Auction Market: Definition, Trading Process, and Examples
An auction market is a type of financial market where buyers and sellers come together to trade assets through an auction-style process. In an auction market, the price of the asset is determined through competitive bidding, with the highest bidder winning the asset.
The trading process in an auction market typically involves several steps. First, the auction is announced, and potential buyers and sellers are invited to participate. The auction can take place in a physical location, such as a traditional auction house, or it can be conducted online through a digital platform.
During the auction, participants submit their bids for the asset being traded. Bids can be made in various formats, such as a fixed price or a range of prices. The auctioneer or the platform hosting the auction facilitates the bidding process and ensures that all bids are recorded accurately.
Once the auction is concluded, the buyer and seller finalize the transaction. The buyer pays the winning bid amount to the seller, and the seller transfers ownership of the asset to the buyer. This transfer of ownership is typically facilitated through legal documentation and financial settlement.
There are various examples of auction markets in different industries. One common example is the art market, where artworks are sold through auctions. Another example is the real estate market, where properties are often sold through auction processes. Auction markets are also prevalent in the financial industry, with stock exchanges and bond auctions being prime examples.
What is an Auction Market?
An auction market is a type of financial market where buyers and sellers come together to trade assets through an auction process. In an auction market, the price of the asset is determined through competitive bidding. This means that buyers place bids to buy the asset, and sellers place offers to sell the asset. The highest bid and lowest offer are matched, and the trade is executed at that price.
Trading Process in an Auction Market
The trading process in an auction market typically involves the following steps:
- Opening: The auction market opens at a specific time, and buyers and sellers can start placing their bids and offers.
- Bidding: Buyers place bids to buy the asset, indicating the price they are willing to pay. Sellers place offers to sell the asset, indicating the price they are willing to sell at.
- Matching: The auction system matches the highest bid with the lowest offer. If there is a match, a trade is executed at that price.
- Clearing: After the trade is executed, the auction market clears the transaction by transferring ownership of the asset from the seller to the buyer.
- Closing: The auction market closes at a specific time, and no more bids or offers can be placed.
The trading process in an auction market is typically transparent and efficient, as it allows buyers and sellers to see the bids and offers of other participants. This helps to ensure that the market price reflects the true value of the asset based on the collective knowledge and opinions of the participants.
Examples of Auction Markets
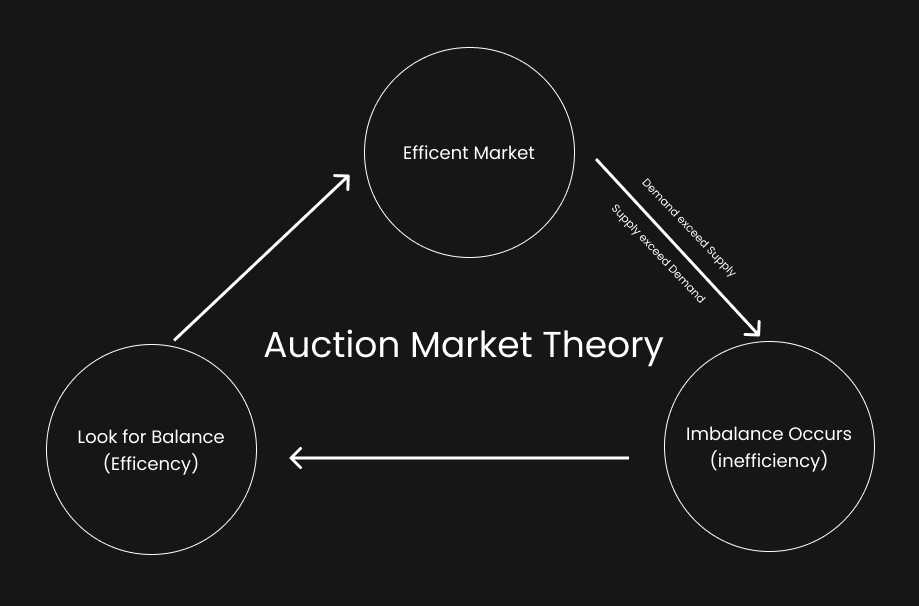
Some examples of auction markets include:
| Market | Asset | Exchange |
|---|---|---|
| Stock Market | Shares of publicly traded companies | New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) |
| Real Estate Market | Properties | Multiple listing service (MLS) |
| Art Market | Artworks | Christie’s, Sotheby’s |
How Does the Trading Process Work?
In an auction market, the trading process involves the buying and selling of goods or services through a competitive bidding system. This system allows buyers and sellers to come together and determine the price at which the transaction will take place.
1. Auction Announcement
The first step in the trading process is the auction announcement. This is when the auction market operator announces the details of the upcoming auction, including the date, time, location, and the items or services that will be up for bidding.
2. Registration

Interested participants must register with the auction market operator to participate in the auction. This registration process may involve providing personal information, paying a registration fee, and agreeing to the terms and conditions of the auction.
3. Bidding
During the auction, participants can place bids on the items or services being auctioned. Bids can be made in person, over the phone, or through an online bidding platform. Bidders can place multiple bids, and the highest bid at any given time becomes the current winning bid.
4. Auctioneer
An auctioneer is responsible for facilitating the bidding process. They announce the current winning bid, accept new bids, and determine when the auction will end. The auctioneer also ensures that the bidding process is fair and transparent.
5. Closing the Auction

Once the auctioneer determines that there are no more bids, they close the auction. The highest bidder at the time of closing is declared the winner and is obligated to complete the transaction by paying the agreed-upon price.
6. Settlement
After the auction is closed, the winning bidder and the seller complete the settlement process. This involves finalizing the payment and transferring ownership of the goods or services. The auction market operator may also collect fees or commissions for facilitating the transaction.
Overall, the trading process in an auction market is designed to create a competitive environment where buyers and sellers can determine fair market prices through open bidding. It provides an efficient and transparent way to conduct transactions and is commonly used in various industries, including art, real estate, and financial markets.
Examples of Auction Markets
There are several well-known examples of auction markets that operate in different industries and sectors. These examples illustrate the diverse range of products and services that can be traded through auction markets.
1. Art Auctions: Art auctions are one of the most famous and glamorous auction markets. These auctions bring together collectors, art enthusiasts, and investors to bid on valuable pieces of artwork. Auction houses like Sotheby’s and Christie’s are renowned for their art auctions.
2. Real Estate Auctions: Real estate auctions are another popular type of auction market. Properties such as houses, commercial buildings, and land are put up for auction, and interested buyers place bids to secure the property. Real estate auctions can be a great way to buy or sell properties quickly and efficiently.
3. Online Auctions: With the rise of the internet, online auctions have become increasingly popular. Platforms like eBay and Amazon Auctions allow individuals and businesses to buy and sell a wide range of products, from electronics to collectibles. Online auctions offer convenience and accessibility to a global audience.
4. Government Auctions: Government auctions are organized by government agencies to sell surplus items, confiscated goods, and other assets. These auctions can include vehicles, equipment, furniture, and even real estate. Government auctions provide an opportunity for individuals and businesses to acquire items at a lower cost.
6. Charity Auctions: Charity auctions are held to raise funds for charitable organizations. These auctions often feature unique experiences, luxury items, and celebrity memorabilia. Bidders participate in the auction with the intention of supporting a cause and acquiring a valuable item or experience.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and widespread use of auction markets across various industries. Whether it’s art, real estate, online products, government assets, stocks, or charity items, auction markets provide a transparent and efficient way to trade goods and services.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
