Payment-in-Kind (PIK) Explained
Payment-in-Kind (PIK) is a financial arrangement that allows borrowers to pay interest or dividends on a loan or investment by issuing additional securities instead of making cash payments. This type of payment is commonly used in situations where the borrower is experiencing financial difficulties and does not have the cash flow to make regular interest or dividend payments.
PIK arrangements can be beneficial for both borrowers and lenders. For borrowers, PIK allows them to conserve cash and maintain liquidity during challenging financial periods. It provides them with the flexibility to meet their interest or dividend obligations without putting additional strain on their cash flow. For lenders or investors, PIK offers the potential for higher returns. The additional securities issued by the borrower can appreciate in value over time, providing the lender or investor with a greater return on their investment.
However, PIK arrangements also come with certain risks and drawbacks. For borrowers, the issuance of additional securities can dilute the ownership stake of existing shareholders, potentially leading to a loss of control. Additionally, if the borrower is unable to generate sufficient cash flow to repay the principal amount of the loan or investment, the PIK arrangement can result in a higher overall debt burden. For lenders or investors, the value of the additional securities issued as PIK payments is not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on market conditions.
How PIK Works
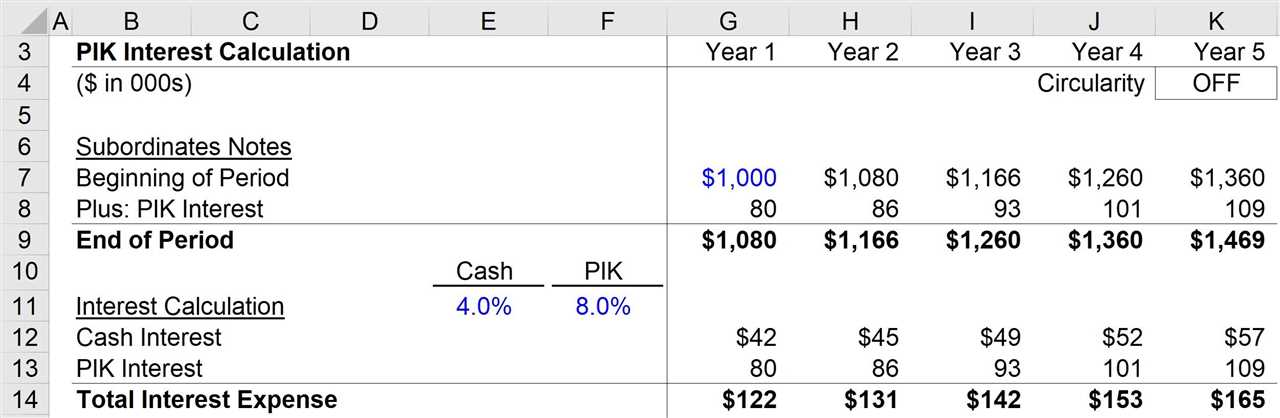
Structure
Benefits
PIK loans can be beneficial for both borrowers and lenders. For borrowers, PIK loans provide a way to conserve cash flow and manage their debt obligations. By deferring interest payments, borrowers can use the cash for other purposes such as investing in their business or funding growth initiatives.
For lenders, PIK loans offer the potential for higher returns. Since the interest payments are added to the principal amount, lenders have the opportunity to earn interest on a larger loan balance. This can be attractive for investors seeking higher yields.
Additionally, PIK loans can be useful in situations where a borrower is experiencing financial difficulties and is unable to make regular interest payments. By allowing the borrower to defer interest payments, PIK loans can provide temporary relief and help the borrower avoid defaulting on their loan.
Risks
While PIK loans offer certain benefits, they also come with risks. One of the main risks is the increased debt burden for the borrower. By deferring interest payments and adding them to the principal amount, the borrower’s debt load continues to grow over time. This can lead to a higher risk of default if the borrower is unable to generate sufficient cash flow to repay the loan.
Another risk is the potential for higher interest costs. Since the interest payments are added to the principal, the borrower may end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan compared to a traditional loan. This can be a significant disadvantage if interest rates rise or if the borrower is unable to refinance the loan at a lower rate in the future.
Overall, PIK loans can be a useful financing option for certain borrowers, but they also come with risks that need to be carefully considered. It is important for borrowers to assess their ability to repay the loan and evaluate the long-term implications of deferring interest payments.
Pros and Cons of Payment-in-Kind (PIK)
Payment-in-Kind (PIK) is a financial instrument that allows borrowers to make interest payments on a loan or bond by issuing additional securities instead of paying cash. While PIK can provide flexibility and short-term relief for borrowers, it also comes with certain risks and drawbacks. Here are some of the pros and cons of using PIK:
Pros:
1. Preservation of cash flow: By using PIK, borrowers can conserve their cash flow and allocate it towards other business needs. This can be especially beneficial for companies that are experiencing temporary financial difficulties or need to invest in growth opportunities.
2. Flexibility: PIK allows borrowers to defer cash payments, providing them with flexibility in managing their financial obligations. This can be useful during times of economic uncertainty or when cash flow is tight.
3. Enhanced liquidity: PIK can increase a company’s liquidity by providing an alternative source of funding. This can be particularly valuable for businesses that have limited access to traditional financing options.
4. Opportunity for higher returns: For investors, PIK can offer the potential for higher returns compared to traditional fixed-income securities. This is because PIK securities often have a higher interest rate or yield, compensating investors for the additional risk involved.
Cons:
1. Increased debt burden: PIK securities add to a company’s overall debt burden, which can negatively impact its creditworthiness and increase its financial risk. This can make it more difficult for the company to secure future financing or negotiate favorable terms.
2. Higher interest costs: PIK securities typically carry higher interest rates than traditional cash-paying securities. This means that borrowers will ultimately pay more in interest over the life of the loan or bond, increasing their overall cost of borrowing.
3. Market perception: The use of PIK can sometimes be viewed negatively by investors and creditors. It may signal financial distress or a lack of confidence in the company’s ability to generate sufficient cash flow to meet its obligations. This can impact the company’s reputation and make it more challenging to attract investment or secure favorable business relationships.
4. Risk of dilution: PIK securities are often issued in the form of additional shares or convertible bonds, which can lead to dilution of existing shareholders’ ownership. This can result in a loss of control or voting power for current shareholders.
Overall, the decision to use PIK should be carefully considered, taking into account the specific financial situation and objectives of the borrower. While PIK can provide short-term benefits, it also carries certain risks that need to be carefully managed.
Payment-in-Kind (PIK) Explained: Pros and Cons
There are several advantages and disadvantages to using PIK as a method of payment. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons:
Pros of PIK:
- Preservation of Cash: One of the main benefits of PIK is that it allows borrowers to preserve cash by not making regular interest or dividend payments. This can be particularly useful for companies that are experiencing financial difficulties or have limited cash flow.
- Flexibility: PIK provides borrowers with flexibility in managing their cash flow. By deferring interest or dividend payments, companies can allocate their cash resources to other areas of their business, such as expansion or investment in new projects.
- Enhanced Liquidity: PIK can also improve a company’s liquidity position. By not having to make regular cash payments, companies can maintain a higher level of cash on hand, which can be used for various purposes, such as working capital needs or debt repayment.
- Attractive to Investors: PIK can be an attractive option for investors seeking higher returns. By receiving additional securities instead of cash payments, investors have the potential to benefit from capital appreciation if the value of the securities increases over time.
Cons of PIK:
- Increased Debt Burden: One of the main disadvantages of PIK is that it increases the overall debt burden of the borrower. By issuing additional securities, the borrower is effectively taking on more debt, which can have long-term implications for the financial health of the company.
- Higher Interest Costs: PIK securities typically carry a higher interest rate compared to traditional cash payments. This is because lenders or investors are taking on additional risk by accepting securities instead of cash. As a result, borrowers may end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan or investment.
- Decreased Ownership: When borrowers issue additional securities as PIK, it dilutes the ownership stake of existing shareholders. This can be a concern for shareholders who may see their ownership percentage decrease over time.
- Market Perception: The use of PIK can sometimes be viewed negatively by the market. Investors and analysts may interpret the use of PIK as a sign of financial distress or poor cash flow management, which can impact the company’s stock price or credit rating.
Overall, PIK can be a useful financial tool for borrowers looking to preserve cash and manage their cash flow effectively. However, it is important to carefully consider the pros and cons before deciding to use PIK as a method of payment.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
