MiFID II Regulations: Key Requirements and Compliance
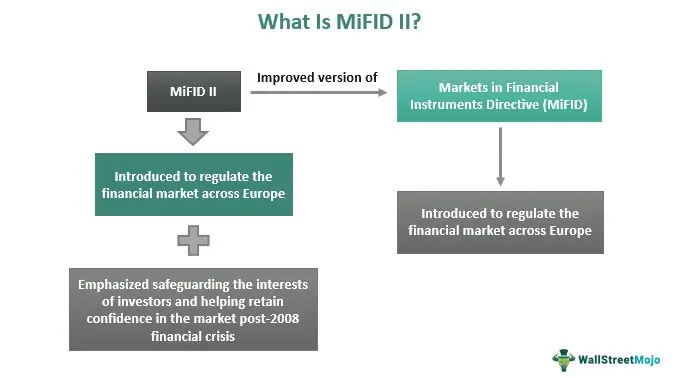
The Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) is a comprehensive set of regulations implemented by the European Union (EU) to regulate financial markets and protect investors. MiFID II builds upon its predecessor, MiFID I, and aims to enhance market transparency, improve investor protection, and promote fair competition.
Under MiFID II, financial institutions and investment firms are subject to a range of key requirements and compliance measures. These include:
- Transaction Reporting: Financial firms are required to report all transactions executed on regulated markets, multilateral trading facilities, and systematic internalizers. This reporting helps regulatory authorities monitor market activity and detect any potential market abuse.
- Best Execution: Investment firms must take all reasonable steps to obtain the best possible result for their clients when executing orders. They must consider factors such as price, costs, speed, likelihood of execution, and settlement. Firms are also required to disclose their execution policies to clients.
- Product Governance: Investment firms must have robust product governance arrangements in place to ensure that the products they offer are suitable for their target market. This includes conducting a thorough assessment of the product’s features, risks, and target investors.
- Client Categorization: Investment firms must categorize their clients as either retail clients, professional clients, or eligible counterparties. This categorization determines the level of regulatory protection and the type of services that can be offered to each client category.
- Inducements and Research: MiFID II introduces stricter rules regarding inducements and the provision of research to clients. Investment firms must ensure that any research they provide is of high quality, objective, and not influenced by any conflicts of interest.
- Organizational Requirements: Investment firms must have adequate organizational and administrative arrangements in place to effectively manage their business operations and comply with regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining proper record-keeping, risk management systems, and internal controls.
- Pre- and Post-Trade Transparency: MiFID II aims to increase transparency in financial markets by requiring firms to publish pre- and post-trade information on trading venues. This information includes details about the instrument traded, the price, and the volume.
- Compliance Monitoring: Investment firms must establish robust compliance monitoring procedures to ensure ongoing compliance with MiFID II requirements. This includes regular internal audits, risk assessments, and the appointment of a compliance officer.
Compliance with MiFID II is essential for financial institutions and investment firms operating within the EU. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and potential loss of business. It is crucial for firms to stay up-to-date with the latest regulatory developments and seek professional advice to ensure full compliance with MiFID II requirements.
Impacts of MiFID II: Market Transparency and Investor Protection
The implementation of MiFID II has had significant impacts on the financial markets, with a focus on increasing market transparency and enhancing investor protection. These impacts can be seen across various aspects of the financial industry, including trading, reporting, and market structure.
1. Increased Market Transparency
One of the key objectives of MiFID II is to improve market transparency by increasing the amount and quality of information available to market participants. This is achieved through the introduction of new reporting requirements and the expansion of pre- and post-trade transparency rules.
Under MiFID II, investment firms are required to report a wide range of data on their trades, including price, volume, and time of execution. This data is then made available to the public and regulators, allowing for greater visibility into market activity. Additionally, trading venues are required to publish data on the prices and volumes of trades, providing market participants with more information to make informed decisions.
2. Enhanced Investor Protection

MiFID II also aims to enhance investor protection by introducing stricter rules and requirements for investment firms. These rules are designed to ensure that investors receive appropriate advice and are provided with clear and accurate information about financial products.
Under MiFID II, investment firms are required to conduct a thorough assessment of their clients’ knowledge and experience before providing investment advice. They must also provide clients with a comprehensive disclosure of costs and charges associated with investment products. These measures are intended to ensure that investors are fully informed and can make well-informed decisions.
3. Changes to Market Structure
The implementation of MiFID II has also led to changes in market structure, particularly in the trading of financial instruments. The introduction of new trading venues, such as organized trading facilities (OTFs), has increased competition and provided investors with more options for executing trades.
Additionally, MiFID II has imposed stricter rules on high-frequency trading (HFT) and dark pools, aiming to reduce the risks associated with these trading practices. HFT firms are now required to register with regulators and adhere to certain obligations, such as providing liquidity during stressed market conditions. Dark pools, which are private trading venues, are subject to stricter transparency requirements to ensure that they do not negatively impact market integrity.
Conclusion
The implementation of MiFID II has had a profound impact on the financial markets, with a focus on increasing market transparency and enhancing investor protection. These impacts can be seen through increased reporting requirements, enhanced investor disclosure, and changes in market structure. Overall, MiFID II aims to create a more transparent and fair financial system that benefits both market participants and investors.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
