What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite measure of human development that takes into account various factors such as life expectancy, education, and income. It was developed by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) as a way to assess and compare the development levels of different countries.
The HDI is based on the idea that development should be measured not only by economic indicators, but also by social and human factors. It provides a more comprehensive picture of a country’s development by considering indicators that reflect the well-being of its people.
The three dimensions of human development that the HDI takes into account are:
- Life expectancy at birth: This indicator measures the average number of years a person is expected to live from birth. It reflects the overall health and healthcare system of a country.
- Educational attainment: This indicator measures the average number of years of education that a person aged 25 or older has received. It reflects the level of education and knowledge within a country.
- Income per capita: This indicator measures the average income per person in a country. It reflects the economic well-being and standard of living.
Each of these dimensions is given equal weight in the calculation of the HDI. The HDI ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 being the highest level of human development.
The HDI is widely used by policymakers, researchers, and development practitioners to assess the progress of countries in achieving human development goals. It provides a useful tool for comparing the development levels of different countries and identifying areas for improvement.
Overall, the Human Development Index (HDI) is an important measure that goes beyond economic indicators to provide a more holistic view of a country’s development. It helps to highlight the importance of investing in healthcare, education, and income equality in order to improve the well-being of people around the world.
How is the Human Development Index (HDI) calculated?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite measure that takes into account three key dimensions of human development: health, education, and income. It provides a comprehensive overview of a country’s overall development and well-being of its population.
To calculate the HDI, several indicators are used to measure each dimension:
1. Health:
The health dimension is measured using life expectancy at birth. This indicator reflects the average number of years a newborn is expected to live, taking into account factors such as healthcare access, disease prevalence, and overall quality of life.
2. Education:
The education dimension is measured using two indicators: mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling. Mean years of schooling represents the average number of years of education received by adults aged 25 and older, while expected years of schooling represents the number of years of education a child is expected to receive, taking into account enrollment rates.
3. Income:
The income dimension is measured using gross national income (GNI) per capita, which reflects the average income of a country’s residents. GNI includes income from both domestic and foreign sources, providing a more comprehensive measure of economic well-being.
Once the indicators for each dimension are calculated, they are normalized using a minimum-maximum approach to ensure comparability across countries. The normalized values are then combined using a geometric mean to calculate the HDI score, which ranges from 0 to 1. A higher score indicates a higher level of human development.
The HDI calculation is updated annually to reflect changes in indicators and to provide an up-to-date assessment of human development worldwide. It allows policymakers, researchers, and the general public to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement in different countries.
| Dimension | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Health | Life expectancy at birth |
| Education | Mean years of schooling |
| Education | Expected years of schooling |
| Income | Gross national income (GNI) per capita |
Overall, the HDI provides a comprehensive and standardized measure of human development, allowing for comparisons across countries and over time. It helps policymakers and stakeholders make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively to improve the well-being of their populations.
The Importance of the Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a crucial tool that measures the overall development and well-being of a country’s population. It provides a comprehensive assessment of a nation’s progress in terms of education, healthcare, and standard of living. The HDI takes into account various factors that contribute to human development, such as life expectancy, education level, and income per capita.
Measuring Human Development
The HDI is calculated by combining three key dimensions of human development: health, education, and income. These dimensions are represented by three indicators: life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, and gross national income per capita. By considering these dimensions and indicators, the HDI provides a more holistic view of a country’s development compared to traditional economic measures, such as GDP.
Health: Life expectancy at birth is a crucial indicator of a population’s overall health and well-being. It reflects the access to healthcare services, quality of healthcare, and overall living conditions. Countries with higher life expectancies generally have better healthcare systems and higher standards of living.
Education: Mean years of schooling is an indicator of the education level within a country. It takes into account both the quantity and quality of education received by individuals. Access to education is essential for personal development, social mobility, and economic growth. Higher levels of education are associated with better employment opportunities and higher income levels.
Income: Gross national income per capita measures the economic well-being of a country’s population. It reflects the average income earned by individuals and households within a nation. Higher income levels indicate a higher standard of living, better access to basic needs, and greater economic opportunities.
For example, if a country has a high HDI score but low life expectancy, it indicates that improvements are needed in the healthcare system. This could involve investing in healthcare infrastructure, improving access to healthcare services, and addressing public health issues.
Similarly, if a country has a high HDI score but low mean years of schooling, it highlights the need for educational reforms. This could include increasing access to quality education, improving the curriculum, and investing in teacher training.
Advocating for Human Development

The HDI plays a crucial role in advocating for human development on a global scale. It provides a comparative measure of development across countries, allowing policymakers and international organizations to identify best practices and learn from successful cases. It also helps in monitoring progress over time and evaluating the effectiveness of development policies and interventions.
Furthermore, the HDI serves as a powerful tool for raising awareness about development disparities and promoting social and economic justice. It highlights the importance of investing in human capital and ensuring equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their socio-economic background.
Why is the Human Development Index (HDI) important?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is an essential tool for measuring and comparing the overall development and well-being of countries. It provides a comprehensive assessment of a nation’s progress by considering factors such as life expectancy, education, and income.
Measuring Development
The HDI takes into account multiple dimensions of human development, providing a more holistic view than traditional economic indicators like GDP. By considering factors such as health, education, and income, the HDI captures the overall quality of life experienced by individuals within a country.
Unlike purely economic measures, the HDI recognizes that development is not solely about wealth accumulation but also about ensuring that people have access to basic necessities and opportunities for growth. It acknowledges that a high GDP does not necessarily translate into improved well-being for all citizens.
Comparing Countries
The HDI allows for meaningful comparisons between countries, enabling policymakers and researchers to identify trends, patterns, and disparities in human development. By ranking countries based on their HDI scores, it provides a clear picture of which nations are making progress and which ones need improvement.
Promoting Equity and Social Justice
By focusing on the well-being of all individuals, including marginalized groups and vulnerable populations, the HDI encourages policymakers to design inclusive policies and programs that promote equal opportunities and reduce inequality.
Furthermore, the HDI serves as a powerful advocacy tool for human rights organizations and civil society groups. It enables them to hold governments accountable for their commitments to improve human development and to advocate for policies that prioritize the well-being of all citizens.
How does the Human Development Index (HDI) impact policy-making?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a crucial tool that impacts policy-making at both national and international levels. It provides policymakers with valuable insights into the overall well-being and development of a country’s population, allowing them to make informed decisions and prioritize areas that require attention and improvement.
1. Identifying Development Priorities
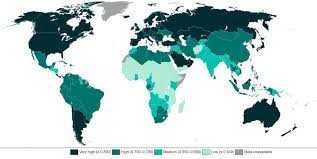
The HDI helps policymakers identify the key areas where development efforts should be focused. By considering factors such as life expectancy, education, and income, the index highlights the areas where a country may be lagging behind and requires policy interventions. For example, if the HDI reveals a low level of education in a particular region, policymakers can allocate resources to improve educational infrastructure and increase access to quality education.
2. Monitoring Progress
The HDI serves as a monitoring tool for policymakers to assess the effectiveness of their policies and programs. By regularly measuring the HDI, policymakers can track the progress made in various development indicators over time. This allows them to evaluate the impact of their policies and make necessary adjustments if the desired outcomes are not being achieved. It also helps in setting realistic targets and benchmarks for future development goals.
3. International Comparisons
The HDI enables policymakers to compare their country’s development performance with that of other nations. This international benchmarking provides valuable insights into the relative strengths and weaknesses of a country’s development efforts. Policymakers can learn from the experiences of countries with higher HDI rankings and adopt successful strategies to improve their own development outcomes. It also helps in identifying best practices and promoting international cooperation for sustainable development.
4. Advocacy and Resource Allocation
The HDI plays a crucial role in advocating for increased resources and support for development initiatives. A low HDI ranking can draw attention to the urgent needs of a country and attract international aid and investment. Policymakers can use the HDI as a persuasive tool to mobilize resources and secure funding for projects aimed at improving the well-being of their population. It also helps in prioritizing resource allocation within a country, ensuring that limited resources are directed towards areas that have the greatest impact on human development.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
