Definition and Calculation
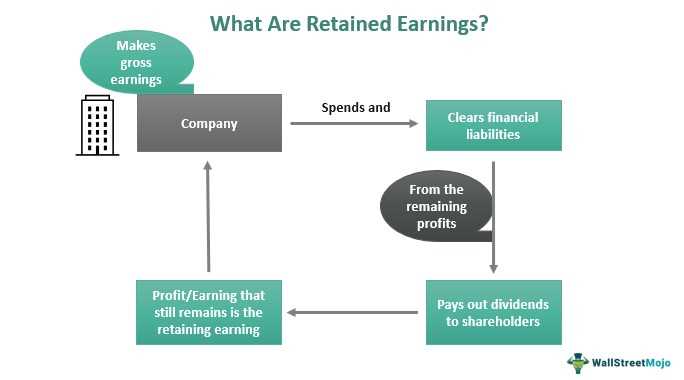
In accounting, retained earnings refer to the portion of a company’s net income that is retained or reinvested back into the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. It represents the accumulated profits of a company over time.
The calculation of retained earnings is relatively straightforward. It begins with the opening balance of retained earnings from the previous accounting period. To this, the net income or loss for the current period is added or subtracted, respectively. Dividends paid to shareholders are then deducted. The resulting figure is the closing balance of retained earnings, which carries forward to the next accounting period.
Retained earnings can be calculated using the following formula:
| Retained Earnings (end of period) = |
For example, if a company has a beginning balance of retained earnings of $100,000, earns a net income of $50,000, and pays dividends of $10,000, the calculation would be as follows:
| Retained Earnings (end of period) = |
Therefore, the closing balance of retained earnings would be $140,000.
Importance in Accounting
- Measure of Profitability: Retained earnings reflect the accumulated profits of a company over time. By analyzing the trend of retained earnings, stakeholders can assess the company’s profitability and its ability to generate consistent earnings.
- Source of Internal Financing: Retained earnings serve as a source of internal financing for a company. Instead of relying on external sources such as loans or issuing new shares, a company can use its retained earnings to fund various activities like expansion, research and development, or debt repayment.
- Indicator of Financial Stability: A healthy level of retained earnings indicates financial stability and resilience. It shows that a company has sufficient profits to cover its obligations, withstand economic downturns, and invest in future growth opportunities.
- Dividend Payments: Companies often distribute a portion of their retained earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. The amount of dividends paid out is influenced by the level of retained earnings. Investors consider dividend payments as a sign of a company’s financial strength and potential for future growth.
- Decision-Making Tool: Retained earnings provide valuable information for decision-making within a company. Management can use the trend of retained earnings to assess the effectiveness of past business strategies, evaluate investment opportunities, and make informed decisions about future financial plans.
Implications for Businesses
Retained earnings play a crucial role in the financial health and growth of businesses. They provide valuable insights and information to business owners, investors, and stakeholders about the profitability and sustainability of a company.
1. Financial Stability

2. Reinvestment and Growth
Retained earnings can be reinvested back into the business to fuel its growth and expansion. By retaining a portion of the profits, companies can fund research and development, purchase new equipment, hire additional staff, or expand their operations. This reinvestment can lead to increased productivity, market share, and competitiveness.
Furthermore, retained earnings can also be used to finance mergers and acquisitions, allowing businesses to expand their reach and diversify their offerings. This strategic use of retained earnings can help companies stay ahead in a competitive market.
3. Dividends and Shareholder Value
Additionally, companies with higher retained earnings may choose to distribute dividends to their shareholders. Dividends are a way for businesses to reward their investors and provide them with a share of the profits. By distributing dividends, companies can attract and retain shareholders, which can positively impact their reputation and stock performance.
4. Borrowing Capacity
On the other hand, a negative balance in retained earnings or consistently low retained earnings may raise concerns among lenders, making it more difficult for a business to secure loans or credit. Therefore, maintaining a healthy level of retained earnings is crucial for businesses that rely on external financing for their operations or expansion.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
