Rider: Definition and How Riders Work

A rider is an additional provision or attachment to an insurance policy that modifies the terms and conditions of the policy. It provides extra coverage or benefits beyond what is typically offered in the base policy. Riders are optional and can be added to a policy for an additional premium.
Riders work by allowing policyholders to customize their insurance coverage to better suit their individual needs. They provide added protection or enhancements to the base policy, giving policyholders more comprehensive coverage. Riders can be added to various types of insurance policies, including life insurance, health insurance, and auto insurance.
How Riders Work
When a policyholder wants to add a rider to their insurance policy, they typically need to request it from their insurance provider. The insurance company will then assess the additional risk associated with the rider and determine the cost of adding it to the policy. The policyholder will be required to pay an additional premium to include the rider in their coverage.
Once the rider is added to the policy, the policyholder will have the extra coverage or benefits specified in the rider. For example, a life insurance policy may have a rider that provides additional coverage in the event of accidental death. If the policyholder dies due to an accident, the rider would pay out an additional benefit on top of the base life insurance coverage.
Benefits of Riders
Riders offer policyholders the flexibility to tailor their insurance coverage to their specific needs. They allow individuals to add extra protection or enhancements to their policies without having to purchase a separate policy. This can be more cost-effective and convenient for policyholders.
Additionally, riders can provide coverage for specific risks or situations that may not be covered in the base policy. For example, a health insurance policy may not cover certain medical treatments or procedures, but a rider can be added to provide coverage for those specific treatments.
Types of Riders
1. Accidental Death Benefit Rider
This rider provides an additional death benefit if the insured dies due to an accident. It can be added to a life insurance policy to provide extra financial protection for the insured’s beneficiaries.
2. Critical Illness Rider
A critical illness rider provides a lump sum payment if the insured is diagnosed with a specified critical illness, such as cancer, heart attack, or stroke. This rider helps cover the costs associated with medical treatment and recovery.
3. Disability Income Rider
A disability income rider pays a monthly benefit to the insured if they become disabled and are unable to work. This rider helps replace lost income and ensures financial stability during a period of disability.
4. Long-Term Care Rider
A long-term care rider provides coverage for long-term care expenses, such as nursing home care or in-home care. This rider can be added to a life insurance policy or a health insurance policy to help cover the costs of extended care.
5. Return of Premium Rider
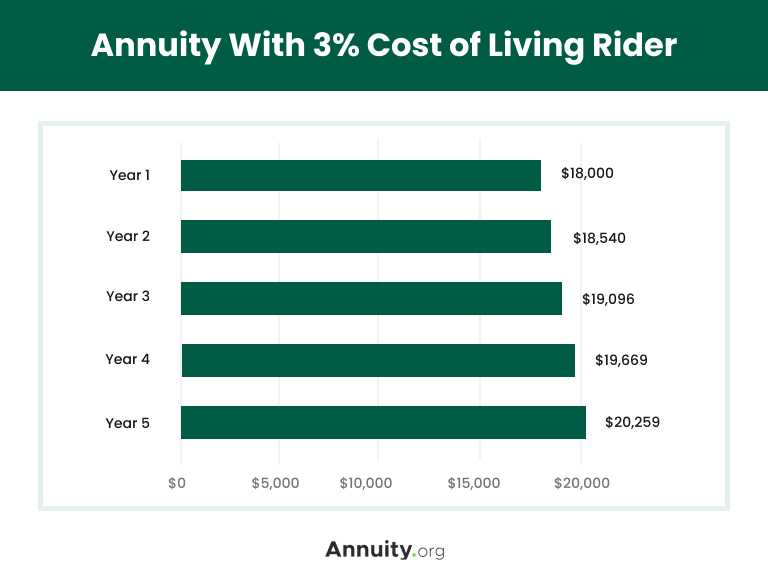
A return of premium rider refunds the premiums paid if the insured survives the policy term. This rider is often added to term life insurance policies and provides a way to recoup the premiums paid if the insured outlives the coverage.
6. Waiver of Premium Rider
A waiver of premium rider waives the premium payments if the insured becomes disabled and is unable to work. This rider ensures that the insurance coverage remains in force even if the insured is unable to pay the premiums due to a disability.
Cost of Riders
Insurance companies typically charge an additional premium for riders. This premium is added to the base premium of the insurance policy. The cost of a rider can range from a few dollars to a significant percentage of the base premium.
The cost of riders also depends on the coverage amount. For example, if you choose a higher coverage amount for a critical illness rider, the premium will be higher compared to a lower coverage amount.
Another factor that affects the cost of riders is the policyholder’s age. Generally, the younger you are, the lower the premium will be. This is because younger individuals are considered to be at a lower risk of developing health conditions or experiencing accidents.
It’s worth noting that the cost of riders is an ongoing expense. You will need to pay the premium for the rider as long as you want to maintain the additional coverage. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the long-term affordability of the rider before adding it to your insurance policy.
| Rider Type | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Accidental Death and Dismemberment | |
| Critical Illness | |
| Waiver of Premium | |
| Long-Term Care |
Example of a Rider
To better understand how a rider works, let’s consider an example. Suppose you have a life insurance policy that provides coverage for your family in case of your untimely demise. However, you also want to have some additional protection in case you become critically ill and are unable to work.
For instance, let’s say you have a life insurance policy with a coverage amount of $500,000 and you add a critical illness rider with a coverage amount of $100,000. If you are diagnosed with a covered critical illness, you will receive a lump sum payment of $100,000, in addition to the death benefit provided by the base life insurance policy.
This additional payment can help cover medical expenses, replace lost income, or pay off debts during your recovery period. It provides an extra layer of financial protection for you and your family, ensuring that you have the necessary funds to cope with a critical illness.
Insurance Categories
1. Life Insurance:
Life insurance provides financial protection to the beneficiaries of the insured individual in the event of their death. It can help cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and provide income replacement for the family.
2. Health Insurance:
Health insurance covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications. It helps individuals and families afford necessary healthcare services and treatments.
3. Auto Insurance:
Auto insurance protects against financial loss in case of accidents, theft, or damage to a vehicle. It can cover repairs, medical expenses, and liability claims resulting from accidents.
4. Home Insurance:
Home insurance provides coverage for homeowners in case of damage or loss to their property. It can protect against fire, theft, natural disasters, and liability claims from injuries that occur on the property.
5. Business Insurance:
Business insurance offers protection for businesses against various risks, such as property damage, liability claims, and loss of income. It can also cover employee injuries and provide coverage for professional services.
Liability insurance protects individuals and businesses from legal claims and lawsuits. It can cover costs related to bodily injury, property damage, and personal injury claims.
7. Disability Insurance:
Disability insurance provides income replacement for individuals who are unable to work due to illness or injury. It can help cover living expenses and maintain financial stability during a period of disability.
8. Travel Insurance:
Travel insurance offers coverage for unexpected events that may occur while traveling, such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, lost luggage, and travel delays.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
