What is Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT)?
Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT) is a financial metric that measures a company’s operating profit after adjusting for taxes. It is a key component in evaluating a company’s financial performance and profitability.
NOPLAT is calculated by subtracting adjusted taxes from operating profit. Adjusted taxes are calculated by multiplying the company’s effective tax rate by its operating profit. This adjustment is made to account for any tax benefits or expenses that are not reflected in the company’s financial statements.
NOPLAT is an important measure because it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s profitability than traditional net income. By adjusting for taxes, NOPLAT allows investors and analysts to compare the profitability of companies in different tax jurisdictions and industries.
NOPLAT is often used in financial statement analysis to calculate other key financial ratios and metrics, such as return on invested capital (ROIC) and economic value added (EVA). These metrics provide insights into a company’s ability to generate profits and create value for its shareholders.
Definition and Calculation of Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT)
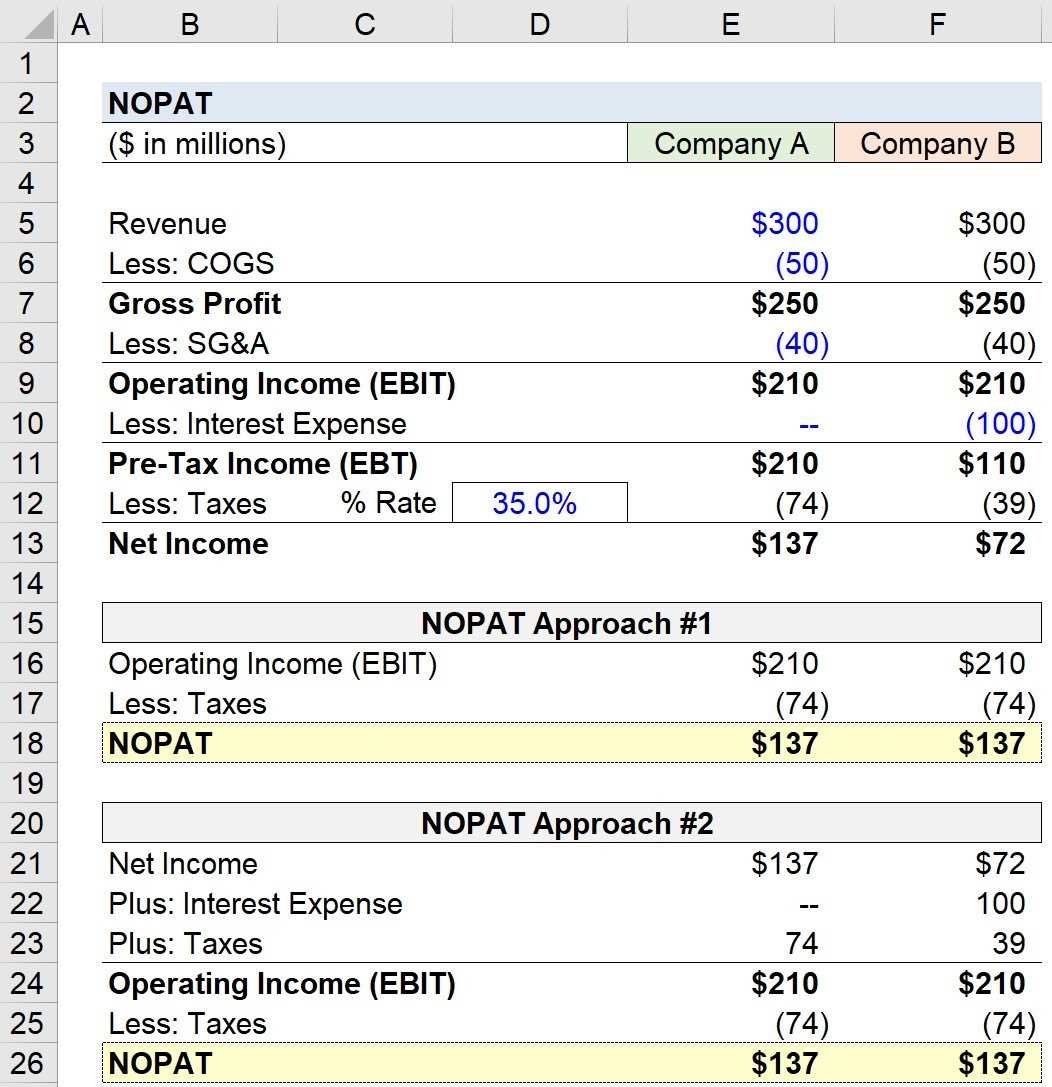
Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT) is a financial metric that measures a company’s profitability by calculating its operating profit after adjusting for taxes. It provides a clearer picture of a company’s operating performance by excluding the impact of taxes.
The calculation of NOPLAT involves subtracting the adjusted taxes from the operating profit. Adjusted taxes are calculated by multiplying the company’s effective tax rate by its operating profit. The effective tax rate is the average tax rate paid by the company, taking into account any tax deductions or credits.
For example, if a company has an operating profit of $1,000,000 and an effective tax rate of 30%, the calculation of NOPLAT would be:
NOPLAT is an important measure in financial statements as it provides a more accurate representation of a company’s profitability. By excluding the impact of taxes, it allows investors and analysts to compare the operating performance of different companies on a more equal basis.
Importance of NOPLAT in Financial Statements
Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT) is a crucial metric in financial statements as it provides valuable insights into a company’s operational profitability. By excluding the effects of taxes and non-operating items, NOPLAT allows investors and analysts to focus solely on the core operating performance of a business.
One of the key advantages of using NOPLAT is its ability to provide a more accurate representation of a company’s profitability compared to traditional net income. Net income can be distorted by various factors, such as tax expenses, one-time gains or losses, and non-operating items like interest income or expenses. By eliminating these factors, NOPLAT provides a clearer picture of a company’s underlying profitability.
NOPLAT is particularly useful for comparing the performance of companies operating in different tax jurisdictions. Taxes can significantly impact a company’s net income, especially when operating in countries with high tax rates. By focusing on NOPLAT, investors can make more meaningful comparisons between companies and assess their operational efficiency without the distortion caused by varying tax rates.
Furthermore, NOPLAT is a valuable tool for assessing a company’s ability to generate sustainable profits. By analyzing the trend of NOPLAT over time, investors can evaluate whether a company’s profitability is improving, declining, or remaining stable. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions and identifying potential risks or opportunities.
Limitations and Criticisms of NOPLAT
While Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes (NOPLAT) is a useful financial metric for evaluating a company’s profitability, it is not without its limitations and criticisms. It is important to consider these factors when using NOPLAT as a measure of a company’s financial performance.
1. Exclusion of Non-operating Items
One of the main criticisms of NOPLAT is that it excludes non-operating items from the calculation. Non-operating items, such as gains or losses from the sale of assets or investments, can have a significant impact on a company’s overall profitability. By excluding these items, NOPLAT may not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health.
2. Reliance on Financial Statements
NOPLAT is calculated based on information from a company’s financial statements, which are subject to manipulation and accounting practices. Companies can use various accounting techniques to inflate or deflate their reported profits, which can distort the accuracy of NOPLAT as a measure of true profitability.
3. Lack of Industry-specific Factors
4. Ignoring the Time Value of Money
NOPLAT does not consider the time value of money, which is the concept that money today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future. By ignoring the time value of money, NOPLAT may not accurately reflect the true economic value of a company’s profits.
5. Lack of Context

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
