Return On Average Equity Definition
Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of a company in relation to its shareholders’ equity. It indicates how efficiently a company is utilizing its equity to generate profits.
ROAE is calculated by dividing the net income of a company by its average shareholders’ equity. The net income is the company’s total revenue minus its expenses, taxes, and interest. Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting its liabilities.
ROAE is expressed as a percentage and is used by investors, analysts, and creditors to assess the financial performance and efficiency of a company. A higher ROAE indicates that a company is generating more profits with its equity, which is favorable for shareholders.
What is Return On Average Equity?
Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability and efficiency of a company in generating returns for its shareholders. It is a key metric used by investors and analysts to assess the financial performance of a company.
ROAE is calculated by dividing the net income of a company by its average shareholders’ equity over a specific period. Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities.
The average shareholders’ equity is calculated by adding the beginning and ending shareholders’ equity for a specific period and dividing it by two. This is done to account for any fluctuations in equity during the period.
ROAE is expressed as a percentage and indicates the return generated on each dollar of equity invested by shareholders. A higher ROAE indicates that a company is more efficient in utilizing its equity to generate profits.
ROAE is a useful metric for comparing the financial performance of companies within the same industry. It provides insights into the effectiveness of a company’s management in generating profits and utilizing its shareholders’ equity.
Investors and analysts use ROAE to assess the profitability and efficiency of a company over time. A consistent and increasing ROAE indicates that a company is effectively utilizing its resources and generating higher returns for its shareholders.
However, it is important to note that ROAE should not be used in isolation to evaluate a company’s financial performance. It should be considered in conjunction with other financial ratios and factors such as revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels.
How is Return On Average Equity Calculated?
Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of a company by comparing its net income to its average shareholders’ equity. It is an important metric that helps investors and analysts assess the efficiency and effectiveness of a company in generating profits from the capital invested by its shareholders.
The formula for calculating ROAE is:
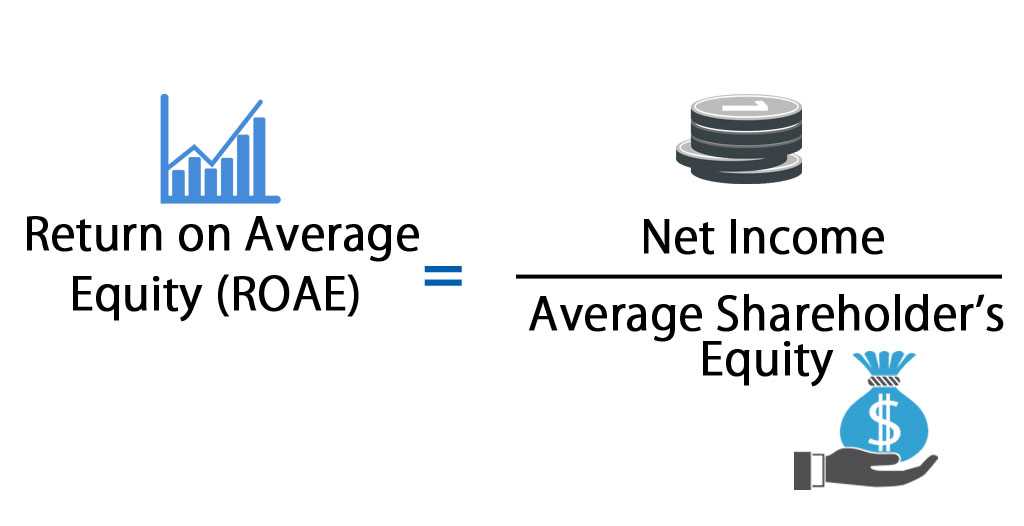
ROAE = (Net Income / Average Shareholders’ Equity) * 100
Net Income is the company’s total earnings after deducting all expenses, taxes, and interest. Average Shareholders’ Equity is calculated by adding the beginning and ending shareholders’ equity for a specific period and dividing it by two.
For example, if a company has a net income of $1 million and an average shareholders’ equity of $10 million, the ROAE would be:
ROAE = ($1,000,000 / $10,000,000) * 100 = 10%
This means that for every dollar of average shareholders’ equity, the company generated a return of 10 cents in net income.
ROAE is often used in conjunction with other financial ratios to evaluate a company’s overall financial performance. It provides insights into how effectively a company is utilizing its shareholders’ equity to generate profits. A higher ROAE indicates better profitability and efficiency, while a lower ROAE may suggest poor financial performance.
What Return On Average Equity Indicates

Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a financial ratio that provides insight into a company’s profitability and efficiency in generating returns for its shareholders. It measures the percentage of profit a company generates for each dollar of average equity invested by its shareholders.
ROAE is an important metric for investors, as it helps them evaluate how effectively a company is utilizing its shareholders’ equity to generate profits. A higher ROAE indicates that a company is efficiently utilizing its equity and generating higher returns for its shareholders.
ROAE is also a useful tool for comparing the performance of different companies within the same industry. It allows investors to assess which companies are more efficient in generating profits and providing returns to their shareholders.
Furthermore, ROAE can provide insights into a company’s financial health and stability. A consistently high ROAE indicates that a company is financially strong and capable of generating sustainable profits. On the other hand, a declining ROAE may indicate potential issues with the company’s profitability or efficiency.
Financial Performance

Financial performance is a critical aspect of any business. It refers to the ability of a company to generate profits and create value for its shareholders. Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a key metric that helps evaluate a company’s financial performance.
ROAE measures the profitability of a company by comparing its net income to its average shareholders’ equity. It indicates how effectively a company is utilizing its equity to generate profits. A higher ROAE suggests that a company is generating more profits with the same amount of equity, which is favorable for shareholders.
Financial performance is crucial for investors and stakeholders as it provides insights into a company’s ability to generate returns on investment. A high ROAE indicates that a company is efficiently utilizing its resources and generating profits, which can attract potential investors and increase shareholder confidence.
Financial performance is not only about profitability but also about sustainability. A company with a high ROAE may be generating short-term profits, but if it is not sustainable in the long run, it may not be a good investment. Therefore, it is essential to analyze other financial ratios and indicators to get a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance.
Efficiency of Capital Utilization
The Return on Average Equity (ROAE) is a key financial ratio that measures the efficiency of capital utilization by a company. It provides insight into how effectively a company is using its shareholders’ equity to generate profits.
By calculating the ROAE, investors and analysts can assess the company’s ability to generate returns for its shareholders. A higher ROAE indicates that the company is utilizing its capital efficiently and generating higher profits, while a lower ROAE suggests that the company may not be utilizing its capital effectively.
Importance of ROAE
ROAE is an important metric for investors as it helps them evaluate the profitability and efficiency of a company. It provides a clear picture of how well a company is utilizing its shareholders’ equity to generate profits.
A high ROAE indicates that the company is generating significant returns on the capital invested by its shareholders. This can be an indication of a well-managed company with strong financial performance. On the other hand, a low ROAE may suggest that the company is not utilizing its capital efficiently and may have underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Interpreting ROAE

When interpreting the ROAE, it is important to compare it with industry benchmarks and the company’s historical ROAE. This allows investors to assess the company’s performance relative to its peers and track its progress over time.
A company with a consistently high ROAE compared to its industry peers may indicate a competitive advantage or a unique business model that allows it to generate higher profits. Conversely, a company with a consistently low ROAE may signal inefficiencies or challenges in utilizing its capital effectively.
Conclusion

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
