What is Overtrading and How to Avoid It?
Overtrading is a common mistake that many traders make, especially beginners. It refers to the excessive buying and selling of securities or assets within a short period of time, often driven by emotions rather than a well-thought-out strategy. Overtrading can lead to significant financial losses and can negatively impact a trader’s overall performance.
One of the main reasons why overtrading occurs is due to a lack of discipline and patience. Traders may feel the need to constantly be in the market, fearing that they might miss out on potential opportunities. However, this impulsive behavior can be detrimental to their trading success.
To avoid overtrading, it is important to have a well-defined trading plan and stick to it. This includes setting clear entry and exit points for each trade, as well as establishing a maximum number of trades per day or week. By following a set of predetermined rules, traders can avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Another effective way to avoid overtrading is to practice proper risk management. This involves determining the appropriate position size for each trade, based on the trader’s risk tolerance and account size. By only risking a small percentage of their capital on each trade, traders can minimize the potential losses associated with overtrading.
Furthermore, it is important to be aware of the psychological factors that can contribute to overtrading. Traders should learn to recognize and control their emotions, such as fear and greed, which can cloud their judgment and lead to impulsive trading decisions. Developing a disciplined mindset and maintaining a calm and rational approach to trading can help prevent overtrading.
Overtrading refers to a situation in which a trader or investor engages in excessive buying and selling of securities or assets, often beyond their financial capacity or market conditions. It is a common phenomenon in the financial markets, especially among inexperienced traders who are driven by emotions and the desire to make quick profits.
Causes of Overtrading
There are several factors that can contribute to overtrading:
- Lack of discipline: Traders who lack discipline may succumb to impulsive trading decisions, leading to overtrading. They may be driven by the fear of missing out on potential opportunities or the need to recover from losses quickly.
- Emotional trading: Emotions such as greed, fear, and excitement can cloud judgment and lead to overtrading. Traders who are emotionally attached to their trades may find it difficult to exit positions, even when it is necessary.
- Overconfidence: Overconfident traders may believe that they can consistently beat the market and make profitable trades. This can lead to excessive trading and taking on unnecessary risks.
- Pressure to perform: Traders who feel the pressure to perform and meet certain targets may engage in overtrading to generate higher returns. This can be driven by external factors such as competition or internal pressure to meet personal financial goals.
Types of Overtrading
Overtrading can manifest in different forms:
- Frequent trading: Traders who excessively buy and sell securities within a short period of time, often incurring high transaction costs and generating minimal returns.
- Overleveraging: Traders who take on excessive leverage or borrow money to fund their trades, amplifying potential losses and increasing financial risk.
- Chasing hot stocks: Traders who constantly chase after stocks that are experiencing significant price movements, hoping to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
- Ignoring risk management: Traders who neglect proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders or diversifying their portfolios, increasing the likelihood of substantial losses.
It is important for traders to be aware of these types of overtrading and the potential risks associated with them.
Causes of Overtrading

Overtrading can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Lack of discipline: One of the main causes of overtrading is a lack of discipline. Traders who do not have a well-defined trading plan and fail to stick to their strategy often end up making impulsive and excessive trades.
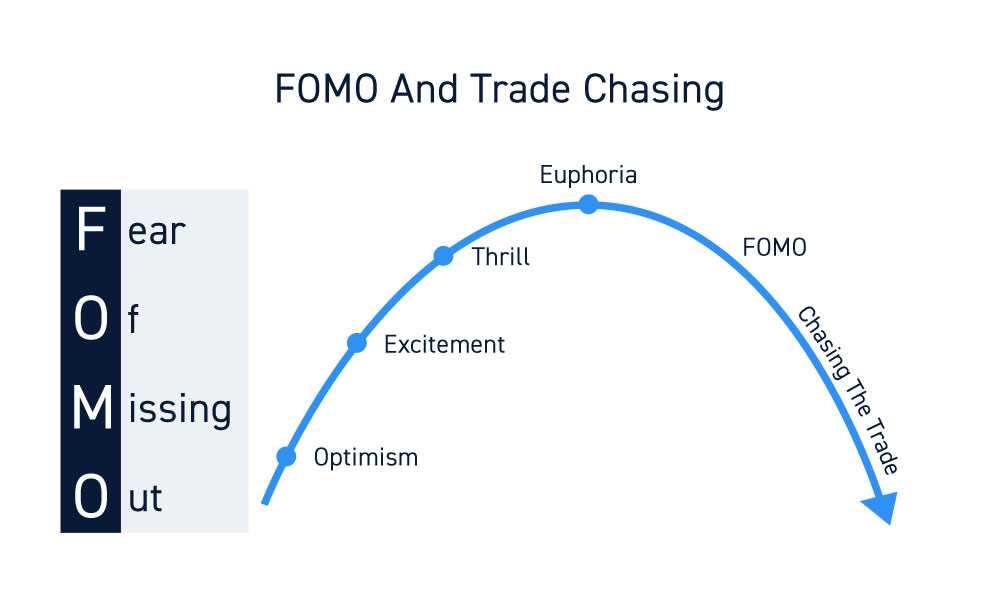
2. Fear of missing out (FOMO): Another common cause of overtrading is the fear of missing out on potential profits. Traders may feel the need to constantly be in the market and take every opportunity that comes their way, even if it does not align with their trading plan.
3. Emotional trading: Emotional trading, driven by fear, greed, or other strong emotions, can also lead to overtrading. Traders who let their emotions dictate their trading decisions are more likely to make impulsive trades and take unnecessary risks.
5. Overconfidence: Overconfidence can also contribute to overtrading. Traders who have experienced a string of successful trades may become overconfident in their abilities and start taking more trades than necessary, leading to overtrading.
7. Lack of risk management: Traders who do not have proper risk management strategies in place are more likely to overtrade. Without a clear plan for managing risk, traders may take on more trades than they can handle, leading to overtrading.
8. Market volatility: High market volatility can also contribute to overtrading. Traders may feel the need to constantly be in the market to take advantage of price movements, but this can result in excessive trading and increased risk.
Overall, overtrading can be caused by a combination of psychological, emotional, and external factors. It is important for traders to be aware of these causes and take steps to avoid falling into the trap of overtrading.
Types of Overtrading
Overtrading can manifest in different ways, depending on the specific actions and behaviors of traders. Here are the three main types of overtrading:
1. Excessive Trading Volume
This type of overtrading occurs when traders engage in an excessive number of trades within a short period. They may be driven by the fear of missing out on potential profits or the desire to constantly be in the market. As a result, they end up executing trades without proper analysis or consideration of risk, leading to poor decision-making and potential losses.
2. Chasing Profits
3. Trading Beyond Available Capital
Trading beyond available capital is a type of overtrading where traders risk more money than they can afford to lose. They may use excessive leverage or margin to amplify their trading positions, hoping to maximize profits. However, this approach can be extremely risky, as it leaves traders vulnerable to significant losses if the market moves against them. It is important for traders to only risk capital that they can afford to lose and to use proper risk management strategies.
| Type of Overtrading | Description |
|---|---|
| Excessive Trading Volume | Engaging in an excessive number of trades without proper analysis or consideration of risk. |
| Chasing Profits | |
| Trading Beyond Available Capital | Risking more money than one can afford to lose by using excessive leverage or margin. |
Effective Ways to Avoid Overtrading
Overtrading can be a detrimental habit for traders, leading to financial losses and increased stress. However, there are several effective ways to avoid overtrading and maintain a disciplined approach to trading. By implementing these strategies, traders can improve their decision-making process and increase their chances of success in the market.
1. Develop a Trading Plan
One of the most important steps in avoiding overtrading is to develop a well-defined trading plan. This plan should outline specific entry and exit points, risk management strategies, and a clear set of rules for trading. By having a plan in place, traders can avoid impulsive and emotional trading decisions, which often lead to overtrading.
2. Set Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is essential for avoiding overtrading. Traders should establish achievable targets for their trades and avoid the temptation to chase after unrealistic profits. By setting realistic goals, traders can stay focused and avoid the urge to trade excessively in an attempt to make up for losses or achieve quick gains.
3. Use Proper Risk Management
Implementing proper risk management techniques is crucial for avoiding overtrading. Traders should determine the maximum amount of capital they are willing to risk on each trade and stick to this limit. By managing risk effectively, traders can avoid the temptation to overtrade and protect their capital from significant losses.
4. Maintain Discipline
Discipline is key to avoiding overtrading. Traders should adhere to their trading plan and avoid deviating from it due to emotions or impulsive decisions. It is important to stay patient and wait for high-probability trade setups, rather than entering trades based on fear of missing out or excitement.
5. Practice Patience
Patience is a virtue in trading, and it is essential for avoiding overtrading. Traders should wait for clear signals and confirmations before entering a trade. Rushing into trades without proper analysis can lead to poor decision-making and increased trading frequency.
6. Keep a Trading Journal
Keeping a trading journal is a valuable tool for avoiding overtrading. Traders should record their trades, including entry and exit points, reasons for entering the trade, and the outcome. By reviewing past trades, traders can identify patterns of overtrading and make necessary adjustments to their trading strategy.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
