What are Least Developed Countries (LDC)?
Least Developed Countries (LDCs) are a group of countries that face significant economic, social, and developmental challenges. These countries have the lowest levels of income, human capital, and economic productivity in the world. The United Nations identifies and categorizes these countries as LDCs based on specific criteria.
Definition and Criteria for LDC Status
The United Nations defines LDCs based on three criteria:
- Low income: LDCs have a gross national income (GNI) per capita of less than $1,045. This criterion helps identify countries with limited economic resources and high poverty rates.
- Economic vulnerability: LDCs have a high economic vulnerability index (EVI) score, which measures the susceptibility of their economies to external shocks, natural disasters, and other crises. This criterion highlights the challenges these countries face in achieving sustainable economic growth and development.
Importance of LDC Classification
The classification of countries as LDCs is important for several reasons:
- International support: LDCs receive special attention and support from the international community, including financial assistance, technical cooperation, and preferential trade agreements. This support aims to help these countries overcome their developmental challenges and achieve sustainable development.
- Policy focus: LDC classification helps policymakers and development organizations prioritize their efforts and resources towards addressing the specific needs and challenges faced by these countries. It guides the formulation of targeted policies and programs to promote inclusive growth and poverty reduction.
- Data and monitoring: LDC classification provides a framework for collecting and analyzing data on the social, economic, and developmental indicators of these countries. This data helps monitor progress, identify trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of development interventions.
Overall, the classification of countries as LDCs serves as a tool for international cooperation and solidarity, aiming to uplift the most vulnerable and disadvantaged nations towards sustainable development and poverty eradication.
Definition and Criteria for LDC Status
Income Criterion
The income criterion is measured by the Gross National Income (GNI) per capita of a country. To be considered an LDC, a country must have a GNI per capita below a certain threshold, which is currently set at $1,036. This criterion reflects the low income levels and poverty prevalent in LDCs.
Human Assets Criterion
The human assets criterion takes into account indicators related to education, health, and nutrition. LDCs typically have low levels of education, high rates of illiteracy, inadequate healthcare systems, and poor nutrition. These factors contribute to the overall underdevelopment of human capital in LDCs.
Economic Vulnerability Criterion

The economic vulnerability criterion assesses the susceptibility of a country to external shocks and economic instability. LDCs often have weak economic structures, high dependence on a few export commodities, limited diversification, and inadequate infrastructure. These vulnerabilities make LDCs more prone to economic crises and hinder their ability to achieve sustainable development.
The combination of these three criteria helps to identify countries that are in the most need of international support and assistance. The classification of LDCs allows for targeted development efforts and the allocation of resources to address the specific challenges faced by these countries.
It is important to note that the list of LDCs is periodically reviewed and updated by the United Nations based on the progress made by each country. Countries that have made significant improvements in their development indicators may graduate from the LDC status, while others may be added to the list if they meet the criteria.
Importance of LDC Classification
The classification of countries as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) is of significant importance in the field of international development. This classification helps to identify and prioritize countries that are in need of special attention and support from the global community.
One of the main reasons why LDC classification is important is because it helps to allocate resources effectively. By identifying the countries that are in the most vulnerable and disadvantaged positions, international organizations, governments, and aid agencies can channel their resources towards these countries to address their specific needs. This ensures that limited resources are directed towards the areas where they can have the greatest impact.
Furthermore, the LDC classification also plays a crucial role in determining eligibility for various forms of international assistance. Many international organizations and donor countries have specific programs and initiatives that are designed to support LDCs. By being classified as an LDC, a country becomes eligible for these programs and can access financial assistance, technical expertise, and capacity-building support.
In addition, the LDC classification helps to raise awareness about the challenges faced by these countries. By highlighting the economic, social, and environmental issues that LDCs are grappling with, the classification brings attention to the need for global cooperation and solidarity. It encourages the international community to work together to find sustainable solutions and promote inclusive development.
Moreover, the LDC classification provides a framework for monitoring progress and evaluating the effectiveness of development efforts. By regularly reviewing the status of LDCs, it is possible to track improvements and identify areas where further interventions are required. This helps to ensure that development strategies are evidence-based and responsive to the evolving needs of these countries.
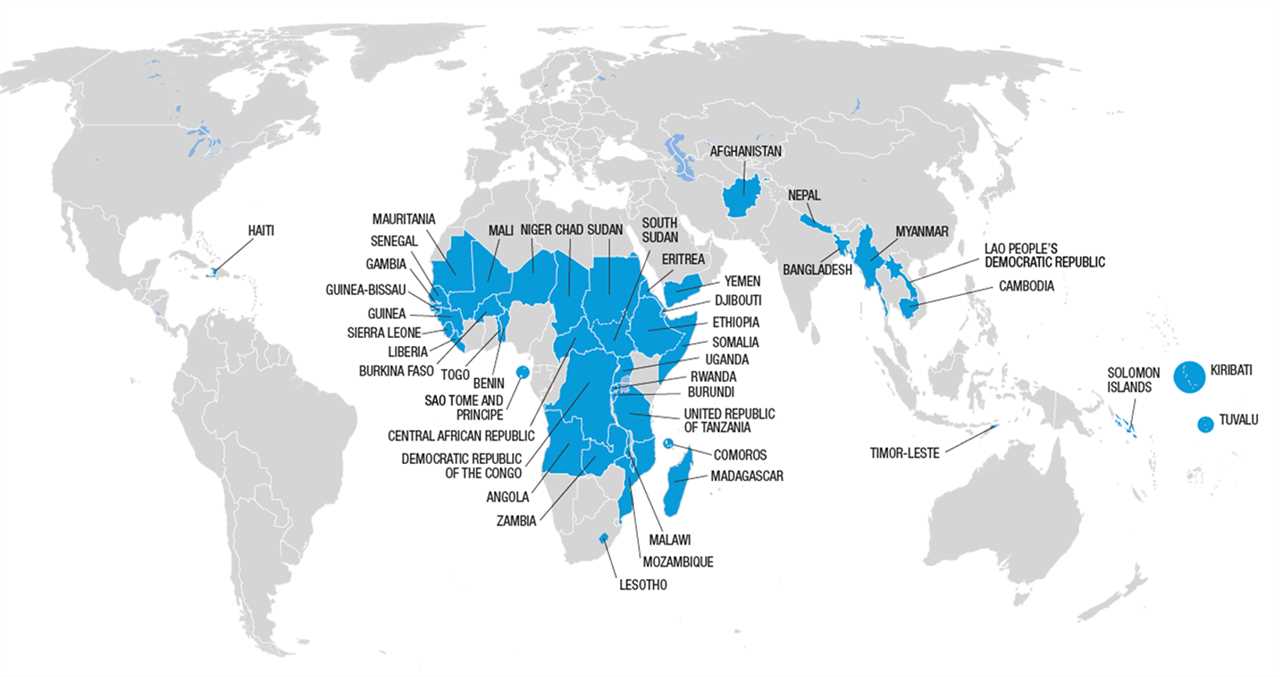
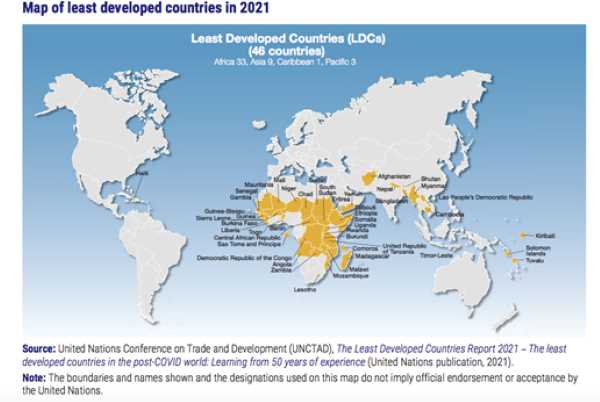
List of Least Developed Countries
The classification of Least Developed Countries (LDCs) is an important tool for identifying and addressing the unique challenges faced by the world’s poorest and most vulnerable nations. As of 2021, there are 46 countries that are officially recognized as LDCs by the United Nations.
These countries are characterized by low levels of income, weak human capital, and limited access to basic services such as education, healthcare, and clean water. They also face significant challenges in terms of infrastructure development, economic diversification, and environmental sustainability.
The list of LDCs includes countries from various regions of the world, including Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. Some of the countries on the list include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Ethiopia, Haiti, Mozambique, Nepal, and Yemen.
Being classified as an LDC has important implications for these countries. It makes them eligible for special support and assistance from the international community, including access to concessional financing, technical assistance, and capacity building. It also provides them with a platform to voice their concerns and advocate for their specific needs and priorities on the global stage.
However, it is important to note that being classified as an LDC is not a permanent status. The UN regularly reviews the list of LDCs and countries can graduate from this status if they make significant progress in terms of economic and social development. On the other hand, countries can also be added to the list if they experience significant setbacks or new challenges.
Economic Opportunities in Emerging Markets

Emerging markets, including many of the least developed countries (LDCs), offer a range of economic opportunities for investors and businesses. These markets are characterized by rapid economic growth, expanding middle classes, and a growing consumer base.
Additionally, emerging markets often have abundant natural resources, which can present opportunities for industries such as mining, agriculture, and energy. These resources can be leveraged to drive economic development and attract foreign investment.
Another advantage of investing in emerging markets is the potential for diversification. By expanding their operations into these markets, businesses can reduce their reliance on mature markets and tap into new sources of revenue.
However, investing in emerging markets also comes with risks. These markets can be volatile and subject to political instability, currency fluctuations, and regulatory changes. It is important for investors and businesses to conduct thorough market research and risk analysis before entering these markets.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
