What is Ulcer Index?
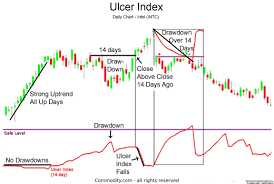
The Ulcer Index (UI) is a technical indicator that measures the downside volatility and risk of an investment or portfolio. It was developed by Peter Martin in the 1980s as a way to quantify the level of discomfort or pain that an investor may experience during a drawdown period.
The Ulcer Index takes into account both the magnitude and duration of drawdowns, providing a more comprehensive measure of risk compared to other volatility indicators such as standard deviation or beta. It is particularly useful for long-term investors who are more concerned with protecting their capital and minimizing losses rather than maximizing returns.
The Ulcer Index is calculated by first determining the percentage drawdown from the highest point of the investment value to any subsequent point in time. The squared values of these drawdown percentages are then summed over a specified period, typically 14 days. Finally, the sum is divided by the number of days in the period and then square rooted to obtain the Ulcer Index value.
A lower Ulcer Index value indicates a lower level of risk and volatility, while a higher value suggests a higher level of risk and potential for larger drawdowns. By monitoring the Ulcer Index, investors can gain insights into the stability and riskiness of their investments and make informed decisions about risk management.
It is important to note that the Ulcer Index is just one tool in a comprehensive risk management strategy and should be used in conjunction with other indicators and analysis techniques. It is not a standalone measure of risk and should be interpreted in the context of the specific investment or portfolio being analyzed.
Utilizing Ulcer Index for Risk Management
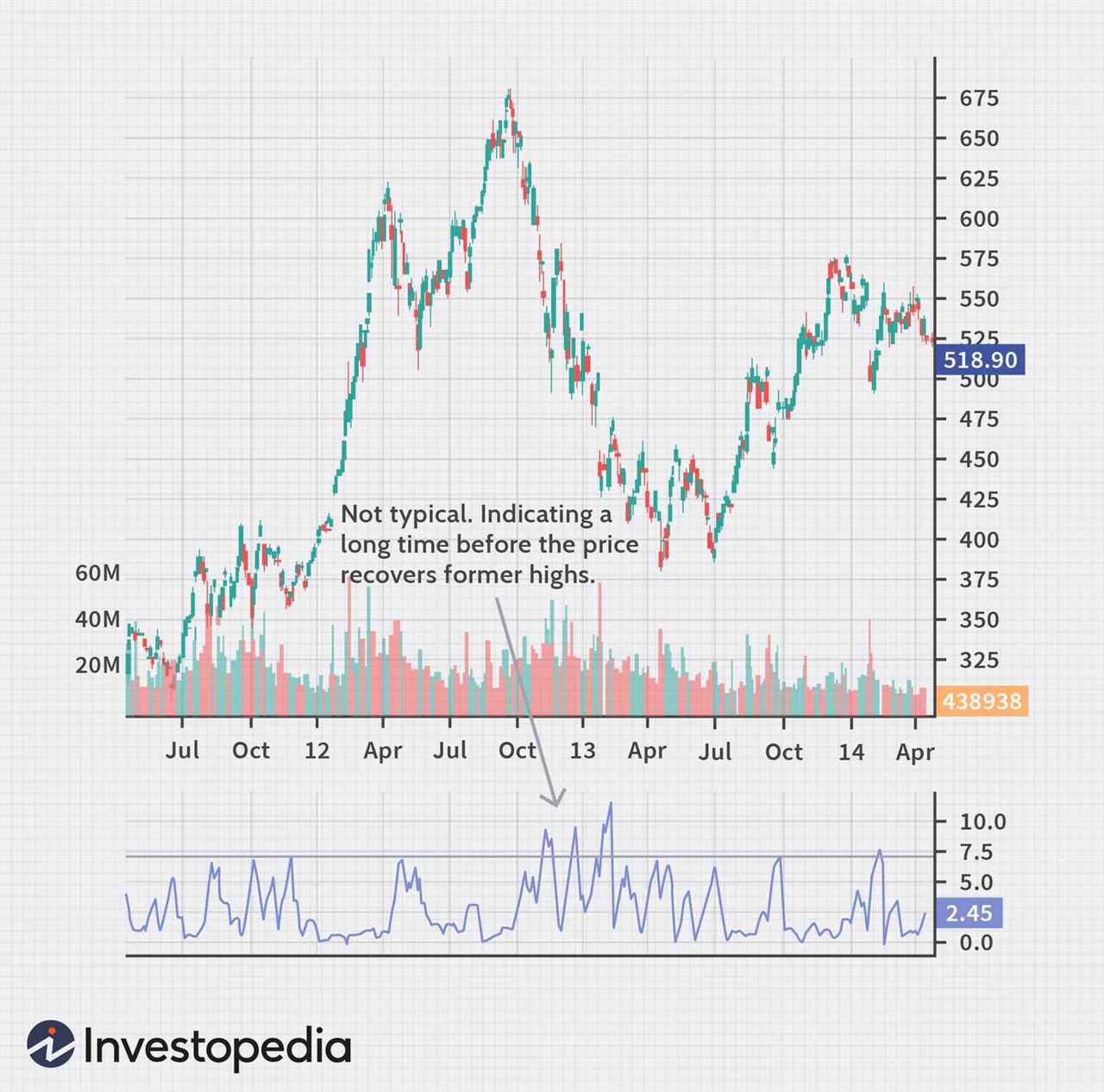
The Ulcer Index (UI) is a technical analysis tool that measures the downside risk of an investment or portfolio. It was developed by Peter Martin in the 1980s and is widely used by traders and investors to assess the volatility and potential drawdown of their holdings.
The UI is calculated by taking the square root of the average of the squared percentage drawdowns over a specified period of time. It provides a more accurate measure of risk compared to traditional volatility measures like standard deviation because it focuses on the magnitude and duration of losses rather than just the overall price movement.
By utilizing the Ulcer Index, investors can gain valuable insights into the potential downside risk of their investments. This information can be used to make informed decisions about portfolio allocation, risk management strategies, and position sizing.
One way to utilize the Ulcer Index is to set a threshold level for acceptable risk. For example, an investor may decide that they are comfortable with a maximum drawdown of 10%. By monitoring the Ulcer Index of their holdings, they can take action if the index exceeds this threshold. This could involve reducing exposure to high-risk assets or implementing hedging strategies to protect against potential losses.
Another way to use the Ulcer Index is to compare the risk profiles of different investments or portfolios. By calculating the Ulcer Index for each investment option, investors can identify which ones have a lower risk profile and may be more suitable for their risk tolerance. This can be particularly useful when constructing a diversified portfolio.
It is important to note that the Ulcer Index is just one tool in a comprehensive risk management strategy. It should be used in conjunction with other indicators and analysis techniques to make well-informed investment decisions.
| Advantages of Utilizing Ulcer Index for Risk Management |
|---|
| Provides a more accurate measure of downside risk compared to traditional volatility measures |
| Helps investors set threshold levels for acceptable risk |
| Allows for comparison of risk profiles between different investments or portfolios |
| Can be used to inform portfolio allocation and risk management strategies |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
