What is Trade Deficit?
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. It is a measure of the imbalance between a nation’s imports and exports, indicating that the country is spending more on foreign goods and services than it is earning from its own exports.
The trade deficit is calculated by subtracting the value of a country’s exports from the value of its imports. If the result is negative, it means that the country has a trade deficit. This deficit can be caused by various factors, such as a lack of competitiveness in domestic industries, high levels of consumer spending, or government policies that encourage imports.
Trade deficits can have both positive and negative impacts on an economy. On one hand, they can indicate a strong domestic demand for foreign goods and services, which can stimulate economic growth. On the other hand, persistent trade deficits can lead to a loss of domestic jobs and industries, as well as an increase in foreign debt.
Examples of trade deficits can be seen in countries like the United States, which has consistently imported more goods than it exports for many years. This has led to debates about the impact of trade deficits on domestic industries and employment.
Definition of Trade Deficit

A trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed its exports during a specific period of time. It is a key indicator of the economic health and competitiveness of a nation in international trade. The trade deficit is calculated by subtracting the value of a country’s exports from the value of its imports.
Trade deficits can occur for various reasons, including a country’s domestic consumption patterns, exchange rates, and global economic conditions. When a country has a trade deficit, it means that it is spending more on foreign goods and services than it is earning from selling its own goods and services abroad.
Trade deficits can have both positive and negative effects on an economy. On one hand, a trade deficit can indicate strong domestic demand and consumption, which can stimulate economic growth. It can also provide consumers with a wider variety of goods and services at competitive prices.
On the other hand, a persistent trade deficit can also be a cause for concern. It can lead to a loss of domestic jobs and industries, as well as a decline in the country’s overall competitiveness. It can also contribute to a growing national debt and dependence on foreign borrowing.
Examples of countries with significant trade deficits include the United States, which has had a long-standing trade deficit with China, and the United Kingdom, which has seen its trade deficit widen in recent years.
Causes of Trade Deficit
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. There are several factors that can contribute to a trade deficit:
1. Economic Factors: A country’s economic conditions can play a significant role in causing a trade deficit. For example, if a country experiences a recession or slow economic growth, it may lead to a decrease in domestic demand for goods and services. This can result in increased imports and a trade deficit.
2. Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can also impact a country’s trade balance. If a country’s currency depreciates relative to other currencies, its exports become cheaper, while imports become more expensive. This can lead to an increase in imports and a trade deficit.
3. Comparative Advantage: Trade deficits can also be caused by a country’s comparative advantage in certain industries. For example, if a country has a strong comparative advantage in producing certain goods, it may import more of those goods from other countries, leading to a trade deficit.
5. Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences can also influence trade deficits. If consumers in a country prefer to buy imported goods over domestically produced goods, it can lead to an increase in imports and a trade deficit.
Overall, trade deficits can be caused by a combination of economic, exchange rate, comparative advantage, government policy, and consumer preference factors. It is important for policymakers to carefully analyze these factors and implement appropriate measures to address trade deficits and promote a more balanced trade environment.
Impact of Trade Deficit
The impact of a trade deficit on an economy can be both positive and negative. It is important to understand the various effects it can have on different aspects of an economy.
1. Employment: A trade deficit can lead to job losses in certain industries. When a country imports more goods than it exports, it means that domestic industries are not able to compete effectively. This can result in layoffs and unemployment in those industries. However, it is important to note that a trade deficit does not necessarily mean a loss of jobs overall, as it can also lead to job gains in other sectors.
2. Domestic Industries: A trade deficit can also have a negative impact on domestic industries. When a country relies heavily on imports, it can lead to a decline in the production and competitiveness of domestic industries. This can hinder the growth and development of key sectors of the economy.
3. Currency Depreciation: A trade deficit can put pressure on a country’s currency. When a country imports more than it exports, it means that it is spending more foreign currency than it is earning. This can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency, making imports more expensive and exports more competitive. However, a depreciated currency can also make a country’s exports more attractive to foreign buyers, which can help to reduce the trade deficit.
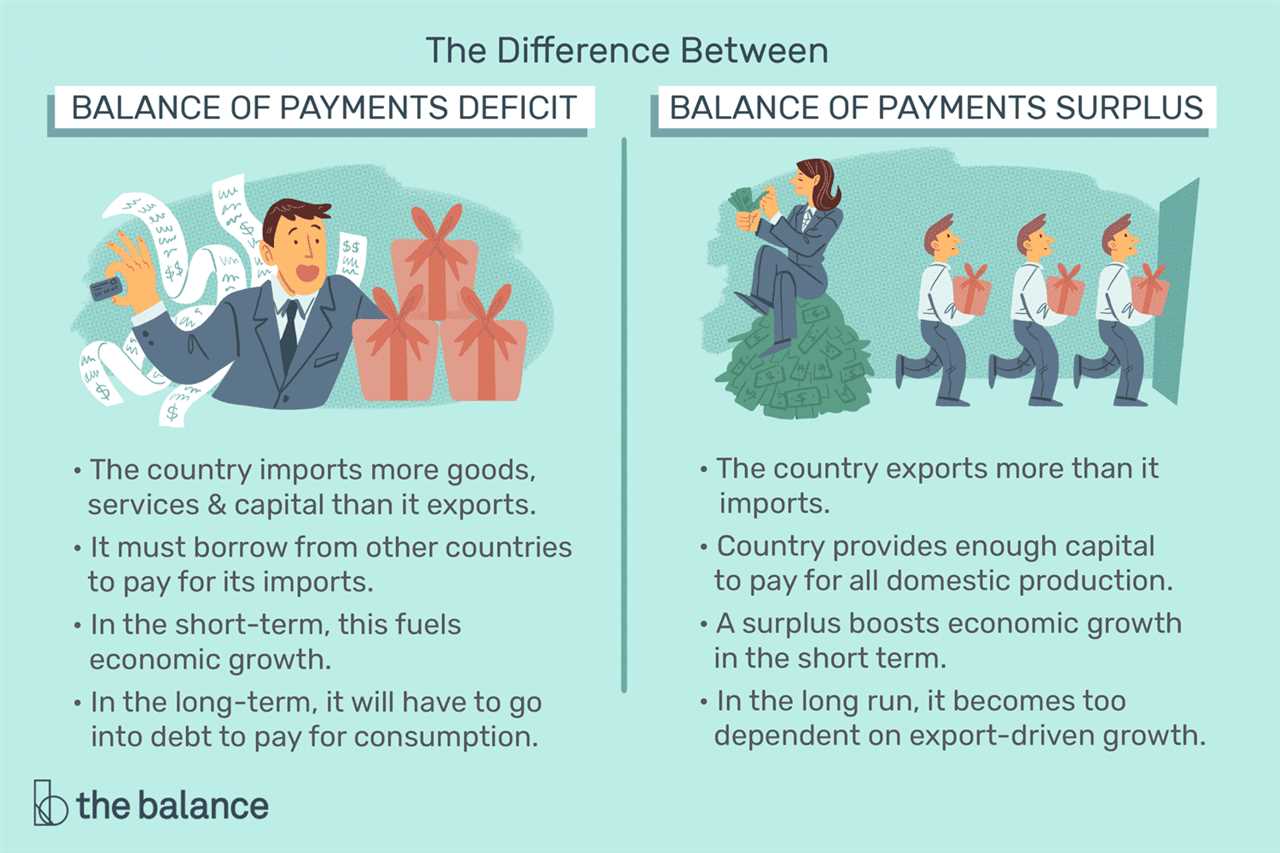
4. Balance of Payments: A trade deficit contributes to a country’s balance of payments deficit. The balance of payments is a record of all the transactions between a country and the rest of the world. A trade deficit means that a country is spending more on imports than it is earning from exports, which can result in a deficit in the overall balance of payments. This can have implications for a country’s financial stability and ability to borrow from foreign sources.
5. Economic Growth: A trade deficit can impact a country’s overall economic growth. While a trade deficit can lead to job losses and hinder the growth of domestic industries, it can also stimulate economic growth in other ways. For example, imports can provide consumers with a wider variety of goods at lower prices, which can increase consumer spending and stimulate economic activity. Additionally, a trade deficit can also attract foreign investment, which can contribute to economic growth.
Examples of Trade Deficit
Trade deficits can occur in various countries and industries around the world. Here are some examples of trade deficits and their impacts:
1. United States
The United States has been experiencing a significant trade deficit for many years. In 2020, the trade deficit reached $678.7 billion, the highest level since 2008. The main contributors to the trade deficit are imports of consumer goods, such as electronics, clothing, and automobiles, from countries like China, Mexico, and Germany. The trade deficit has led to concerns about job losses in domestic industries and the competitiveness of American businesses.
2. United Kingdom

The United Kingdom also faces a trade deficit, primarily due to its reliance on imports of goods and services. The trade deficit in 2020 was £111 billion. The main contributors to the deficit are imports of machinery, vehicles, and pharmaceutical products. The trade deficit has raised concerns about the country’s economic stability and its ability to compete in the global market.
3. Australia
Australia has a long history of trade deficits, mainly driven by imports of consumer goods and petroleum products. The trade deficit in 2020 was AUD 17.1 billion. The country relies heavily on imports for its domestic consumption, leading to a persistent trade deficit. The trade deficit has put pressure on the Australian dollar and raised concerns about the country’s economic dependence on foreign goods.
4. India
India has been experiencing a trade deficit for many years, primarily due to its dependence on imports of crude oil, electronic goods, and machinery. The trade deficit in 2020 was $98.6 billion. The trade deficit has put pressure on the Indian rupee and raised concerns about the country’s ability to achieve self-sufficiency in key industries.
| Country | Year | Trade Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 2020 | $678.7 billion |
| United Kingdom | 2020 | £111 billion |
| Australia | 2020 | AUD 17.1 billion |
| India | 2020 | $98.6 billion |
These examples highlight the global nature of trade deficits and their impact on various economies. Trade deficits can lead to concerns about job losses, economic stability, and the competitiveness of domestic industries. Governments often implement policies to address trade deficits, such as imposing tariffs or promoting domestic production. However, achieving a balanced trade position remains a complex challenge for many countries.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
