What is a Take-Profit Order TP?
A Take-Profit Order TP is a type of trading order that allows traders to set a specific price at which they want to close a position and take profit. It is a predetermined level at which traders want to exit a trade to lock in their gains.
Take-profit orders are commonly used in trading to manage risk and ensure that traders do not miss out on potential profits. By setting a take-profit level, traders can remove the emotional aspect of trading and stick to their predetermined trading plan.
For example, let’s say a trader buys a stock at $50 per share and sets a take-profit order at $60. When the stock price reaches $60, the take-profit order is triggered, and the trader’s position is automatically closed, locking in a $10 profit per share.
Definition, Use in Trading, and Example

How it works
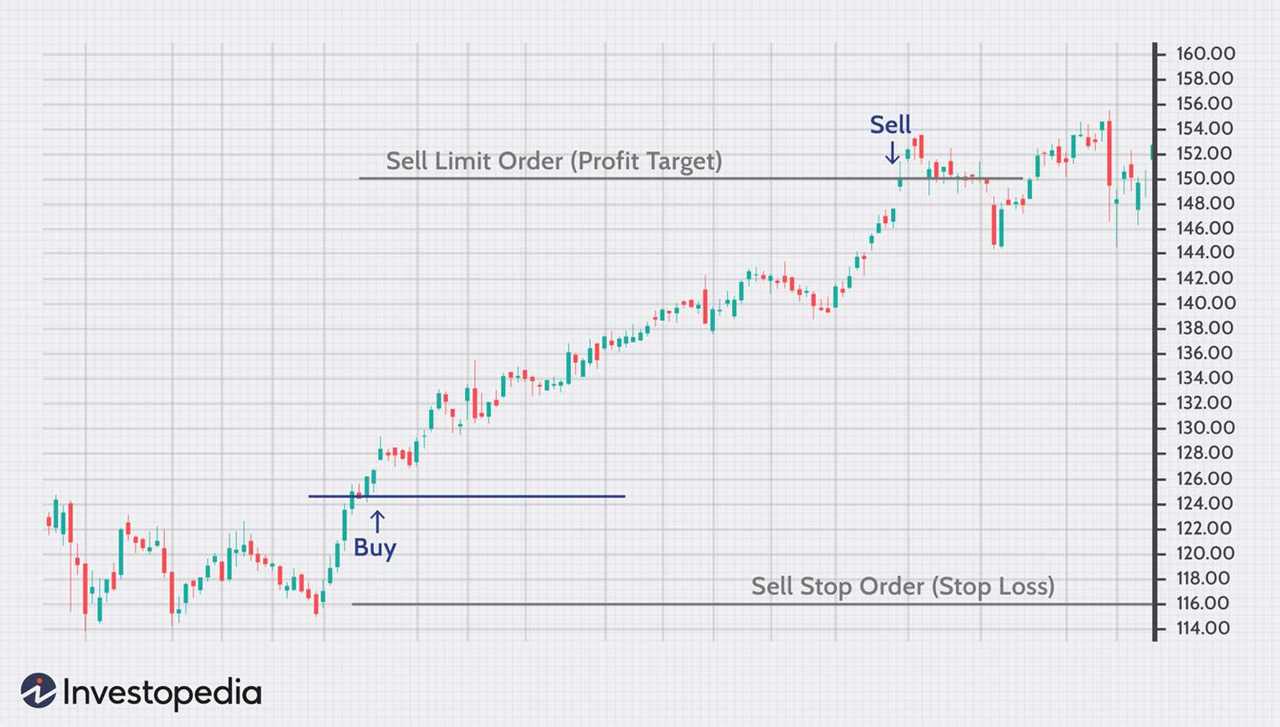
When a trader enters a trade, they can set a take-profit level at which they want to exit the trade with a profit. Once the market reaches or exceeds this level, the take-profit order is triggered, and the position is automatically closed. This allows traders to secure their gains without having to constantly monitor the market.
Take-profit orders are typically placed above the current market price for long positions and below the current market price for short positions. The specific level at which the take-profit order is set depends on the trader’s trading strategy, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Advantages of using Take-Profit Orders
Using take-profit orders in trading offers several advantages:
- Locking in profits: Take-profit orders allow traders to secure their profits by automatically closing a position when the desired profit level is reached.
- Removing emotions from trading: By setting a take-profit level in advance, traders can avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions like greed or fear.
- Time-saving: Take-profit orders eliminate the need for constant monitoring of the market, allowing traders to focus on other trading opportunities or activities.
Example
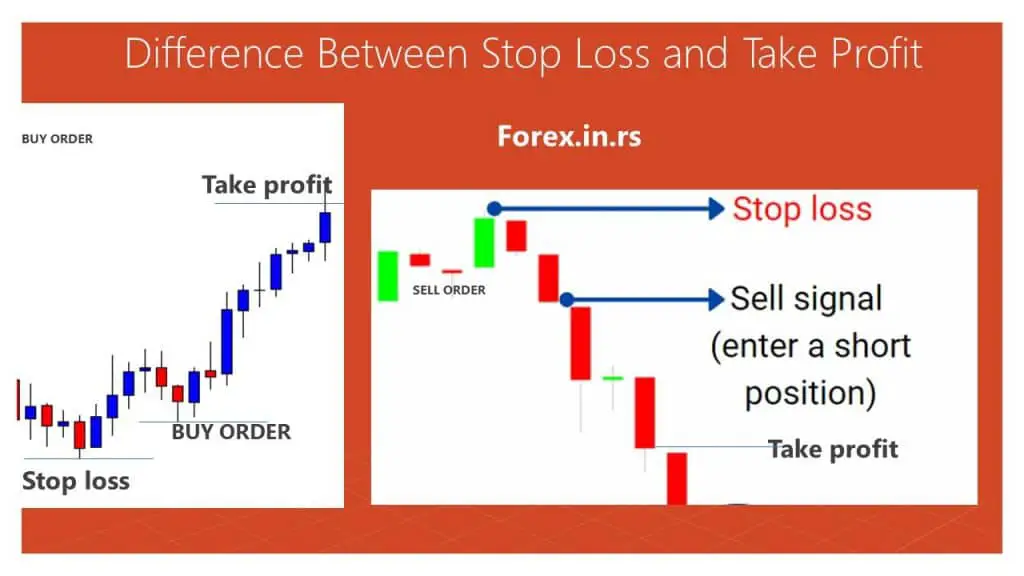
Let’s say a trader buys 100 shares of a stock at $50 per share. They believe the stock will increase in value and want to take profits once it reaches $60 per share. The trader can place a take-profit order at $60, specifying the number of shares they want to sell. If the stock price reaches or exceeds $60, the take-profit order will be executed, and the trader will sell the specified number of shares at the market price, locking in their profit.
| Trade | Shares | Entry Price | Take-Profit Price | Profit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buy | 100 | $50 | – | – |
| Sell (Take-Profit) | 100 | – | $60 | $1,000 |
Overall, take-profit orders are a valuable tool for traders to manage their risk and secure their profits in the dynamic world of trading.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
