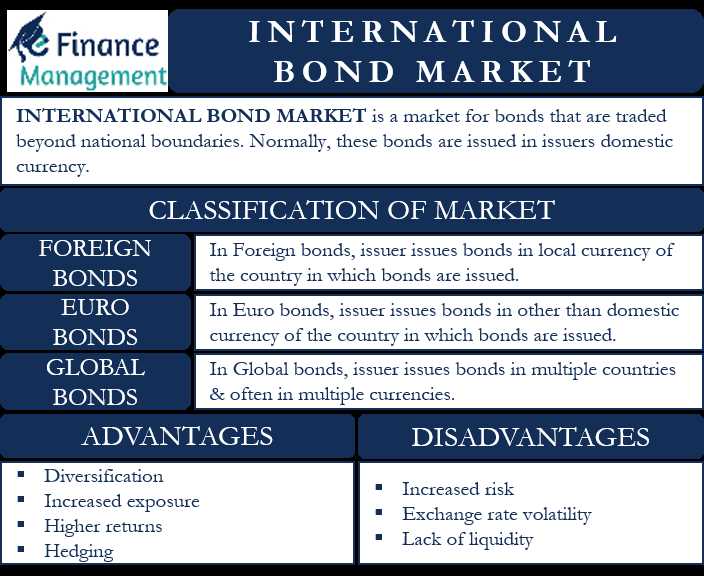
What are International Bonds?
International bonds are debt securities issued by a foreign entity in a currency other than the domestic currency of the issuer. These bonds are typically issued by governments, corporations, or supranational organizations to raise capital from international investors. They provide an opportunity for investors to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to different markets and currencies.
International bonds are traded in the international bond market, which is a global marketplace where investors can buy and sell bonds issued by various countries and companies. This market is highly liquid and offers a wide range of investment options.
Features of International Bonds
International bonds have several key features that distinguish them from domestic bonds:
- Currency: International bonds are denominated in a currency other than the domestic currency of the issuer. This allows investors to invest in different currencies and potentially benefit from currency fluctuations.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on international bonds is typically higher than domestic bonds to compensate investors for the additional risk associated with investing in foreign markets.
- Risk: Investing in international bonds carries certain risks, including currency risk, political risk, and economic risk. These risks can affect the value and performance of the bonds.
- Diversification: International bonds provide investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios by investing in different countries and currencies. This can help reduce the overall risk of the portfolio.
Overall, international bonds offer investors the potential for higher returns and diversification benefits. However, they also come with additional risks that investors should carefully consider before investing.
Types of International Bonds
International bonds are debt securities issued by governments, corporations, and other entities in a foreign country’s market. These bonds allow investors to diversify their portfolios and access opportunities beyond their domestic markets. There are several types of international bonds available to investors:
1. Sovereign Bonds
2. Corporate Bonds
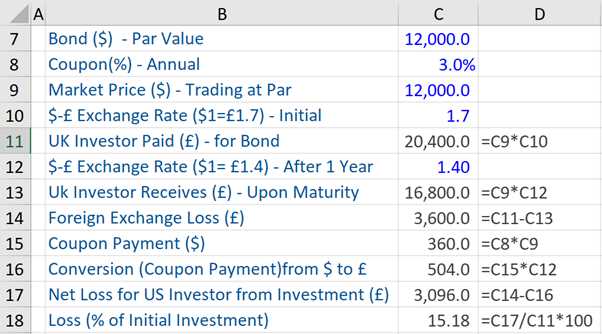
Corporate bonds are issued by companies to raise capital for various purposes, such as expanding operations, acquiring other companies, or refinancing existing debt. These bonds offer higher yields compared to sovereign bonds but also carry higher credit risk. Examples of international corporate bonds include bonds issued by multinational corporations like Apple, Microsoft, and Toyota.
3. Supranational Bonds
Supranational bonds are issued by international organizations like the World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and European Investment Bank (EIB). These bonds are used to finance development projects in emerging economies and promote economic stability. Supranational bonds are considered low-risk investments due to the backing of these reputable institutions.
4. Emerging Market Bonds
Emerging market bonds are issued by governments and corporations in developing countries. These bonds offer higher yields compared to bonds from developed countries but also carry higher credit risk. Investors interested in higher returns may consider investing in emerging market bonds, but they should be aware of the additional risks associated with these investments.
5. Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds are a hybrid form of debt and equity. These bonds can be converted into a predetermined number of the issuer’s common stock at a specified price. Convertible bonds offer investors the potential for capital appreciation if the issuer’s stock price rises. These bonds are commonly issued by companies in the technology and healthcare sectors.
6. Foreign Currency Bonds
Foreign currency bonds are issued in a currency other than the issuer’s domestic currency. These bonds allow investors to gain exposure to foreign currencies and potentially benefit from currency appreciation. However, investing in foreign currency bonds also exposes investors to currency exchange rate risk.
Investors should carefully consider their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and the specific characteristics of each type of international bond before making investment decisions. Diversification and thorough research are essential when investing in international bonds to mitigate risks and maximize potential returns.
| Type of International Bond | Characteristics | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Sovereign Bonds | Issued by national governments | Low risk |
| Corporate Bonds | Issued by companies | Medium to high risk |
| Supranational Bonds | Issued by international organizations | Low risk |
| Emerging Market Bonds | Issued by governments and corporations in developing countries | Medium to high risk |
| Convertible Bonds | Can be converted into common stock | Medium risk |
| Foreign Currency Bonds | Issued in a foreign currency | Medium to high risk |
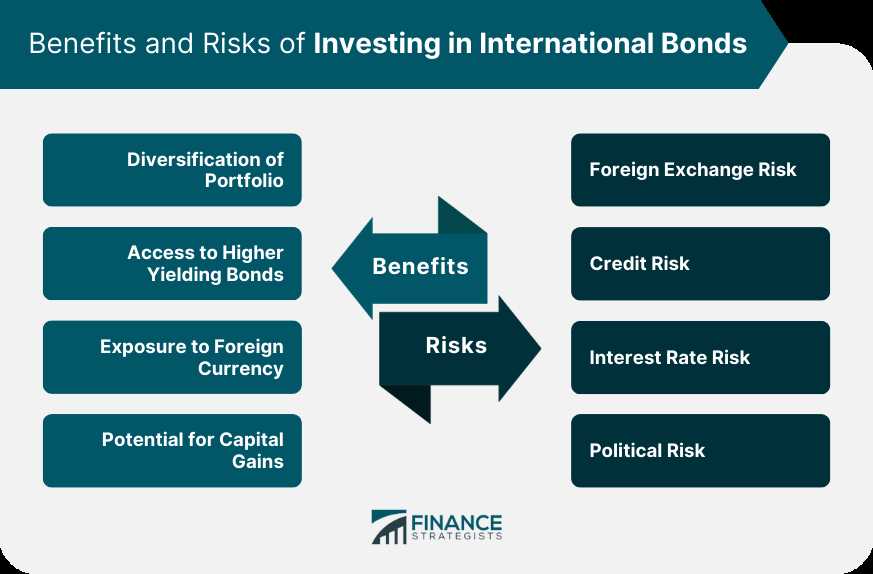
Benefits and Risks of Investing in International Bonds
Investing in international bonds can offer several benefits to investors. Here are some of the key advantages:
Diversification: International bonds provide an opportunity to diversify an investment portfolio. By investing in bonds from different countries, investors can spread their risk and reduce the impact of any single country’s economic or political events on their investment.
Access to Global Markets: Investing in international bonds allows investors to access global markets and take advantage of investment opportunities in different countries. This can provide exposure to different currencies, interest rates, and economic conditions.
Currency Diversification: International bonds denominated in different currencies can provide investors with an opportunity to diversify their currency exposure. This can help protect against currency fluctuations and provide potential gains if the investor’s home currency strengthens against the bond’s currency.
Despite these benefits, investing in international bonds also carries some risks that investors should be aware of:
Foreign Exchange Risk: Investing in international bonds exposes investors to foreign exchange risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of the bond and the investor’s returns. Currency risk can be mitigated through hedging strategies, but it adds an additional layer of complexity to the investment.
Political and Economic Risks: Investing in international bonds means being exposed to the political and economic risks of different countries. Political instability, changes in government policies, and economic downturns can all impact the value of international bonds.
Legal and Regulatory Risks: Different countries have different legal and regulatory frameworks for bond issuances. Investors need to be aware of the legal and regulatory risks associated with investing in international bonds, including potential changes in tax laws, disclosure requirements, and investor protections.
Liquidity Risk: Some international bond markets may have lower liquidity compared to domestic markets. This can make it more difficult to buy or sell bonds at desired prices, potentially impacting the investor’s ability to exit the investment when needed.
Overall, investing in international bonds can offer attractive opportunities for diversification and potentially higher returns. However, it is important for investors to carefully consider the risks involved and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions in international bond markets.
Examples of International Bonds
International bonds are issued by various entities, including governments, corporations, and international organizations. These bonds provide investors with an opportunity to diversify their portfolios and potentially earn higher returns. Here are some examples of international bonds:
1. United States Treasury Bonds: These bonds are issued by the U.S. government and are considered one of the safest investments in the world. They are denominated in U.S. dollars and are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
2. European Union Bonds: The European Union issues bonds to finance various projects and initiatives. These bonds are denominated in euros and are backed by the collective creditworthiness of the EU member states.
3. Emerging Market Bonds: Many developing countries issue international bonds to attract foreign investment. These bonds offer higher yields but also come with higher risks. Examples include bonds issued by countries like Brazil, India, and China.
4. Corporate Bonds: Many multinational corporations issue international bonds to raise capital. These bonds are backed by the creditworthiness of the issuing company and can provide investors with exposure to different industries and sectors.
5. World Bank Bonds: The World Bank issues bonds to finance development projects in various countries. These bonds are considered low-risk investments and are backed by the resources and guarantees of the World Bank.
6. Sovereign Bonds: Sovereign bonds are issued by national governments to finance their budget deficits or fund infrastructure projects. Examples include bonds issued by countries like Germany, Japan, and Australia.
Overall, international bonds can be a valuable addition to an investor’s portfolio, providing opportunities for diversification and potentially higher returns. However, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
