Ethereum’s Blockchain Technology
Ethereum’s blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records all transactions and smart contracts on the Ethereum network. It is a key component of the Ethereum platform, providing a secure and transparent way to store and verify data.
Each transaction on the Ethereum blockchain is grouped into blocks, which are then added to the chain in a chronological order. This ensures that the entire history of transactions is preserved and can be audited by anyone. Additionally, the blockchain provides a high level of security, as each block is linked to the previous one through cryptographic hashes.
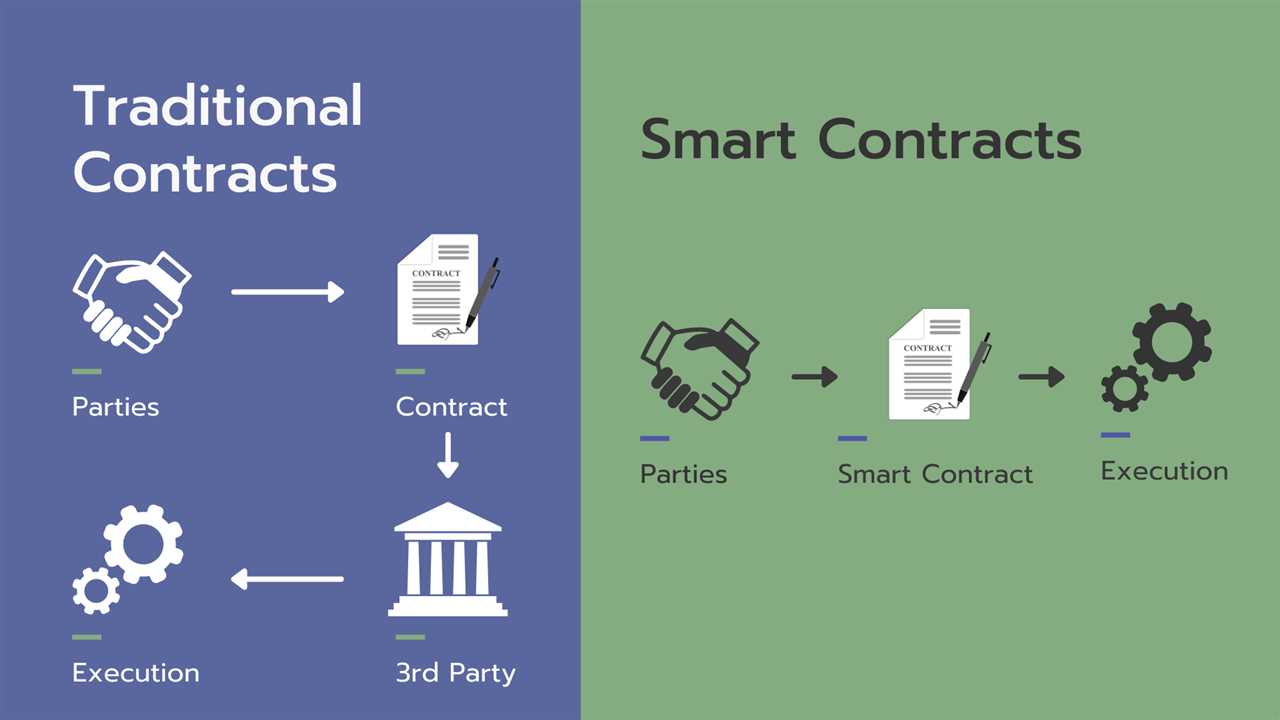
One of the key features of Ethereum’s blockchain technology is its ability to support smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute when certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud.
Ethereum’s blockchain technology also enables the development of decentralized applications (DApps). DApps are applications that run on the Ethereum network and are not controlled by any single entity. They provide a wide range of functionalities, including financial services, gaming, and decentralized exchanges.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)

Smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) are two of the key features that make Ethereum stand out in the blockchain space. These innovative technologies have the potential to revolutionize various industries and transform the way we interact with digital services.
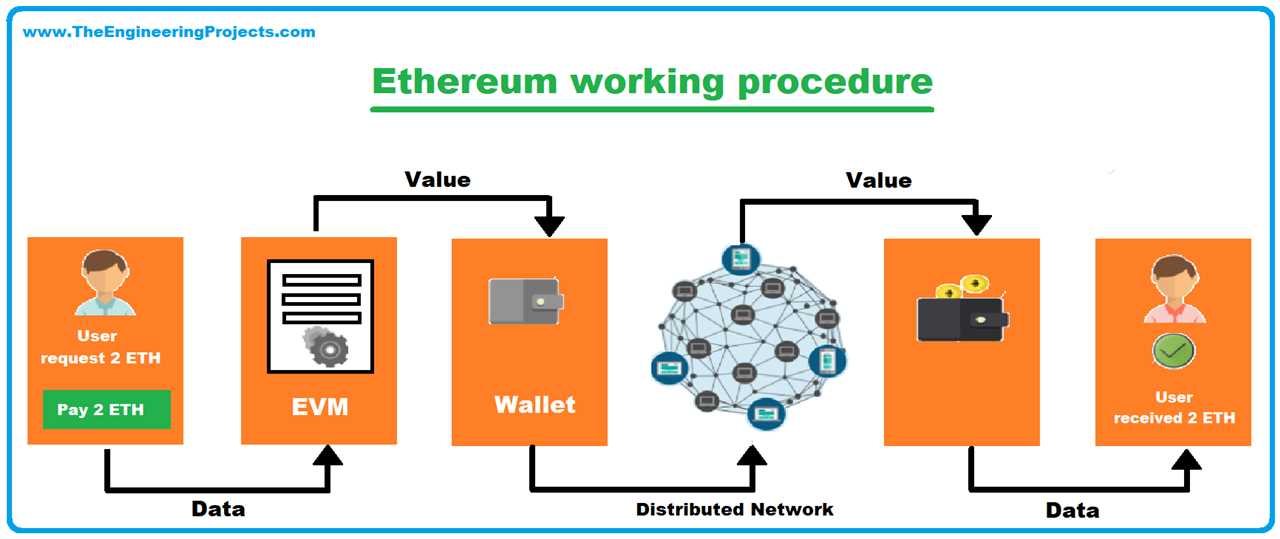
Ethereum’s smart contracts are powered by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a decentralized runtime environment that executes the code of smart contracts. This allows developers to create and deploy their own smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, opening up a world of possibilities for creating decentralized applications.
Decentralized applications, or DApps, are applications that run on a decentralized network, such as Ethereum. These applications are not controlled by a single entity or authority, making them resistant to censorship and single points of failure. DApps leverage the power of smart contracts to provide transparent, secure, and trustless services to users.
One of the most well-known examples of a DApp built on Ethereum is CryptoKitties, a game where users can buy, sell, and breed virtual cats. Each cat is represented by a unique token on the Ethereum blockchain, and the breeding process is governed by smart contracts. This showcases the potential of DApps to disrupt traditional industries and create new forms of digital assets and experiences.
Furthermore, Ethereum’s decentralized nature allows for the interoperability of DApps. This means that different DApps can interact with each other, enabling the creation of complex systems and ecosystems. For example, a decentralized finance (DeFi) DApp can interact with an NFT marketplace DApp, allowing users to use their NFTs as collateral for loans.
Ethereum’s Consensus Mechanism and Mining

Ethereum, like many other blockchain platforms, relies on a consensus mechanism to validate and secure transactions on its network. The consensus mechanism used by Ethereum is called “Proof of Work” (PoW).
Mining on the Ethereum network involves using specialized hardware, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), to perform the necessary calculations. The computational power required for mining has increased significantly over the years, leading to the emergence of large-scale mining operations.
Proof of Stake works differently from Proof of Work. Instead of miners competing to solve mathematical problems, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. Validators are selected randomly, and their chances of being chosen are proportional to the amount of cryptocurrency they hold.
The shift to Proof of Stake is expected to make the Ethereum network more environmentally friendly and reduce the reliance on energy-intensive mining operations. It will also allow for faster transaction processing and lower fees.
Overall, Ethereum’s consensus mechanism and mining play a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of the network. The transition to Proof of Stake is an important milestone for Ethereum, as it aims to address some of the scalability and energy consumption challenges associated with Proof of Work.
The Future of Ethereum and its Impact on the ALTCOINS Market
Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, has been making waves in the world of blockchain technology. With its smart contract functionality and decentralized applications (DApps), Ethereum has revolutionized the way we think about digital transactions and the potential for blockchain technology.
But what does the future hold for Ethereum? And how will its evolution impact the ALTCOINS market?
One of the most exciting developments on the horizon for Ethereum is the implementation of Ethereum 2.0. This upgrade aims to address some of the scalability issues that have plagued the network, allowing for faster and more efficient transactions. With Ethereum 2.0, the network will transition from a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism, which will significantly reduce the energy consumption associated with mining.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
