What is a Master Limited Partnership (MLP)?
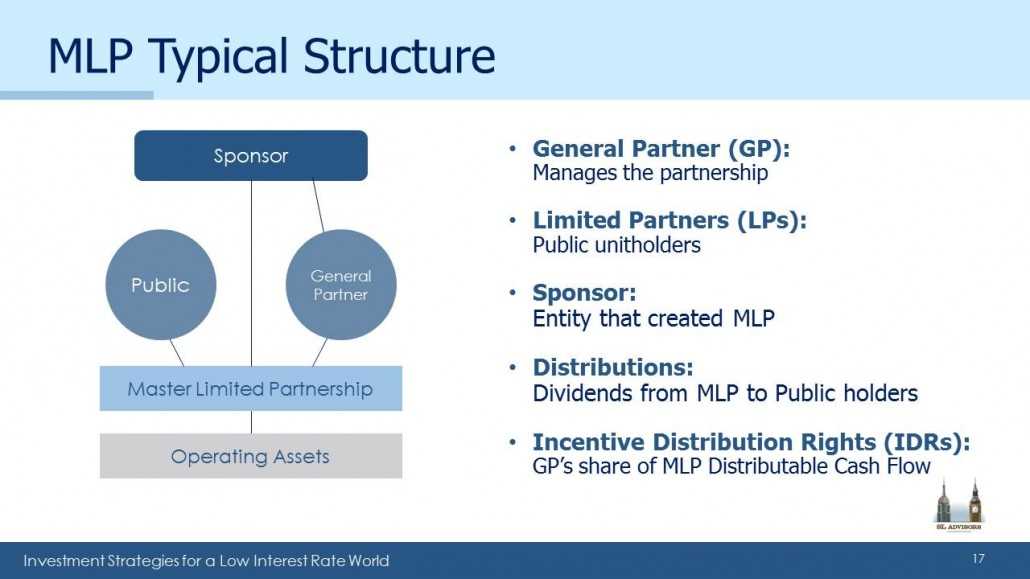
A Master Limited Partnership (MLP) is a type of business structure that combines the tax benefits of a partnership with the liquidity of a publicly traded company. MLPs are typically formed in the energy sector, specifically in the oil and gas industry, but they can also be found in other industries such as real estate and infrastructure.
MLPs are designed to provide investors with a steady stream of income through the distribution of cash flows generated by the underlying assets of the partnership. These assets can include pipelines, storage facilities, and other energy-related infrastructure. The income generated by the MLP is typically tax-advantaged, as MLPs are not subject to corporate income taxes.
Benefits of Investing in MLPs
There are several benefits to investing in MLPs:
- Tax Advantages: MLPs are structured in a way that allows them to avoid corporate income taxes. Instead, the tax liability is passed through to the individual investors, who are only taxed on their share of the partnership’s income.
- Liquidity: MLPs are traded on major stock exchanges, providing investors with the ability to easily buy and sell units of the partnership.
- Diversification: MLPs offer investors the opportunity to diversify their portfolios by gaining exposure to the energy sector or other industries through a single investment.
Risks of Investing in MLPs
While MLPs offer attractive benefits, there are also risks to consider:
- Market Volatility: The value of MLP units can be subject to significant fluctuations based on market conditions and the performance of the underlying assets.
- Interest Rate Risk: MLPs are often sensitive to changes in interest rates, which can impact the cost of financing for the partnership and the value of its assets.
- Regulatory Risk: MLPs are subject to regulatory changes that could impact their ability to operate or the tax advantages they offer.
- Commodity Price Risk: MLPs in the energy sector are particularly exposed to fluctuations in commodity prices, which can impact the profitability of their underlying assets.
Definition and Overview of MLPs in Alternative Investments
A Master Limited Partnership (MLP) is a type of investment vehicle that combines the tax benefits of a limited partnership with the liquidity of publicly traded securities. MLPs are typically formed by energy companies, such as oil and gas pipeline operators, and are designed to generate income for investors through the distribution of cash flows.
MLPs are structured as publicly traded partnerships, which means that they are traded on major stock exchanges just like regular stocks. However, unlike traditional corporations, MLPs are not subject to corporate income taxes. Instead, the tax liability is passed through to the individual investors, who are responsible for paying taxes on their share of the partnership’s income.
One of the key advantages of investing in MLPs is the potential for high yields. MLPs are required by law to distribute a significant portion of their income to investors in the form of cash distributions. This can result in attractive dividend yields, making MLPs an attractive investment option for income-focused investors.
In addition to the potential for high yields, MLPs also offer the benefit of diversification. MLPs typically own and operate a portfolio of energy infrastructure assets, such as pipelines, storage facilities, and processing plants. This allows investors to gain exposure to the energy sector without having to invest directly in individual companies.
Investment Considerations
While MLPs offer attractive income potential and diversification benefits, there are some important considerations to keep in mind before investing in them.
First, MLPs are subject to certain risks, including commodity price volatility, regulatory changes, and interest rate fluctuations. These factors can impact the performance of MLPs and the income generated for investors.
Second, MLPs have complex tax implications. Investors in MLPs are required to file a Schedule K-1 form with their tax returns, which can be more complicated than filing a regular tax return. It is important to consult with a tax advisor to fully understand the tax implications of investing in MLPs.
Finally, MLPs are not suitable for all investors. They are typically more suitable for long-term investors who are seeking income and are willing to accept the risks associated with investing in the energy sector.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
