Definition and Explanation of Butterfly Spread
A butterfly spread is a popular options trading strategy that involves the simultaneous purchase and sale of three options contracts with the same expiration date but different strike prices. It is a neutral strategy that can be used when the trader expects the underlying asset to stay within a certain price range.
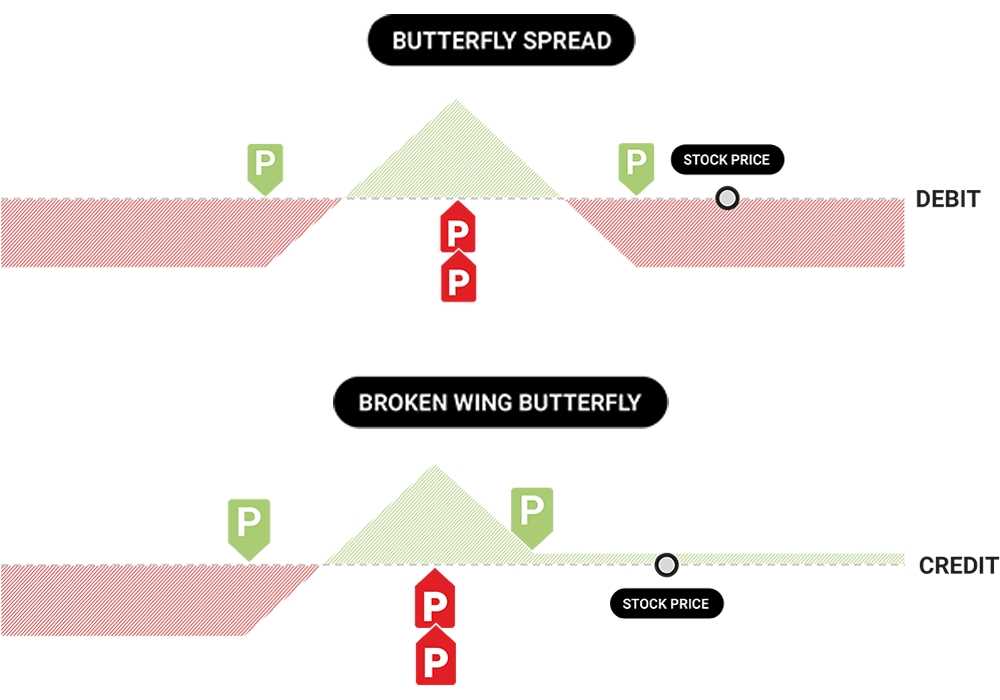
The butterfly spread gets its name from the shape of the profit and loss graph that it creates. When plotted on a graph, the resulting pattern resembles the wings of a butterfly, with a narrow body and wider wings. This graph shows the potential profit or loss at expiration based on the underlying asset’s price.
How Does a Butterfly Spread Work?
To construct a butterfly spread, the trader buys one option contract at a lower strike price, sells two option contracts at a middle strike price, and buys one option contract at a higher strike price. The middle strike price is usually chosen to be equidistant from the lower and higher strike prices.
If the underlying asset’s price at expiration is below the lower strike price or above the higher strike price, the butterfly spread will result in a loss. The maximum loss is limited to the initial cost of the spread.
When to Use a Butterfly Spread?
Traders often use butterfly spreads when they anticipate a period of consolidation or when they want to hedge an existing position. By using this strategy, traders can limit their risk while still having the potential for a small profit.
Types of Butterfly Spread
A butterfly spread is a popular options trading strategy that involves the use of multiple options contracts with different strike prices. There are several types of butterfly spreads, each with its own unique characteristics and potential profit/loss outcomes.
1. Call Butterfly Spread: This type of butterfly spread is created using call options. It involves buying one call option with a lower strike price, selling two call options with a middle strike price, and buying one call option with a higher strike price. The goal of a call butterfly spread is to profit from a limited price range where the underlying asset’s price remains relatively stable.
2. Put Butterfly Spread: Similar to the call butterfly spread, the put butterfly spread is created using put options. It involves buying one put option with a lower strike price, selling two put options with a middle strike price, and buying one put option with a higher strike price. The objective of a put butterfly spread is also to profit from a limited price range where the underlying asset’s price remains relatively stable.
3. Long Call Butterfly Spread: This type of butterfly spread is created by buying one call option with a lower strike price, selling two call options with a middle strike price, and buying one call option with a higher strike price. The long call butterfly spread is used when the trader expects a moderate increase in the underlying asset’s price.
4. Long Put Butterfly Spread: Similar to the long call butterfly spread, the long put butterfly spread is created by buying one put option with a lower strike price, selling two put options with a middle strike price, and buying one put option with a higher strike price. It is used when the trader expects a moderate decrease in the underlying asset’s price.
5. Short Call Butterfly Spread: This type of butterfly spread is created by selling one call option with a lower strike price, buying two call options with a middle strike price, and selling one call option with a higher strike price. The short call butterfly spread is used when the trader expects the underlying asset’s price to remain relatively stable.
6. Short Put Butterfly Spread: Similar to the short call butterfly spread, the short put butterfly spread is created by selling one put option with a lower strike price, buying two put options with a middle strike price, and selling one put option with a higher strike price. It is used when the trader expects the underlying asset’s price to remain relatively stable.
Each type of butterfly spread has its own risk/reward profile and is suitable for different market conditions. Traders and investors use butterfly spreads to take advantage of specific price movements or to hedge their positions against potential losses. It is important to thoroughly understand the characteristics and potential outcomes of each type of butterfly spread before implementing them in options trading strategies.
Example of Butterfly Spread
Let’s take a look at an example to understand how a butterfly spread works. Suppose the stock price of XYZ Company is currently trading at $100 per share. You believe that the stock price will remain relatively stable in the near future, but you expect a slight increase in volatility.
Step 1: Establish the Options Positions
To create a butterfly spread, you would need to establish three options positions:
- Buy one at-the-money call option with a strike price of $100
- Sell two out-of-the-money call options with a strike price of $105
- Buy one further out-of-the-money call option with a strike price of $110
By buying and selling these options, you are creating a spread with a limited risk and a limited profit potential.
Step 2: Calculate the Maximum Profit and Loss

The maximum profit and loss of a butterfly spread can be calculated as follows:
- Maximum loss = Net premium paid
In our example, let’s assume the net premium paid for the options positions is $3 per share.
Step 3: Analyze the Payoff Diagram
Once you have established the options positions and calculated the maximum profit and loss, you can analyze the payoff diagram to understand the potential outcomes of the butterfly spread.
The payoff diagram of a butterfly spread typically looks like a butterfly, hence the name. It shows that the maximum profit is achieved when the stock price is equal to the strike price of the middle call options ($105 in our example), and the maximum loss is incurred when the stock price is below the strike price of the lower call options ($100 in our example) or above the strike price of the higher call options ($110 in our example).
By analyzing the payoff diagram, you can assess the risk-reward profile of the butterfly spread and make informed decisions about whether to enter into this options strategy.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
