What are Indirect Loans?
How do Indirect Loans Work?

The process of obtaining an indirect loan typically involves the following steps:
- The borrower expresses interest in obtaining a loan through the intermediary, such as a car dealership.
- The intermediary collects the necessary information and documents from the borrower, including their financial details and credit history.
- The intermediary submits the loan application to multiple lenders on behalf of the borrower.
- The lenders review the loan application and make a decision on whether to approve or deny the loan.
- If the loan is approved, the lender provides the funds to the intermediary.
- The intermediary then disburses the funds to the borrower, and the borrower is responsible for repaying the loan to the lender.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Indirect Loans
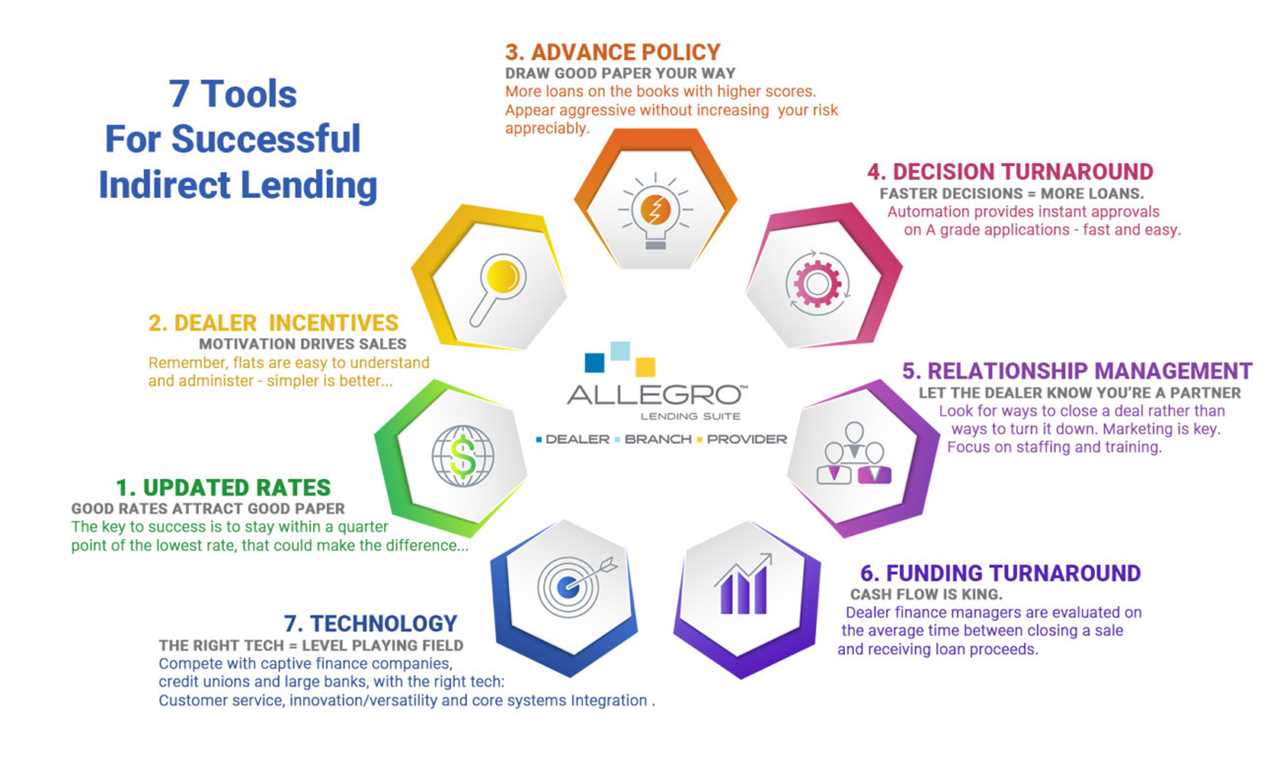
Indirect loans offer several advantages for borrowers:
- Convenience: Borrowers can obtain financing through an intermediary without having to directly contact multiple lenders.
- Access to Multiple Lenders: Intermediaries often work with multiple lenders, which increases the chances of finding a loan with favorable terms and conditions.
- Streamlined Application Process: Intermediaries help simplify the loan application process by collecting and organizing the necessary documents.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- Higher Interest Rates: Indirect loans may come with higher interest rates compared to direct loans, as intermediaries may add their own fees and commissions.
Overall, indirect loans can be a convenient option for borrowers who prefer to have a middleman handle the loan application process. However, it is important for borrowers to carefully review the terms and conditions of the loan and ensure that they are getting the best possible deal.
The Process of Obtaining an Indirect Loan
Obtaining an indirect loan involves several steps that borrowers need to follow in order to secure financing for their desired purchase. Here is a breakdown of the typical process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Research and Choose a Dealership |
| 2 | Select a Vehicle |
| 3 | Negotiate the Price |
| 4 | Submit a Loan Application |
| 5 | Dealer Submits the Application to Lenders |
| 6 | Lenders Review the Application |
| 7 | Loan Approval or Denial |
| 8 | Loan Documentation and Signing |
| 9 | Vehicle Delivery |
Firstly, borrowers need to research and choose a dealership that offers indirect financing options. This can be done by visiting different dealerships or researching online. Once a dealership is selected, borrowers can proceed to the next step.
The second step involves selecting a vehicle that meets the borrower’s needs and preferences. This includes considering factors such as make, model, year, and features. The dealership may have a wide range of vehicles to choose from.
After selecting a vehicle, borrowers need to negotiate the price with the dealership. This step is crucial as it determines the final cost of the vehicle and the loan amount that needs to be financed.
Once the price is agreed upon, borrowers need to submit a loan application to the dealership. The application typically requires personal and financial information, such as employment details, income, and credit history.
After receiving the loan application, the dealership submits it to multiple lenders who specialize in indirect financing. These lenders review the application and assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
Based on their evaluation, the lenders make a decision regarding loan approval or denial. If approved, the borrower can proceed to the next step. If denied, the borrower may need to explore other financing options or reconsider their vehicle choice.
If the loan is approved, the borrower needs to complete the necessary loan documentation and sign the loan agreement. This includes reviewing and signing the loan terms, interest rate, repayment schedule, and any other relevant documents.
Once the loan documentation is completed, the dealership arranges for the delivery of the vehicle to the borrower. This marks the final step of the process, and the borrower can now enjoy their new vehicle.
It is important for borrowers to carefully navigate the process of obtaining an indirect loan to ensure they secure the best financing terms and make an informed decision about their purchase.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Indirect Loans
Indirect loans can offer several benefits to borrowers, but they also come with some drawbacks. It is important to weigh these factors before deciding to pursue an indirect loan.
Benefits of Indirect Loans:

- Convenience: One of the main advantages of indirect loans is the convenience they offer. Borrowers can apply for a loan through a dealership or other intermediary, eliminating the need to visit multiple lenders or go through a lengthy application process.
- Access to Multiple Lenders: Indirect loans provide borrowers with access to a wide range of lenders. This increases the chances of finding a loan with favorable terms and interest rates.
- Opportunity to Build Credit: For borrowers with limited or poor credit history, indirect loans can provide an opportunity to build credit. Making timely payments on an indirect loan can help improve credit scores over time.
Drawbacks of Indirect Loans:
- Higher Interest Rates: Indirect loans may come with higher interest rates compared to direct loans. This is because the dealership or intermediary may add their own markup to the loan, increasing the overall cost for the borrower.
- Potential for Hidden Fees: Borrowers should be aware that there may be hidden fees associated with indirect loans. These can include origination fees, documentation fees, and other charges that may not be immediately apparent.
- Limited Negotiation Power: When obtaining an indirect loan, borrowers may have limited negotiation power compared to securing a loan directly from a lender. The terms and conditions of the loan are often set by the dealership or intermediary, leaving little room for negotiation.
- Dependency on Third Parties: Indirect loans involve multiple parties, including the borrower, dealership, and lender. This can lead to potential delays or complications in the loan process, as well as a lack of direct control over the loan terms.
Real-life Examples of Indirect Loans
Indirect loans are a common financing option for various types of purchases, including cars, homes, and even personal loans. Here are some real-life examples of how indirect loans work in different scenarios:
1. Car Loans
When purchasing a car from a dealership, many buyers opt for indirect loans. The dealership acts as an intermediary between the buyer and the lender. The buyer fills out a loan application at the dealership, and the dealership then sends the application to multiple lenders to find the best loan terms. Once approved, the lender provides the funds to the dealership, and the buyer makes monthly payments to the lender.
2. Home Mortgages
Indirect loans are also prevalent in the real estate market. Homebuyers often work with mortgage brokers who connect them with lenders. The mortgage broker collects the necessary financial information from the buyer and submits it to multiple lenders to find the best mortgage terms. Once approved, the lender provides the funds to the mortgage broker, and the buyer makes monthly mortgage payments to the lender.
3. Personal Loans
Indirect loans can also be used for personal financing needs. For example, if someone needs a personal loan, they can work with a loan broker. The loan broker will gather the borrower’s financial information and submit it to various lenders to find the best loan terms. Once approved, the lender provides the funds to the loan broker, and the borrower makes monthly payments to the lender.
Overall, indirect loans provide borrowers with the convenience of having a third party handle the loan application process and connect them with multiple lenders. This can save borrowers time and effort in searching for the best loan terms on their own.
| Pros of Indirect Loans | Cons of Indirect Loans |
|---|---|
|
|

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
