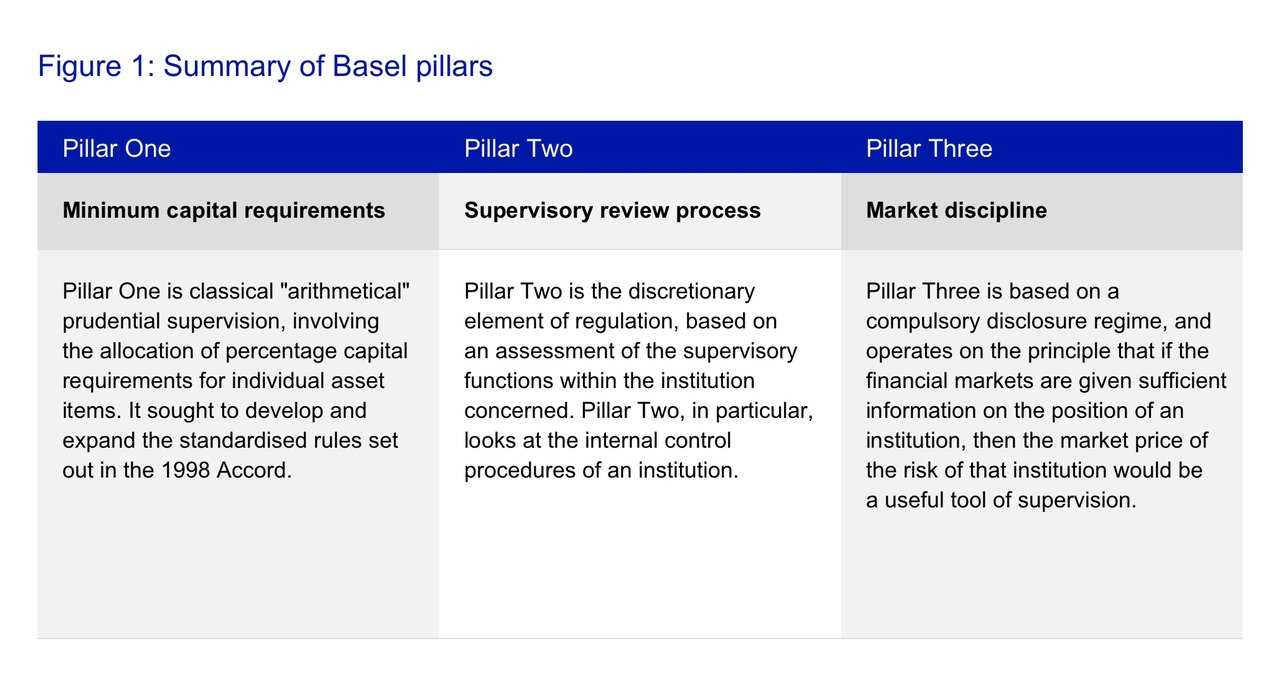
The first pillar sets out the minimum capital requirements that banks must meet based on the risks they face. It classifies risks into credit risk, operational risk, and market risk, and provides specific methodologies for calculating the capital required for each type of risk.
The second pillar emphasizes the importance of supervisory review and evaluation of banks’ risk management practices. It requires supervisors to assess the adequacy of banks’ capital, risk management processes, and internal controls, and take corrective actions if necessary.
The third pillar promotes market discipline by requiring banks to disclose relevant information about their risk profile, capital adequacy, and risk management practices. This allows market participants to make more informed decisions and exert market discipline on banks.
Overall, Basel II represents a significant step forward in the regulation of banks and aims to create a more resilient and stable banking system.
Basel II is an international regulatory framework that sets out the minimum capital requirements for banks and other financial institutions. It was developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), which is a global regulatory body consisting of central banks and banking supervisors from various countries.
The main purpose of Basel II is to enhance the stability and soundness of the banking system by ensuring that banks maintain adequate capital to absorb losses. The framework takes into account the risks that banks face and requires them to hold capital in proportion to those risks.
Basel II introduces a more risk-sensitive approach to capital adequacy compared to its predecessor, Basel I. It classifies risks into three categories: credit risk, market risk, and operational risk. Banks are required to assess and measure these risks using standardized or advanced approaches, depending on their size and complexity.
Under Basel II, banks are also required to have robust risk management systems in place. They must establish processes for identifying, measuring, monitoring, and controlling risks. This includes conducting regular stress tests to assess the impact of adverse events on their capital adequacy.
Another important aspect of Basel II is the supervisory review process. Regulators play a key role in ensuring that banks comply with the framework and have adequate risk management practices. They conduct regular assessments of banks’ capital adequacy and risk management systems, and can impose additional capital requirements or other measures if necessary.
Overall, Basel II is aimed at promoting a more resilient and stable banking system. It seeks to align capital requirements with the risks that banks face and encourages them to adopt sound risk management practices. By doing so, it aims to reduce the likelihood of financial crises and protect depositors and investors.
Purpose of Basel II
Basel II is a set of international banking regulations developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) with the aim of promoting stability and soundness in the global banking system. The primary purpose of Basel II is to establish a framework for banks to assess and manage their risks more effectively.
One of the main goals of Basel II is to improve the risk management practices of banks by requiring them to hold adequate capital to cover their risks. This is achieved through the implementation of a risk-based capital framework, which takes into account the specific risks that banks are exposed to, such as credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
By requiring banks to hold sufficient capital to cover their risks, Basel II aims to reduce the likelihood of bank failures and financial crises. It also aims to enhance the resilience of the banking system by ensuring that banks have enough capital to absorb losses during periods of economic stress.
Another important purpose of Basel II is to promote transparency and disclosure in the banking sector. The regulations require banks to provide more detailed information about their risk management practices, capital adequacy, and risk exposures. This increased transparency allows market participants, regulators, and investors to make more informed decisions and assess the financial health of banks more accurately.
Overall, the purpose of Basel II is to create a more robust and resilient banking system that can withstand financial shocks and contribute to the stability of the global economy. By setting standards for risk management, capital adequacy, and transparency, Basel II aims to foster confidence in the banking sector and promote the efficient allocation of capital.
Key Features of Basel II
Basel II is a set of international banking regulations that aims to improve the stability and soundness of the global financial system. It introduces several key features that banks and financial institutions must adhere to in order to mitigate risks and ensure financial stability.
1. Risk-based Capital Adequacy
One of the main features of Basel II is the implementation of a risk-based capital adequacy framework. Under this framework, banks are required to hold capital in proportion to the risks they undertake. The level of capital required is determined by assessing the credit, market, and operational risks faced by the bank. This ensures that banks have sufficient capital to absorb potential losses and maintain their solvency.
2. Pillar Structure
Basel II follows a three-pillar structure that provides a comprehensive framework for banks to assess and manage risks:
3. Enhanced Risk Management
Basel II emphasizes the importance of robust risk management practices. Banks are required to have comprehensive risk management frameworks in place, including policies, processes, and systems to identify, measure, monitor, and control risks. This includes credit risk assessment, stress testing, and the use of advanced risk models.
4. Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP)
Under Basel II, regulatory authorities are responsible for conducting a Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP) to assess banks’ risk management practices, internal controls, and capital adequacy. This process helps ensure that banks are operating in a safe and sound manner and have sufficient capital to withstand potential risks.
5. International Consistency
Basel II aims to promote international consistency in banking regulations and standards. It provides a common framework that allows for comparability and consistency across different jurisdictions. This helps prevent regulatory arbitrage and ensures a level playing field for banks operating globally.
Overall, Basel II introduces key features that enhance risk management, promote transparency, and improve the stability of the global financial system. By implementing these features, banks can better assess and manage risks, leading to a more resilient and secure banking sector.
Regulatory Reforms under Basel II
Basel II, the international regulatory framework for banks, introduced significant reforms to enhance the stability and soundness of the global banking system. These reforms aimed to address the weaknesses identified in the previous Basel I framework and to ensure that banks have adequate capital to withstand financial shocks.
Under Basel II, regulatory reforms were implemented in several key areas:
- Capital Adequacy: Basel II introduced a more risk-sensitive approach to capital adequacy. Banks are required to hold capital based on the risk profile of their assets, taking into account credit, market, and operational risks. This approach ensures that banks allocate capital more accurately and in line with their risk exposures.
- Supervisory Review Process: Basel II introduced a supervisory review process to ensure that banks’ risk management practices are effective and that they have adequate capital to support their risk profiles. Supervisors are required to conduct regular assessments of banks’ risk management frameworks and capital adequacy, and take corrective actions if necessary.
- Market Discipline: Basel II emphasized the importance of market discipline in promoting transparency and accountability in the banking sector. Banks are required to disclose information on their risk profiles, capital adequacy, and risk management practices to market participants. This enables market participants to make informed decisions and exert market discipline on banks.
- Operational Risk: Basel II introduced a specific framework for managing operational risk, which includes risks arising from internal processes, people, systems, and external events. Banks are required to establish robust operational risk management frameworks and allocate capital to cover potential operational losses.
These regulatory reforms under Basel II aimed to strengthen the resilience of the banking system and enhance its ability to withstand financial shocks. By adopting a more risk-sensitive approach to capital adequacy and emphasizing effective risk management practices, Basel II sought to reduce the likelihood of banking crises and promote the stability of the global financial system.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in Implementing Basel II
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in implementing the Basel II framework. These bodies are responsible for overseeing and enforcing the regulations set forth by Basel II. They ensure that financial institutions comply with the requirements and guidelines outlined in the framework.
One of the main responsibilities of regulatory bodies is to assess the risk management practices of banks and other financial institutions. They evaluate the adequacy of the risk management systems put in place by these institutions to identify, measure, and manage risks. This assessment helps regulatory bodies determine whether banks are following the guidelines set by Basel II.
Regulatory bodies also conduct regular inspections and audits of financial institutions to ensure compliance with Basel II regulations. They review the banks’ risk management processes, internal controls, and capital adequacy. If any discrepancies or violations are found, regulatory bodies have the authority to take appropriate actions, such as imposing fines or penalties.
In addition to monitoring compliance, regulatory bodies provide guidance and support to financial institutions in implementing Basel II. They offer clarifications on the requirements and guidelines, answer questions, and provide training and education to ensure a smooth transition to the new framework.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies collaborate with international counterparts to promote consistency and harmonization in implementing Basel II across different jurisdictions. They participate in international forums and working groups to share best practices, exchange information, and address any challenges or issues that may arise during the implementation process.
Overall, regulatory bodies play a critical role in ensuring the effective implementation of Basel II. Their oversight and enforcement activities help maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system by promoting sound risk management practices and ensuring compliance with international standards.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
