Definition of Debt Issue

A debt issue refers to the process of raising funds by a company through the issuance of debt securities to investors. Debt securities can take various forms, such as bonds, notes, or debentures, and they represent a contractual obligation for the company to repay the borrowed amount along with periodic interest payments.
When a company decides to issue debt, it essentially borrows money from investors who purchase these debt securities. The company then becomes liable to repay the principal amount borrowed, usually at a predetermined maturity date, and make regular interest payments to the investors.
Types of Debt Issues
There are different types of debt issues that a company can choose from, depending on its specific needs and financial goals. Some common types of debt issues include:
- Bonds: Bonds are long-term debt securities with a maturity period typically exceeding one year. They are usually issued by governments, municipalities, and large corporations.
- Notes: Notes are shorter-term debt securities with a maturity period ranging from a few months to a few years. They are commonly issued by corporations to meet their short-term financing needs.
- Debentures: Debentures are unsecured debt securities that are backed only by the general creditworthiness and reputation of the issuing company. They do not have any specific collateral backing.
The Process of Debt Issue
The process of issuing debt involves several steps:
- Planning: The company determines its financing needs and decides on the amount of debt it wants to raise.
- Documentation: The company prepares the necessary legal documents, such as a prospectus or offering memorandum, which provide detailed information about the debt issue.
- Underwriting: The company may engage the services of an underwriter, such as an investment bank, to help sell the debt securities to investors.
- Marketing and Pricing: The company promotes the debt issue to potential investors and determines the interest rate or coupon rate at which the securities will be issued.
- Allocation and Closing: Once the debt securities are sold, the company allocates them to the investors and completes the closing process, including the transfer of funds.
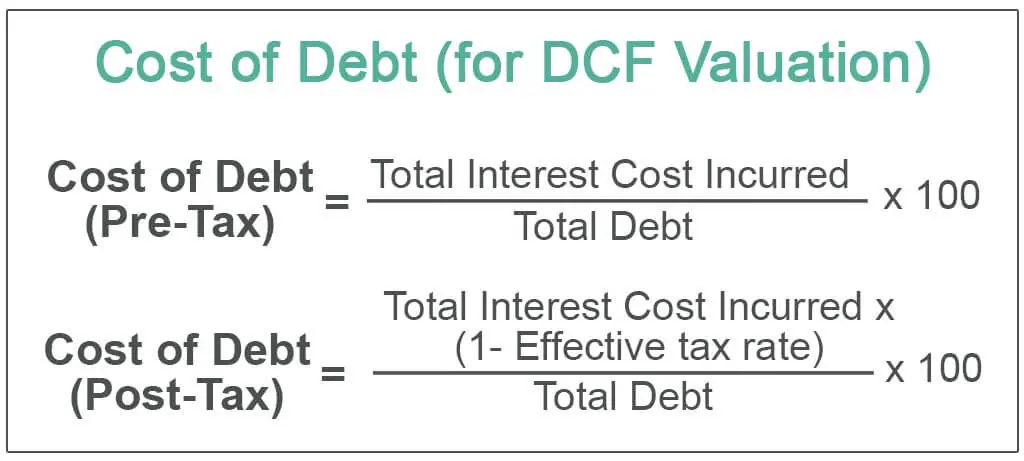
Costs of Debt Issue
Issuing debt securities involves various costs for the company, including:
- Underwriting Fees: The underwriter charges a fee for its services in helping the company sell the debt securities.
- Legal and Administrative Costs: The company incurs expenses related to legal and administrative work, such as drafting the necessary documents and complying with regulatory requirements.
- Interest Payments: The company is obligated to make regular interest payments to the investors, which adds to its overall cost of borrowing.
Overall, debt issues play a crucial role in a company’s financing strategy, allowing it to raise capital for various purposes, such as funding expansion plans, refinancing existing debt, or supporting day-to-day operations. However, it is important for companies to carefully consider the costs and risks associated with issuing debt before proceeding with such financing activities.
Process of Debt Issue
Debt issue refers to the process of borrowing money by a company or organization through the issuance of debt securities, such as bonds or notes. This process involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure a successful debt issue.
- Assessing the need for debt: Before initiating a debt issue, the company needs to evaluate its financial situation and determine if taking on debt is necessary. This involves analyzing the company’s cash flow, current debt levels, and future financial obligations.
- Preparing the offering documents: The next step involves preparing the necessary offering documents, which provide detailed information about the debt issue. These documents typically include a prospectus or offering memorandum that outlines the terms of the debt, such as interest rates, maturity dates, and any associated risks.
- Engaging underwriters: To facilitate the debt issue, companies often engage the services of underwriters. Underwriters are financial institutions or investment banks that help sell the debt securities to investors. They assist in pricing the debt, marketing the offering, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Marketing and pricing the debt: Once the offering documents are prepared and underwriters are engaged, the company begins marketing the debt to potential investors. This involves conducting roadshows, making presentations, and providing information to attract investors. The underwriters work with the company to determine the optimal pricing for the debt securities.
- Managing the debt: Once the debt issue is complete, the company needs to manage the debt effectively. This includes making regular interest payments to investors, monitoring the debt’s performance, and ensuring compliance with any covenants or obligations outlined in the debt agreement.
The process of debt issue can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and coordination. However, it provides companies with a valuable source of funding to support their operations, growth, and strategic initiatives.
Costs of Debt Issue
When a company decides to issue debt, there are several costs associated with the process. These costs can have a significant impact on the overall financial health of the company and should be carefully considered before proceeding with a debt issue.
One of the main costs of a debt issue is the interest expense. When a company borrows money, it is required to pay interest on the borrowed amount. The interest rate is determined by various factors, including the creditworthiness of the company and prevailing market rates. Higher interest rates can increase the cost of borrowing and reduce the profitability of the company.
In addition to interest expense, there are other costs involved in the debt issue process. These include legal fees, underwriting fees, and administrative costs. Legal fees are incurred to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and to draft the necessary documentation for the debt issue. Underwriting fees are paid to investment banks or financial institutions that assist in the sale of the debt securities. Administrative costs include expenses related to the management and servicing of the debt.
Another cost to consider is the potential impact on the company’s credit rating. When a company issues debt, it increases its overall debt burden, which can negatively affect its creditworthiness. A lower credit rating can result in higher borrowing costs in the future and make it more difficult for the company to raise additional funds. It is important for companies to carefully assess the impact of a debt issue on their credit rating and overall financial position.
Lastly, there are indirect costs associated with a debt issue. These include the potential loss of flexibility and control over the company’s operations. When a company takes on debt, it may be required to meet certain financial covenants or restrictions imposed by the lenders. These covenants can limit the company’s ability to make certain business decisions or require it to maintain certain financial ratios. This loss of flexibility can hinder the company’s ability to respond to changing market conditions or pursue growth opportunities.
Corporate Debt
Corporate debt refers to the borrowing of funds by a corporation to finance its operations or investment activities. It is a common practice for companies to issue debt securities, such as bonds or debentures, to raise capital from investors. This allows the company to access additional funds without diluting ownership or control.
There are several reasons why corporations may choose to issue debt. Firstly, it provides an alternative source of funding to supplement internal cash flows. This is particularly important for companies that have limited cash reserves or are experiencing a temporary cash shortfall. Secondly, debt financing can offer tax advantages, as interest payments on debt are often tax-deductible. This can help reduce the overall tax liability of the company.
When the debt securities are issued, investors purchase them and provide the company with the funds it needs. In return, the company promises to repay the principal amount of the debt at maturity and make periodic interest payments to the investors. The terms of the debt securities are legally binding and enforceable, providing investors with a level of security.
Issuing corporate debt comes with costs that companies need to consider. Firstly, there are direct costs associated with the issuance process, such as underwriting fees, legal fees, and administrative expenses. Additionally, companies need to consider the cost of servicing the debt, including interest payments and potential penalties for late payments.
Overall, corporate debt is an important tool for companies to raise capital and finance their operations. It allows companies to access funds quickly and efficiently, while also providing investors with an opportunity to earn a return on their investment. However, companies need to carefully consider the costs and risks associated with debt issuance to ensure it aligns with their financial goals and capabilities.
Corporate Debt
Corporate debt refers to the borrowing of funds by a company from various sources, such as banks, financial institutions, or individual investors, to finance its operations or expansion. It is a common practice for companies to issue debt securities, such as bonds or debentures, to raise capital.
Types of Corporate Debt
There are several types of corporate debt that a company can issue:
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities that are issued by companies to raise long-term capital. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity date.
- Debentures: Debentures are unsecured debt instruments that are backed by the general creditworthiness of the company. They have a fixed interest rate and maturity date.
- Commercial Paper: Commercial paper is a short-term debt instrument that is issued by companies to meet their short-term financing needs. It usually has a maturity period of less than one year.
- Bank Loans: Companies can also borrow funds from banks in the form of loans. These loans can be short-term or long-term, depending on the company’s financing requirements.
Benefits of Corporate Debt
Corporate debt can provide several benefits to companies:
- Access to Capital: By issuing debt securities, companies can raise capital to finance their operations, invest in new projects, or expand their business.
- Tax Deductibility: Interest payments on corporate debt are usually tax-deductible, which can help reduce the company’s overall tax liability.
- Flexibility: Corporate debt allows companies to have more flexibility in managing their capital structure and financial obligations.
Risks of Corporate Debt
While corporate debt can provide benefits, it also comes with certain risks:
- Interest Payments: Companies need to make regular interest payments on their debt, which can be a financial burden if the company is facing cash flow issues.
- Default Risk: There is always a risk that a company may default on its debt obligations, especially if it is facing financial difficulties.
- Restrictions: When a company issues debt, it may come with certain restrictions, such as limitations on dividend payments or additional borrowing.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
