Hydrocarbons: Definition and Overview
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are the fundamental building blocks of many important substances, including fossil fuels, natural gas, and petroleum. Hydrocarbons are found in various forms, ranging from simple molecules like methane (CH4) to complex structures like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
What are Hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are chemical compounds that consist solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They are classified as organic compounds because they are primarily derived from living organisms or their remains. Hydrocarbons can be found in both natural and synthetic forms.
Types of Hydrocarbons
There are several types of hydrocarbons, each with its own unique structure and properties:
- Alkanes: These are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. Examples include methane, ethane, and propane.
- Alkenes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Examples include ethene and propene.
- Alkynes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. Examples include ethyne and propyne.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: These are cyclic hydrocarbons with alternating double bonds. Examples include benzene and naphthalene.
In addition to these basic types, hydrocarbons can also be classified based on their carbon chain length, branching, and functional groups present.
Hydrocarbon Companies and Industry
These companies are involved in activities such as oil and gas exploration, drilling, refining crude oil, and manufacturing various petroleum products. The hydrocarbon industry also supports other sectors like transportation, energy generation, and petrochemical manufacturing.
Uses of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons have numerous applications in our daily lives. Some of the common uses of hydrocarbons include:
- Energy production: Hydrocarbons are the primary source of energy worldwide. Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are burned to generate electricity, heat homes, and power vehicles.
- Transportation: Hydrocarbons, particularly gasoline and diesel, are used as fuels for cars, trucks, airplanes, and ships.
- Petrochemical industry: Hydrocarbons serve as raw materials for the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, rubber, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
- Heating and cooking: Natural gas, a hydrocarbon, is commonly used for heating homes and cooking food.
- Chemical synthesis: Hydrocarbons are essential for the synthesis of various chemicals, including solvents, lubricants, and detergents.
What are Hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are the simplest form of organic compounds and are found abundantly in nature. Hydrocarbons are the main components of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
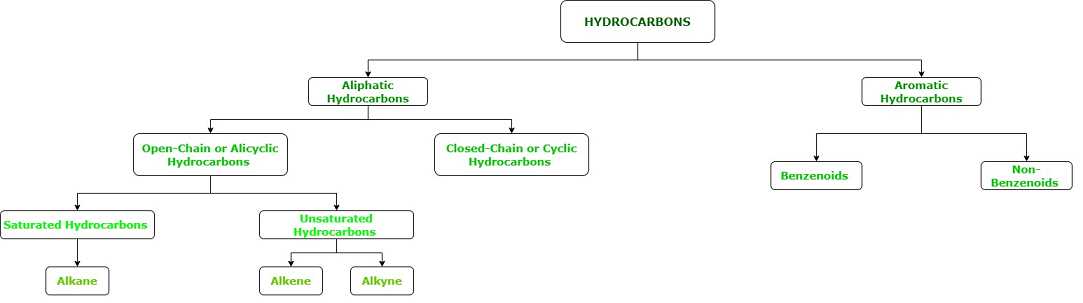
Hydrocarbons can be classified into two main types: aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are further divided into three subcategories: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Aromatic hydrocarbons, on the other hand, contain a ring structure of carbon atoms.
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons have a wide range of uses in various industries. They are used as fuels for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. They are also used as raw materials in the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, and chemicals. Additionally, hydrocarbons play a crucial role in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agricultural products.
Types of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that consist of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They can be classified into several different types based on their molecular structure and properties. Here are some of the main types of hydrocarbons:
1. Alkanes
2. Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They have the general formula CnH2n and are more reactive than alkanes. Alkenes are used in the production of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
3. Alkynes
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They have the general formula CnH2n-2 and are even more reactive than alkenes. Alkynes are used in the production of synthetic fibers, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial applications.
4. Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Aromatic hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that contain a benzene ring or other similar aromatic rings. They have a unique structure and exhibit special properties. Aromatic hydrocarbons are used in the production of dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
5. Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are hydrocarbons that have carbon atoms arranged in a ring structure. They can be thought of as a combination of alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons. Cycloalkanes are used as solvents and in the production of synthetic fibers.
6. Halogenated Hydrocarbons
Halogenated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that contain one or more halogen atoms (such as chlorine, fluorine, or bromine) in addition to carbon and hydrogen. They have various industrial uses, including as solvents, refrigerants, and flame retardants.
These are just a few examples of the many types of hydrocarbons that exist. Each type has its own unique properties and applications, making hydrocarbons an essential part of various industries and everyday life.
Hydrocarbon Companies and Industry
Hydrocarbons play a crucial role in various industries, and many companies are involved in their production, exploration, and distribution. These companies are at the forefront of the hydrocarbon industry, driving innovation and meeting the global demand for energy.
Some of the major hydrocarbon companies include:
1. ExxonMobil: ExxonMobil is one of the largest publicly traded international oil and gas companies. With operations in more than 40 countries, ExxonMobil explores, produces, and sells hydrocarbons, including crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products.
2. Chevron: Chevron is another leading energy company engaged in the exploration, production, and refining of hydrocarbons. It operates in various segments, including upstream, downstream, and chemicals, and is committed to delivering reliable and affordable energy to meet the world’s growing needs.
3. Royal Dutch Shell: Royal Dutch Shell is a global group of energy and petrochemical companies. It is involved in the exploration, production, refining, and marketing of hydrocarbons. Shell is known for its commitment to sustainable development and is actively investing in renewable energy sources.
4. BP: BP, formerly British Petroleum, is a multinational oil and gas company. It operates in all areas of the oil and gas industry, including exploration, production, refining, distribution, and marketing. BP is focused on delivering energy solutions while reducing its carbon footprint.
5. TotalEnergies: TotalEnergies is a French multinational energy company that operates in all segments of the hydrocarbon industry. It explores, produces, refines, and markets oil and gas products. TotalEnergies is committed to sustainable development and is investing in renewable and low-carbon energy sources.
These companies, along with many others, are vital to meeting the world’s energy needs. They invest heavily in research and development to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and explore new sources of hydrocarbons. Additionally, they contribute significantly to the economies of the countries in which they operate.
While the hydrocarbon industry has faced challenges and criticism due to its environmental impact, these companies are actively working towards cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions. They are investing in renewable energy sources, carbon capture technologies, and are exploring ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Uses of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons play a vital role in various industries and everyday life. They are used in a wide range of applications due to their unique properties. Here are some of the major uses of hydrocarbons:
1. Fuel: Hydrocarbons are primarily used as fuels. They are the main component of gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel, which power vehicles, airplanes, and other forms of transportation. Hydrocarbons release energy when burned, making them an efficient source of fuel.
2. Heating and Cooking: Hydrocarbons such as natural gas and propane are commonly used for heating homes and cooking. They provide a clean and efficient source of energy for these purposes.
3. Electricity Generation: Hydrocarbons are used in power plants to generate electricity. Natural gas and coal, which are rich in hydrocarbons, are burned to produce steam, which drives turbines and generates electricity.
5. Lubricants: Hydrocarbons are used as lubricants in machinery and engines to reduce friction and wear. Motor oil, for example, is a hydrocarbon-based lubricant that helps to keep engines running smoothly.
6. Pharmaceuticals: Hydrocarbons are used in the production of pharmaceutical drugs. They serve as solvents, carriers, and reactants in the synthesis of various medications.
7. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Hydrocarbons are commonly used in the production of cosmetics and personal care products. They are used as emollients, solvents, and viscosity regulators in creams, lotions, and other beauty products.
8. Plastics and Packaging: Hydrocarbons are essential for the production of plastics and packaging materials. They are used to create a wide range of plastic products, including bottles, containers, films, and fibers.
9. Asphalt and Road Construction: Hydrocarbons are used in the production of asphalt, which is used for road construction. Asphalt is a mixture of hydrocarbons and aggregates that provides a durable and smooth surface for roads.
10. Cleaning and Degreasing: Hydrocarbons are used as solvents in cleaning and degreasing applications. They are effective in removing dirt, grease, and other contaminants from various surfaces.
These are just a few examples of the many uses of hydrocarbons. Their versatility and abundance make them indispensable in numerous industries and contribute to our modern way of life.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
