What is Demand-Pull Inflation?
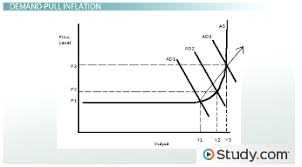
Demand-pull inflation is a type of inflation that occurs when the demand for goods and services in an economy exceeds the supply. This imbalance between supply and demand leads to an increase in the overall price level of goods and services. In other words, it is a situation where there is “too much money chasing too few goods.”
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation
There are several factors that can contribute to demand-pull inflation:
- Increased consumer spending: When consumers have more money to spend, they tend to increase their purchases of goods and services. This increased demand can put pressure on prices to rise.
- Government spending: When the government increases its spending on infrastructure projects or social programs, it can stimulate demand in the economy. This increased demand can lead to inflationary pressures.
- Low interest rates: When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, and consumers and businesses are more likely to take on debt to finance purchases. This increased spending can drive up prices.
- Strong economic growth: When an economy is experiencing strong economic growth, there is often increased demand for goods and services. This increased demand can lead to inflation.
Impact of Demand-Pull Inflation on the Economy
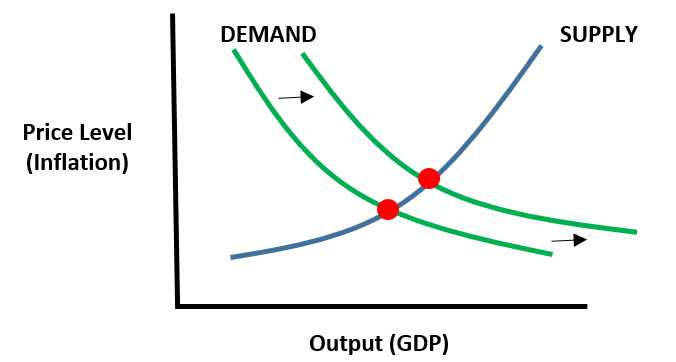
Demand-pull inflation can have both positive and negative effects on the economy:
- Positive effects: Demand-pull inflation can be a sign of a growing economy. It can indicate that consumers have more purchasing power and businesses are thriving. This can lead to increased investment and job creation.
- Negative effects: However, demand-pull inflation can also lead to negative consequences. It can erode the purchasing power of consumers, especially those on fixed incomes. It can also lead to higher production costs for businesses, which can result in lower profits and potential layoffs.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds the supply, leading to an increase in prices. There are several factors that can contribute to the occurrence of demand-pull inflation:
| 1. Increase in consumer spending |
|---|
| When consumers have more disposable income, they are likely to increase their spending. This increase in consumer spending creates a higher demand for goods and services, which can lead to inflationary pressures. |
| 2. Expansionary fiscal policy |
| Expansionary fiscal policy, such as increased government spending or tax cuts, can stimulate economic growth and increase aggregate demand. This increase in aggregate demand can outpace the economy’s ability to produce goods and services, resulting in inflation. |
| 3. Expansionary monetary policy |
| Expansionary monetary policy, such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply, can also stimulate economic growth and increase aggregate demand. However, if the increase in aggregate demand exceeds the economy’s capacity to produce, it can lead to demand-pull inflation. |
| 4. Increase in government spending |
| When the government increases its spending on goods and services, it can create additional demand in the economy. If this additional demand is not met with an increase in supply, it can result in inflation. |
| 5. Increase in exports |
| When a country’s exports increase, it can lead to an increase in aggregate demand. If the increase in aggregate demand is not matched by an increase in supply, it can result in demand-pull inflation. |
These are just a few of the factors that can contribute to demand-pull inflation. It is important for policymakers to carefully monitor these factors and take appropriate measures to manage inflationary pressures and maintain price stability in the economy.
Impact of Demand-Pull Inflation on the Economy
One of the main effects of demand-pull inflation is a decrease in the purchasing power of consumers. As prices rise, individuals are able to buy fewer goods and services with the same amount of money. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can have a negative impact on businesses and overall economic growth.
Additionally, demand-pull inflation can lead to an increase in production costs for businesses. As demand increases, businesses may need to hire more workers or invest in new equipment to meet the rising demand. These additional costs can be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices, further exacerbating the inflationary pressures.
Furthermore, demand-pull inflation can also lead to income redistribution within the economy. As prices rise, individuals and businesses that are able to increase their prices or wages faster than the rate of inflation may benefit, while those who are unable to do so may suffer. This can lead to increased income inequality and social unrest.
On the positive side, demand-pull inflation can also stimulate economic growth. As demand increases, businesses may invest in new projects and expand their operations, creating jobs and increasing productivity. This can lead to higher wages and overall economic prosperity.
However, it is important to note that the positive effects of demand-pull inflation are often temporary and can be outweighed by the negative consequences. If inflation becomes too high and uncontrollable, it can lead to economic instability, as individuals and businesses struggle to keep up with rising prices.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
