Capital Structure: Definition and Importance
The capital structure of a company refers to the way it finances its operations through a combination of debt and equity. It represents the mix of long-term sources of funds that a company uses to support its activities and investments. The capital structure decision is crucial for a company as it determines its financial stability, risk profile, and ability to generate returns for its shareholders.
Definition of Capital Structure
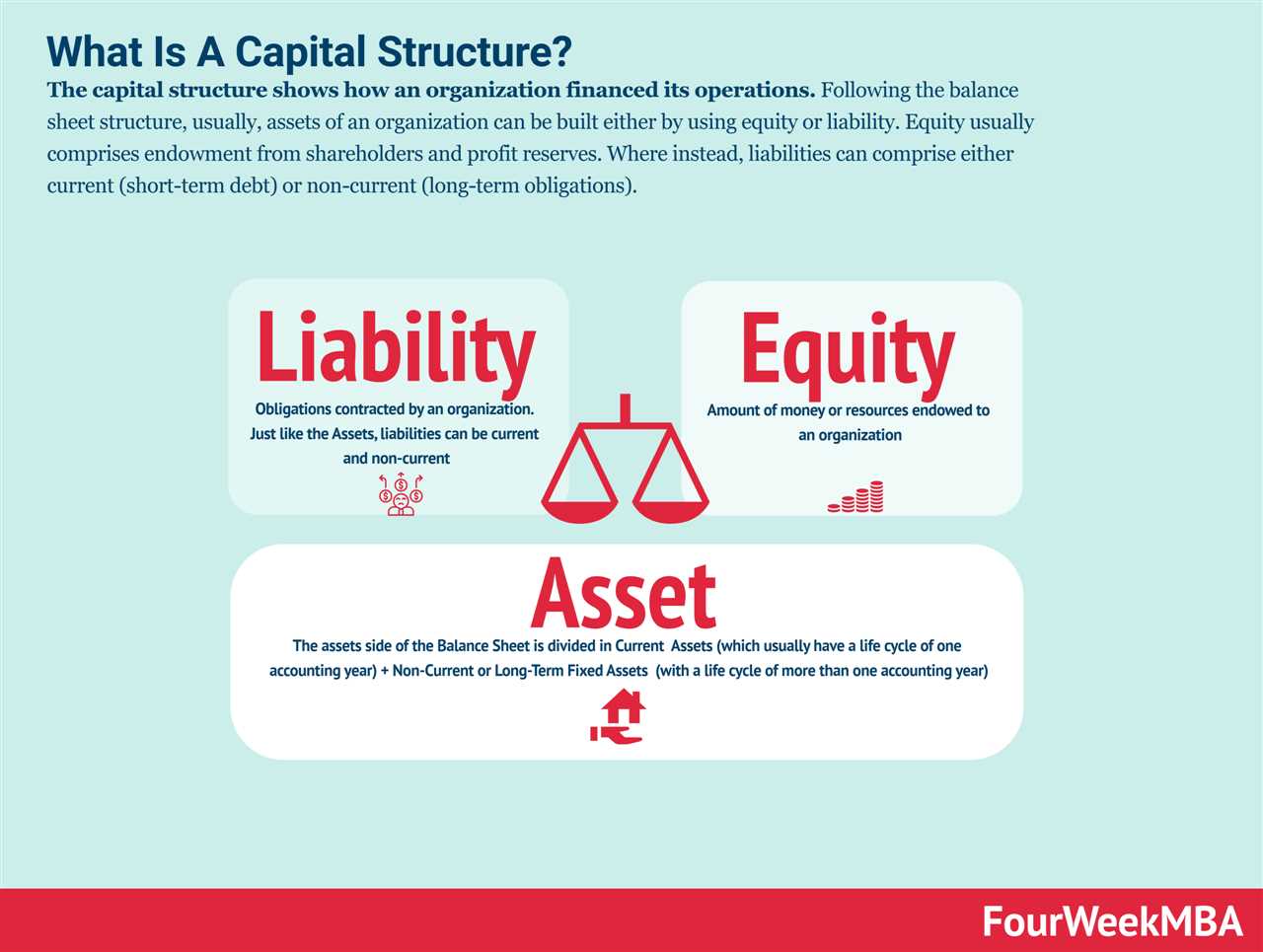
Capital structure is the composition of a company’s liabilities, including long-term debt, short-term debt, preferred equity, and common equity. It is a reflection of how a company chooses to finance its operations and investments. The two primary components of capital structure are debt and equity.
Debt: Debt represents the borrowed funds that a company must repay over time, typically with interest. It can include bank loans, bonds, and other forms of debt financing. By taking on debt, a company increases its financial leverage, which can amplify returns but also increase the risk of financial distress.
Equity: Equity represents the ownership stake in a company held by its shareholders. It can be in the form of common stock or preferred stock. Equity financing does not require repayment, but it entitles shareholders to a share of the company’s profits and voting rights. By issuing equity, a company dilutes existing shareholders’ ownership but also reduces its financial risk.
Importance of Capital Structure
The capital structure decision is crucial for several reasons:
1. Financial Stability: A well-balanced capital structure can provide financial stability to a company by ensuring it has access to the necessary funds to meet its obligations and pursue growth opportunities. By maintaining an appropriate mix of debt and equity, a company can minimize the risk of insolvency and bankruptcy.
3. Cost of Capital: The capital structure affects the cost of capital for a company. Debt financing typically has a lower cost compared to equity financing due to the tax deductibility of interest payments. By optimizing the capital structure, a company can minimize its overall cost of capital and improve its profitability.
4. Investor Perception: The capital structure can influence how investors perceive a company. A highly leveraged company may be seen as riskier, while a company with a conservative capital structure may be viewed as more stable. The capital structure decision can impact a company’s ability to attract investors and access capital markets.
In corporate finance, the term “capital structure” refers to the mix of different sources of funding that a company uses to finance its operations and investments. It represents the proportion of debt and equity in a company’s financial structure. The capital structure decision is crucial for a company as it affects its financial stability, risk profile, and ability to generate returns for its shareholders.
Importance of Capital Structure
The capital structure of a company plays a significant role in determining its overall financial health and performance. Here are some key reasons why capital structure is important:
- Cost of Capital: The capital structure affects the cost of capital for a company. Debt financing generally has a lower cost compared to equity financing. By optimizing the mix of debt and equity, a company can minimize its overall cost of capital and maximize its profitability.
- Financial Flexibility: A well-balanced capital structure provides a company with financial flexibility. By having a mix of debt and equity, a company can access different sources of funding and adjust its capital structure based on its changing financial needs.
- Risk Management: The capital structure also plays a crucial role in managing the risk of a company. Too much debt can increase the financial risk and make a company vulnerable to economic downturns. On the other hand, too much equity can dilute the ownership and control of existing shareholders.
- Investor Perception: The capital structure of a company can influence the perception of investors and creditors. A well-structured capital base with an optimal mix of debt and equity can enhance the credibility and attractiveness of a company to potential investors and lenders.
Factors Affecting Capital Structure
The capital structure decision is influenced by several factors, including:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Risk | The level of risk associated with a company’s operations and industry. |
| Financial Risk | The risk of financial distress due to high levels of debt. |
| Tax Considerations | The impact of taxes on the cost of debt and equity financing. |
| Market Conditions | The prevailing market conditions and availability of financing options. |
| Company Size | The size and scale of the company’s operations. |
| Growth Opportunities | The potential for future growth and investment opportunities. |
By considering these factors, a company can determine the optimal capital structure that aligns with its financial goals and risk tolerance.
The Importance of Capital Structure in Corporate Finance
Capital structure refers to the way a company finances its operations by utilizing a combination of debt and equity. It plays a crucial role in corporate finance as it determines how a company raises funds to support its growth and operations.
One of the key reasons why capital structure is important in corporate finance is because it affects the overall cost of capital. The cost of capital is the rate of return that a company must earn on its investments to satisfy its shareholders and creditors. By carefully managing the capital structure, a company can optimize its cost of capital and maximize its profitability.
Another reason why capital structure is important is because it influences the risk profile of a company. Debt financing introduces financial leverage, which can amplify both the returns and the risks associated with a company’s operations. By striking the right balance between debt and equity, a company can manage its risk exposure and ensure its long-term sustainability.
Furthermore, capital structure also impacts the company’s ability to attract investors and creditors. A well-structured capital base with a mix of debt and equity signals financial stability and confidence to potential investors. It demonstrates that the company has a solid financial foundation and is capable of meeting its financial obligations.
Types of Capital Structure and Examples
Capital structure refers to the way a company finances its operations through a combination of debt and equity. There are various types of capital structure that a company can adopt, depending on its financial goals and risk appetite. Here are some common types of capital structure:
1. Debt Capital Structure
A debt capital structure is one where a company relies heavily on debt financing to fund its operations. This can include bank loans, bonds, and other forms of debt. The advantage of a debt capital structure is that it allows the company to leverage its assets and generate higher returns on equity. However, it also increases the company’s financial risk, as it needs to make regular interest and principal payments.
2. Equity Capital Structure
An equity capital structure is one where a company relies primarily on equity financing to fund its operations. This can include issuing shares of stock to investors in exchange for capital. The advantage of an equity capital structure is that it does not require regular interest or principal payments, reducing the financial risk for the company. However, it dilutes the ownership of existing shareholders and may limit the company’s ability to raise additional funds in the future.
3. Hybrid Capital Structure
A hybrid capital structure is a combination of debt and equity financing. This can include a mix of bank loans, bonds, and equity investments. The advantage of a hybrid capital structure is that it allows the company to take advantage of the benefits of both debt and equity financing. It provides the company with the flexibility to adjust its capital structure based on its financial needs and market conditions.
Examples of different capital structures can be found in various industries. For instance, technology startups often rely on equity financing from venture capitalists and angel investors to fund their growth. On the other hand, established companies in capital-intensive industries like manufacturing or utilities may have a higher proportion of debt in their capital structure to finance their operations and investments.
| Company | Capital Structure |
|---|---|
| Company A | 70% debt, 30% equity |
| Company B | 40% debt, 60% equity |
| Company C | 50% debt, 50% equity |
These examples illustrate the different combinations of debt and equity financing that companies can adopt to meet their financial objectives. It is important for companies to carefully consider their capital structure and strike a balance between debt and equity to optimize their financial performance and manage their risk effectively.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
