Transaction Exposure: Definition
Transaction exposure is a concept in risk management that refers to the potential impact of fluctuations in exchange rates on the financial performance of a company. It arises when a company engages in international transactions, such as importing or exporting goods or services, and the settlement of these transactions is denominated in a foreign currency.
When a company has transaction exposure, it faces the risk that the exchange rate between the foreign currency and its domestic currency will change unfavorably before the transaction is settled. This can result in a loss or gain for the company, depending on the direction of the exchange rate movement.
Transaction exposure is an important concept in risk management because it can have a significant impact on a company’s financial performance. Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the cost of imported goods, the price competitiveness of exported goods, and the value of foreign currency-denominated assets and liabilities.
For example, if a company imports goods from a foreign country and the domestic currency strengthens against the foreign currency before the transaction is settled, the cost of the imported goods will increase. This can lead to lower profit margins or higher prices for customers.
On the other hand, if a company exports goods to a foreign country and the domestic currency weakens against the foreign currency before the transaction is settled, the revenue from the export will increase when converted back into the domestic currency. This can result in higher profit margins or lower prices for customers.
Hedging Strategies for Transaction Exposure
To mitigate the risks associated with transaction exposure, companies can employ various hedging strategies. These strategies involve using financial instruments, such as forward contracts, options, and futures, to lock in exchange rates for future transactions.
One common hedging strategy is to enter into a forward contract, which allows the company to buy or sell a specific amount of foreign currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. By doing so, the company can eliminate the uncertainty of future exchange rate movements and protect its financial performance.
Another hedging strategy is to use options, which give the company the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of foreign currency at a predetermined exchange rate within a specified period. This provides the company with flexibility in managing its transaction exposure.
Transaction exposure is a critical concept in risk management that refers to the potential impact of fluctuations in exchange rates on the financial performance of a company. It arises from the exposure to foreign currency transactions, such as buying or selling goods or services in a different currency.
When a company engages in international trade, it is exposed to the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. If the exchange rate between the domestic currency and the foreign currency changes unfavorably, it can lead to financial losses for the company. On the other hand, if the exchange rate changes favorably, it can result in financial gains.
Transaction exposure is particularly relevant for companies that have significant foreign currency transactions, as it can have a significant impact on their financial statements. It is important for companies to assess and manage transaction exposure to minimize potential losses and maximize potential gains.
There are various factors that contribute to transaction exposure, including the volume of foreign currency transactions, the time period of the transactions, and the volatility of exchange rates. Companies need to carefully analyze these factors to determine the level of transaction exposure they face.
Once the transaction exposure is identified, companies can employ various hedging strategies to mitigate the risk. Hedging involves using financial instruments, such as forward contracts, options, or futures, to protect against adverse exchange rate movements. By hedging their foreign currency transactions, companies can lock in a specific exchange rate and reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their financial performance.
It is important for companies to regularly monitor and assess their transaction exposure, as exchange rates can be highly volatile and unpredictable. By staying informed about market trends and implementing effective risk management strategies, companies can minimize the potential negative impact of transaction exposure on their financial performance.
Transaction Exposure: Example
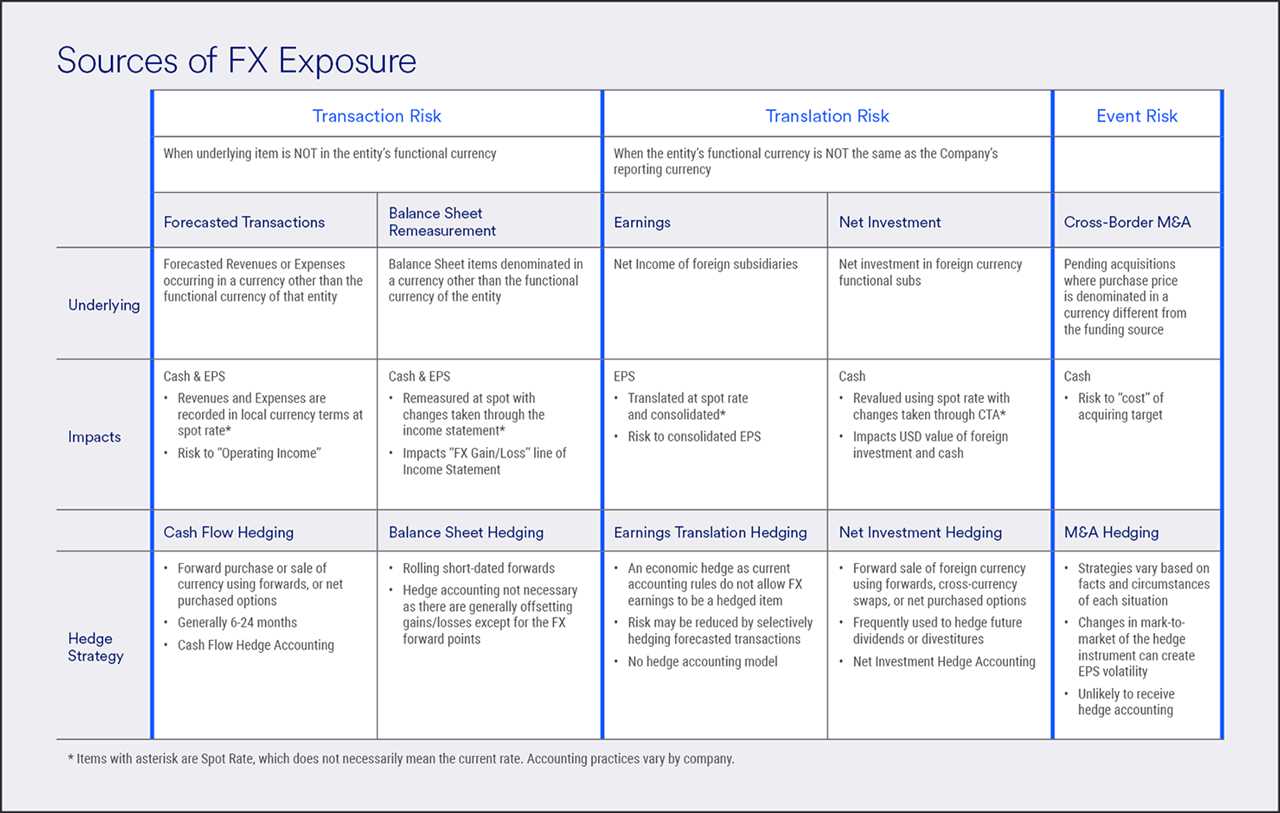
Transaction exposure refers to the risk that a company faces when conducting international transactions, such as importing or exporting goods or services, due to fluctuations in exchange rates. To better understand this concept, let’s consider an example:
ABC Company, based in the United States, imports electronic components from a supplier in Japan. The agreed-upon price for the components is 1,000,000 Japanese yen. At the time of the agreement, the exchange rate is 1 USD = 100 JPY, so the cost of the components in USD is $10,000.
However, due to the volatility of exchange rates, the value of the Japanese yen decreases, and the new exchange rate becomes 1 USD = 110 JPY. As a result, when ABC Company pays for the components, they now have to pay $9,090.91 instead of the original $10,000.
Transaction exposure can have a significant impact on a company’s profitability, especially for businesses that engage in frequent international transactions. To mitigate this risk, companies can employ various hedging strategies, such as:
- Forward contracts: ABC Company could enter into a forward contract with a financial institution, which would allow them to lock in the exchange rate at the time of the agreement. This would protect them from any future fluctuations in the exchange rate.
- Options contracts: Another hedging strategy is to use options contracts, which give the company the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell currencies at a predetermined price. This provides flexibility in managing transaction exposure.
- Natural hedging: Companies can also engage in natural hedging by matching their foreign currency inflows and outflows. For example, if ABC Company generates revenue in Japanese yen from selling products in Japan, they can use these funds to pay for their imports, eliminating the need for currency conversion.
- Netting: Netting involves offsetting the value of multiple transactions denominated in different currencies. This can help reduce transaction exposure by consolidating the company’s foreign currency obligations.
By implementing these hedging strategies, companies can minimize the impact of transaction exposure on their financial performance and ensure more stable cash flows.
Real-Life Case Study Demonstrating Transaction Exposure
Transaction exposure is a concept in risk management that refers to the potential impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the financial performance of a company. To better understand this concept, let’s take a look at a real-life case study.
Company XYZ is a multinational corporation based in the United States. It operates in multiple countries and conducts business transactions in various currencies. One of its subsidiaries, XYZ International, is based in Europe and imports raw materials from the United States.
Let’s assume that the exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) is 1 USD = 0.85 EUR. XYZ International has a purchase agreement with a US supplier to import raw materials worth $1 million. The payment is due in three months.
However, during this period, the exchange rate between the USD and the EUR changes, and 1 USD = 0.80 EUR. As a result, when XYZ International makes the payment in euros, it will have to pay 1.25 million euros instead of the initially expected 1.18 million euros.
This change in the exchange rate creates transaction exposure for XYZ International. The company will incur a loss of 70,000 euros due to the unfavorable exchange rate movement. This loss can have a significant impact on the company’s financial performance and profitability.
To mitigate this transaction exposure, XYZ International can implement hedging strategies. One possible strategy is to enter into a forward contract with a financial institution. This contract would allow the company to lock in the exchange rate at the current rate of 0.85 EUR/USD for the future payment.
By entering into a forward contract, XYZ International eliminates the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Regardless of how the exchange rate changes in the future, the company will only have to pay 1.18 million euros for the raw materials, ensuring stability and predictability in its financial transactions.
Transaction Exposure: Hedging Strategies
Transaction exposure refers to the risk that a company faces when conducting international transactions, where changes in exchange rates can impact the value of these transactions. To mitigate this risk, companies can employ various hedging strategies.
Forward Contracts
One common hedging strategy for transaction exposure is the use of forward contracts. A forward contract is an agreement between two parties to exchange a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. By entering into a forward contract, a company can lock in the exchange rate for a future transaction, eliminating the risk of exchange rate fluctuations.
Options Contracts
Another hedging strategy is the use of options contracts. Options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate within a certain period of time. Companies can use options to protect themselves against unfavorable exchange rate movements while still allowing them to benefit from favorable movements.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are another effective hedging strategy for transaction exposure. In a currency swap, two parties agree to exchange a specified amount of currency and then exchange it back at a later date. This allows companies to hedge their exposure to exchange rate fluctuations by locking in a fixed exchange rate for the duration of the swap.
Natural Hedging

Natural hedging involves offsetting transaction exposure by matching inflows and outflows in the same currency. For example, if a company has both sales and expenses in a foreign currency, any fluctuations in the exchange rate will have a balanced impact on both sides of the transaction. This strategy can help reduce the overall transaction exposure without the need for financial instruments.
Netting

Netting is another technique that can be used to hedge transaction exposure. It involves consolidating multiple transactions denominated in the same currency and offsetting them against each other. By doing so, companies can reduce the overall exposure to exchange rate fluctuations and minimize the impact on their financial position.
Conclusion
When dealing with transaction exposure, it is crucial for companies to implement effective hedging strategies to mitigate the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Whether through the use of forward contracts, options contracts, currency swaps, natural hedging, or netting, companies can protect themselves from potential losses and ensure the stability of their international transactions.
| Hedging Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Contracts | Locks in exchange rate | No flexibility if exchange rate moves in favor |
| Options Contracts | Allows for flexibility | Premium cost |
| Currency Swaps | Locks in exchange rate for duration of swap | Requires counterparty |
| Natural Hedging | No need for financial instruments | Relies on balanced exposure |
| Netting | Reduces exposure through offsetting | Requires multiple transactions in same currency |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
