Distribution in Kind: Definition, Benefits, and About Payments
Distribution in kind is a method of distributing assets or investments directly to the shareholders or investors, rather than converting them into cash. This type of distribution allows the shareholders to receive their share of the assets in the form of physical property or securities.
There are several benefits associated with distribution in kind. Firstly, it provides shareholders with the opportunity to directly own and control the assets or investments. This can be particularly advantageous if the distributed assets have the potential for growth or appreciation.
Additionally, distribution in kind can help to minimize transaction costs and taxes. By avoiding the need to sell the assets and convert them into cash, shareholders can potentially reduce brokerage fees and capital gains taxes that would have been incurred through a traditional cash distribution.
Furthermore, distribution in kind allows shareholders to diversify their investment portfolios. By receiving assets or securities instead of cash, shareholders have the opportunity to hold a broader range of investments, which can help to spread risk and potentially enhance returns.
It is important to note that distribution in kind may not always be suitable or practical for all shareholders or investments. Certain assets may be difficult to distribute in kind, such as illiquid investments or assets with complex ownership structures. Additionally, shareholders may prefer cash distributions for various reasons, such as needing immediate liquidity or having a preference for cash investments.
What is Distribution in Kind?
This type of distribution can occur in various situations, such as retirement plans, trusts, or corporate transactions. In the context of retirement planning, distribution in kind refers to the distribution of assets from a retirement account to the account holder upon reaching retirement age.
For example, if an individual has a 401(k) retirement account, they may have the option to receive their distribution in the form of specific investments held within the account, such as stocks or bonds, instead of receiving cash.
Overall, distribution in kind provides individuals with an alternative to receiving cash payments and allows them to directly receive assets or property that may have long-term value or potential for growth.
Benefits of Distribution in Kind
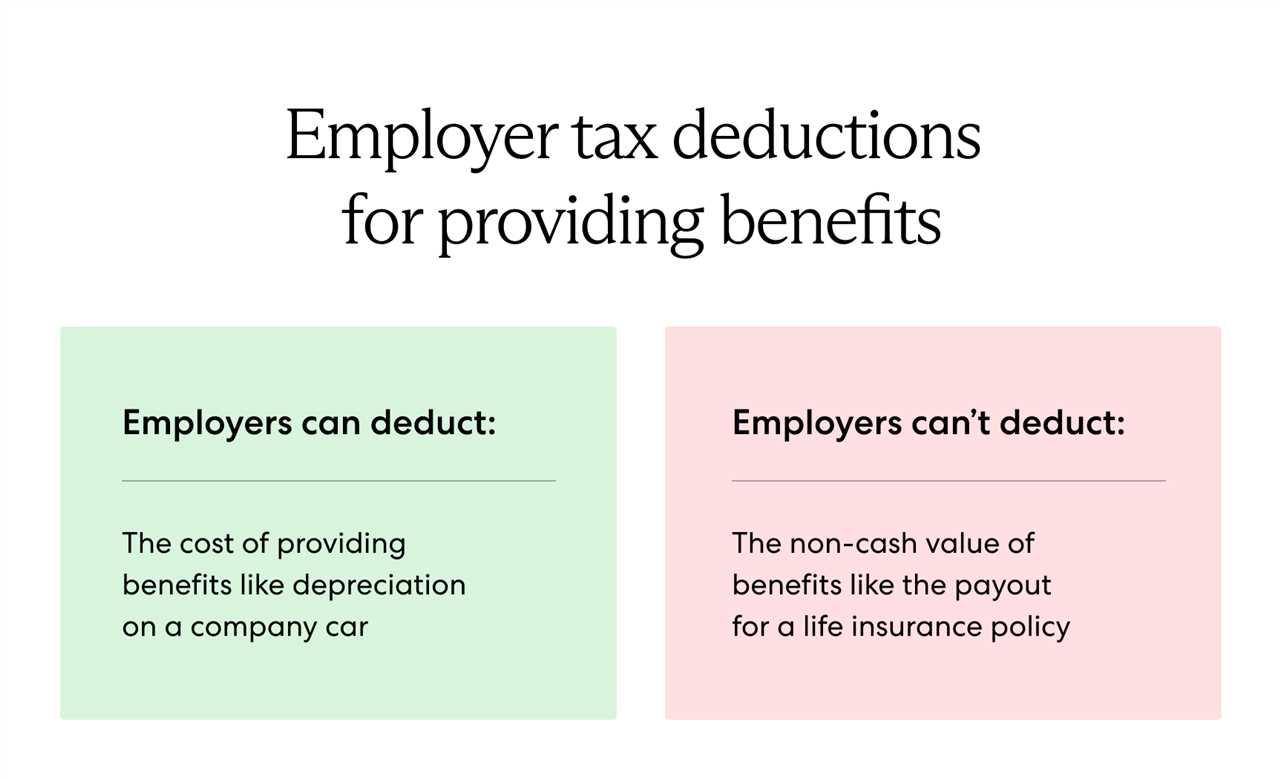
Distribution in kind refers to the process of distributing assets or property directly to the beneficiaries of a retirement plan or investment account, rather than converting them into cash. This method offers several benefits to both the plan participants and the plan sponsor.
One of the main advantages of distribution in kind is that it allows the beneficiaries to receive the assets in their physical form. This means that they can take ownership of the actual property, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, rather than just receiving the cash value. This can be particularly beneficial if the assets have sentimental value or if the beneficiaries have a specific use for them.
Another benefit is that distribution in kind can help to minimize taxes. When assets are distributed in cash, the beneficiaries may be subject to income taxes on the amount received. However, if the assets are distributed in kind, the beneficiaries may be able to defer the taxes until they decide to sell the assets. This can potentially result in significant tax savings, especially if the assets have appreciated in value over time.
Distribution in kind also offers flexibility and control to the beneficiaries. By receiving the assets directly, they have the option to hold onto them, sell them, or transfer them to another investment account. This gives them the freedom to make decisions based on their individual financial goals and circumstances.
Furthermore, distribution in kind can be a cost-effective option for the plan sponsor. Converting assets into cash and then distributing the funds can involve transaction fees and administrative costs. By distributing the assets directly, these expenses can be minimized or eliminated altogether.
It is important to note that distribution in kind may not be suitable for all retirement plans or investment accounts. Certain restrictions or limitations may apply, depending on the specific circumstances and regulations. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine if distribution in kind is the right option for your situation.
About Payments in Distribution in Kind
1. Timing of Payments: In distribution in kind, payments are made in the form of assets rather than cash. The timing of these payments can vary depending on the specific retirement plan and the rules set by the plan administrator. It is important to be aware of the payment schedule and plan accordingly.
2. Valuation of Assets: The assets that are distributed in kind need to be valued accurately. This valuation is typically done by a professional appraiser or an independent third party. The value of the assets will determine the amount of payment you receive. It is important to ensure that the valuation is fair and accurate.
3. Tax Implications: Payments received through distribution in kind may have tax implications. The tax treatment of these payments can vary depending on the type of assets received and your individual tax situation. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand the tax implications and plan accordingly.
4. Options for Payments: In distribution in kind, you may have options for receiving payments. For example, if you receive shares of stock, you may have the option to hold onto the shares or sell them. It is important to carefully consider your options and make decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
5. Documentation and Reporting: It is important to keep proper documentation of the payments received through distribution in kind. This includes keeping records of the assets received, their value, and any tax-related information. It is also important to report these payments accurately on your tax returns to ensure compliance with tax laws.
6. Considerations for Estate Planning: Distribution in kind can also have implications for estate planning. If you plan to pass on your assets to your heirs, it is important to consider how the distribution in kind will impact your estate plan. Consulting with an estate planning attorney can help you navigate these considerations.
How Distribution in Kind Works
Distribution in kind is a method of distributing assets to shareholders or investors in their original form rather than in cash. This means that instead of receiving cash, shareholders receive physical assets such as stocks, bonds, or other securities.
The process of distribution in kind involves several steps. First, the company or fund that is making the distribution must determine the value of the assets to be distributed. This is typically done by calculating the fair market value of the assets at the time of distribution.
Once the value of the assets has been determined, the company or fund will allocate a certain number of shares or units to each shareholder or investor. This allocation is usually based on the proportionate ownership or investment of each individual.
After the allocation has been made, the company or fund will transfer the physical assets to the shareholders or investors. This can be done through various means, such as electronic transfer of securities or physical delivery of certificates.
Once the assets have been transferred, the shareholders or investors become the legal owners of the assets. They can choose to hold onto the assets or sell them in the open market. If they decide to sell, they will receive cash for the assets based on the current market price.
One important thing to note is that distribution in kind may have tax implications for the shareholders or investors. Depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances, the distribution may be subject to capital gains tax or other taxes. It is important for shareholders to consult with a tax advisor or accountant to understand the potential tax consequences.
In summary, distribution in kind is a method of distributing assets to shareholders or investors in their original form. It involves determining the value of the assets, allocating shares or units to each individual, transferring the assets, and potentially incurring tax implications. This method can provide flexibility and diversification for shareholders or investors.
Considerations for Distribution in Kind
1. Tax Implications
One of the key considerations is the potential tax implications of a distribution in kind. Depending on the nature of the assets being distributed, you may be subject to capital gains taxes or other tax obligations. It is important to consult with a tax professional to fully understand the tax implications before making a decision.
2. Liquidity Needs
Another important consideration is your liquidity needs. If you require immediate access to cash, a distribution in kind may not be the best option. While the assets being distributed may have value, they may not be easily convertible to cash. It is important to assess your current financial situation and determine if a distribution in kind aligns with your liquidity needs.
3. Diversification
Diversification is a key principle in investment management. When considering a distribution in kind, it is important to assess how this decision may impact your overall investment portfolio. If the assets being distributed are heavily concentrated in a particular sector or asset class, it may result in an imbalance in your portfolio. This can increase your exposure to risk and potentially impact your long-term investment goals.
4. Transaction Costs
It is also important to consider the transaction costs associated with a distribution in kind. Depending on the nature of the assets being distributed, there may be costs involved in transferring ownership or liquidating the assets. These costs can vary and may impact the overall value of the distribution. It is important to carefully evaluate the potential transaction costs before proceeding with a distribution in kind.
Overall, a distribution in kind can be a viable option for certain individuals, depending on their specific circumstances. It is important to carefully consider these factors and consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to make an informed decision. By doing so, you can ensure that a distribution in kind aligns with your financial goals and objectives.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
