What Is a Closed Economy?
A closed economy is an economic system in which a country does not engage in international trade or financial transactions with other countries. In a closed economy, all economic activities, such as production, consumption, and investment, are confined within the boundaries of the country.
In a closed economy, there are no imports or exports of goods and services. This means that all the goods and services consumed within the country are produced domestically, and there is no exchange of goods and services with other countries. Similarly, there are no financial flows, such as foreign investments or loans, between the closed economy and the rest of the world.
One of the key characteristics of a closed economy is that it is self-sufficient in terms of its economic activities. It relies solely on its own resources and capabilities to meet the needs and demands of its population. This means that the closed economy produces all the goods and services required for consumption and investment within its own borders.
Another important aspect of a closed economy is that it operates under a fixed exchange rate system. This means that the value of the country’s currency is fixed in relation to another currency or a basket of currencies. The fixed exchange rate helps to maintain stability in the closed economy and prevents fluctuations in the value of the currency.
Overall, a closed economy is a self-contained economic system that does not engage in international trade or financial transactions. It relies on its own resources and operates under a fixed exchange rate system. While closed economies were more common in the past, today most countries have adopted open economies and engage in global trade and financial transactions.
A closed economy is a system in which a country does not engage in international trade or financial transactions with other countries. In a closed economy, all economic activities, such as production, consumption, and investment, are conducted within the boundaries of the country.
Characteristics of a Closed Economy
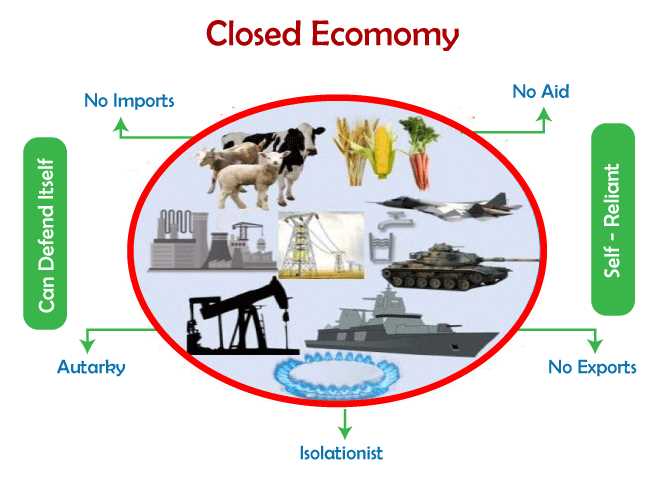
One of the key characteristics of a closed economy is that it is self-sufficient. It produces all the goods and services it needs internally, without relying on imports from other countries. This means that the country must have a diverse range of industries to meet the demands of its population.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of a Closed Economy

There are both advantages and disadvantages to having a closed economy. One advantage is that it can protect domestic industries from foreign competition. By restricting imports, the government can promote the growth of domestic industries and protect jobs. This can be particularly important for developing countries that are trying to build up their industries.
However, a closed economy also has its disadvantages. One major disadvantage is that it can lead to inefficiencies and lack of innovation. Without competition from foreign firms, domestic industries may have less incentive to improve their products and processes. This can result in lower quality goods and higher prices for consumers.
Another disadvantage is that a closed economy can limit opportunities for economic growth. By not participating in international trade, the country misses out on potential markets for its goods and services. It also misses out on the benefits of foreign investment, which can bring in new technologies and expertise.
Why Are There None Today?
1. Trade Liberalization: The shift towards open economies can be attributed to the liberalization of trade. Many countries have implemented policies that promote free trade and reduce barriers to international trade. This has led to increased economic integration and the dismantling of closed economies.
2. Globalization: Globalization has played a significant role in the decline of closed economies. With advancements in technology and transportation, it has become easier for countries to engage in international trade and exchange goods and services. This has encouraged countries to open up their economies and participate in the global marketplace.
3. Economic Benefits: Open economies offer several economic benefits that closed economies cannot match. By opening up their economies, countries can attract foreign direct investment, access new markets, and benefit from economies of scale. This can lead to increased economic growth, job creation, and improved living standards.
4. Access to Resources and Expertise: Closed economies often lack access to resources and expertise that can be obtained through international trade. By opening up their economies, countries can tap into global supply chains and access a wide range of resources, including raw materials, technology, and skilled labor. This can enhance productivity and competitiveness in the global market.
5. Political Considerations: The decline of closed economies can also be attributed to political considerations. Many countries have realized that engaging in international trade and opening up their economies can lead to improved diplomatic relations and political stability. By participating in the global economy, countries can foster cooperation and build alliances with other nations.
| Reasons for the Decline of Closed Economies |
|---|
| Trade Liberalization |
| Globalization |
| Economic Benefits |
| Access to Resources and Expertise |
| Political Considerations |
The Shift to Open Economies and Globalization
In recent decades, there has been a significant shift from closed economies to open economies, driven by the forces of globalization. This shift has had a profound impact on the way countries conduct business and interact with each other.
Open economies are characterized by the free flow of goods, services, capital, and information across national borders. This means that countries engage in international trade, allowing them to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage.
Globalization has played a crucial role in facilitating this shift towards open economies. Advances in technology, particularly in transportation and communication, have made it easier for countries to connect and engage in trade. This has led to increased economic interdependence among nations.
One of the key benefits of open economies is the potential for economic growth. By participating in international trade, countries can access larger markets and take advantage of economies of scale. This can lead to increased productivity, innovation, and job creation.
Open economies also promote competition, which can drive efficiency and improve the quality of goods and services. When countries are exposed to competition from foreign firms, they are incentivized to improve their own products and processes to remain competitive in the global marketplace.
However, the shift to open economies is not without challenges. It can lead to increased income inequality, as some individuals and industries may be negatively affected by globalization. It can also create vulnerabilities in the form of economic shocks, as countries become more interconnected and susceptible to external economic events.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
